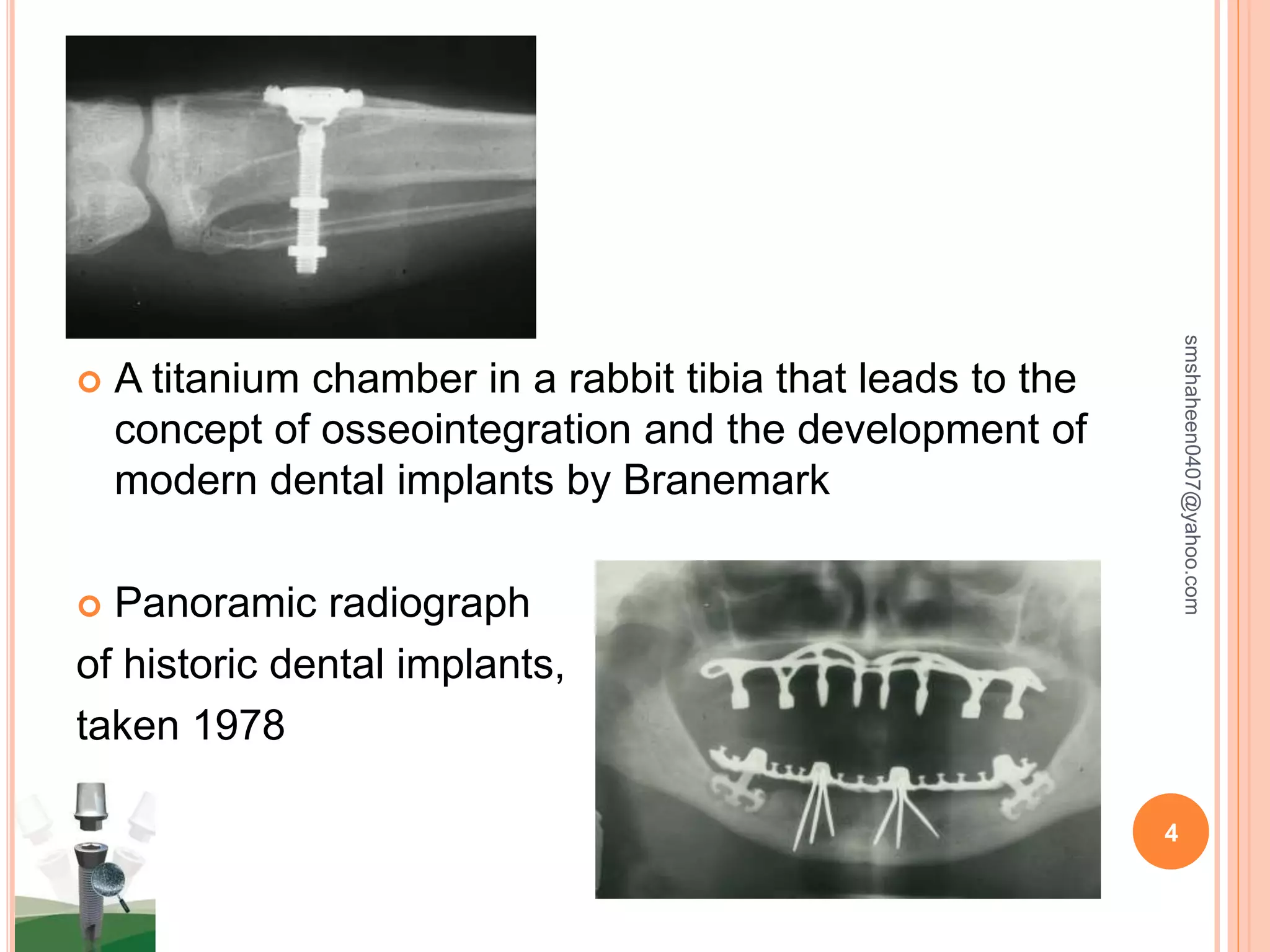
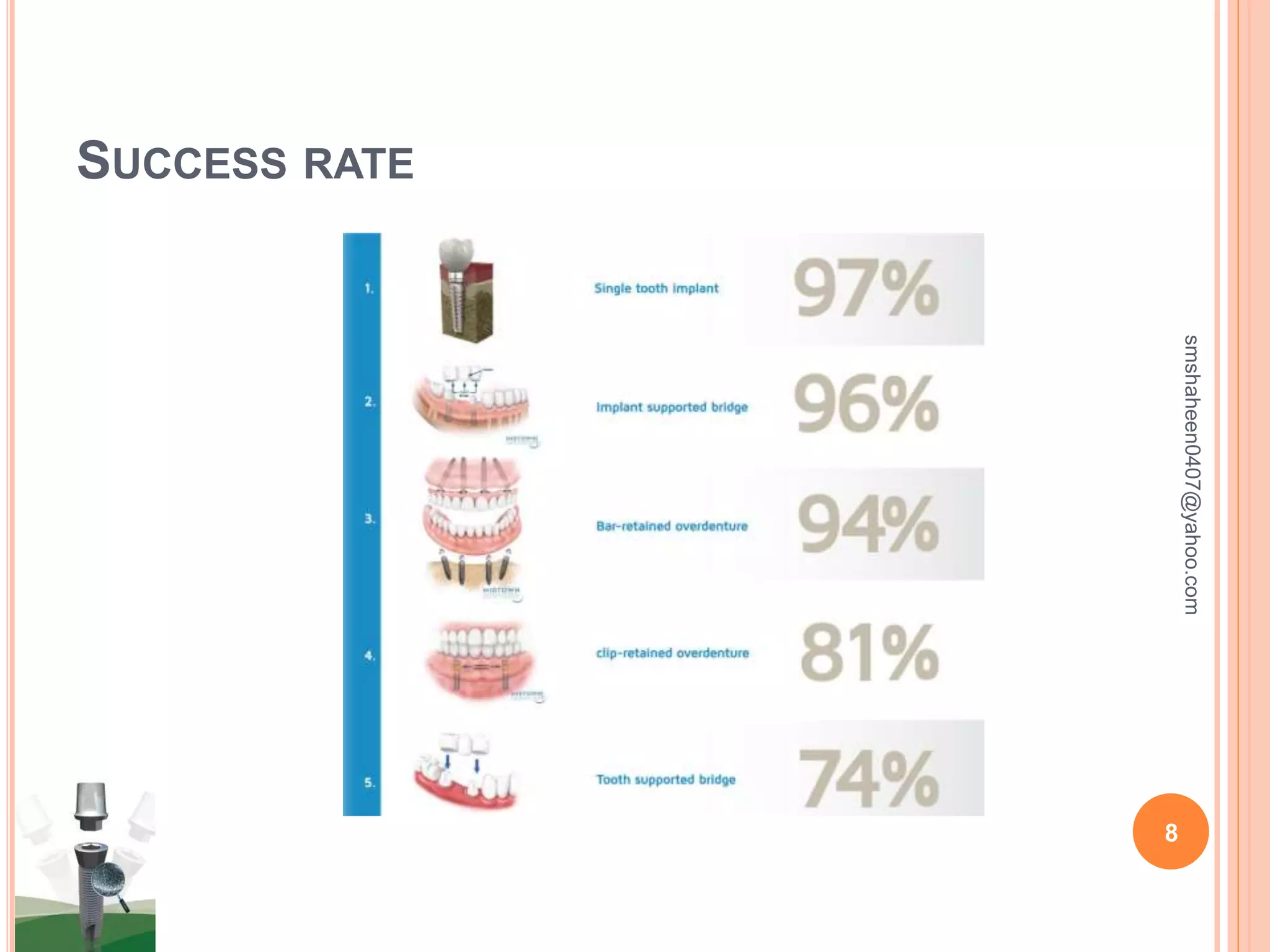
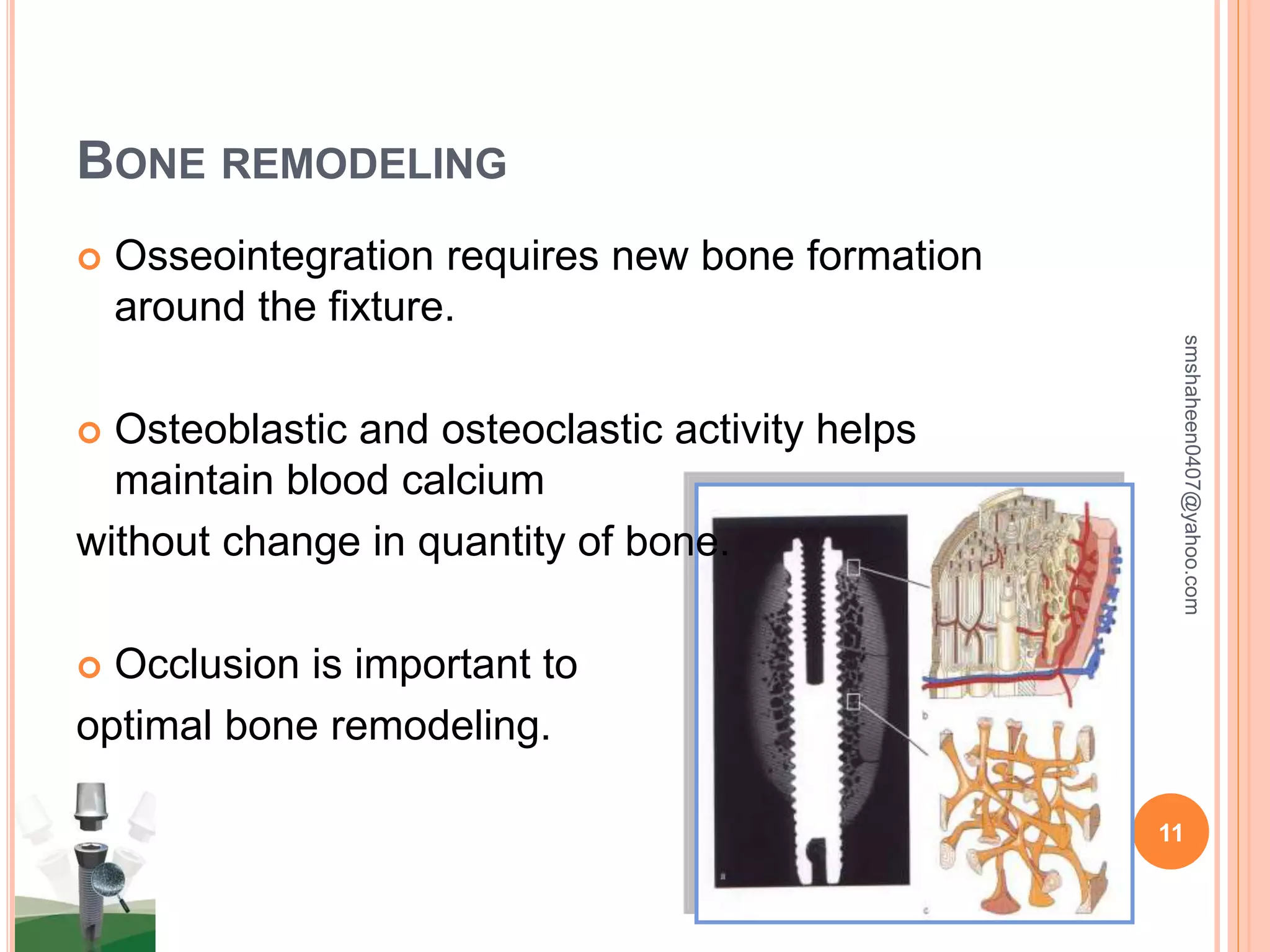
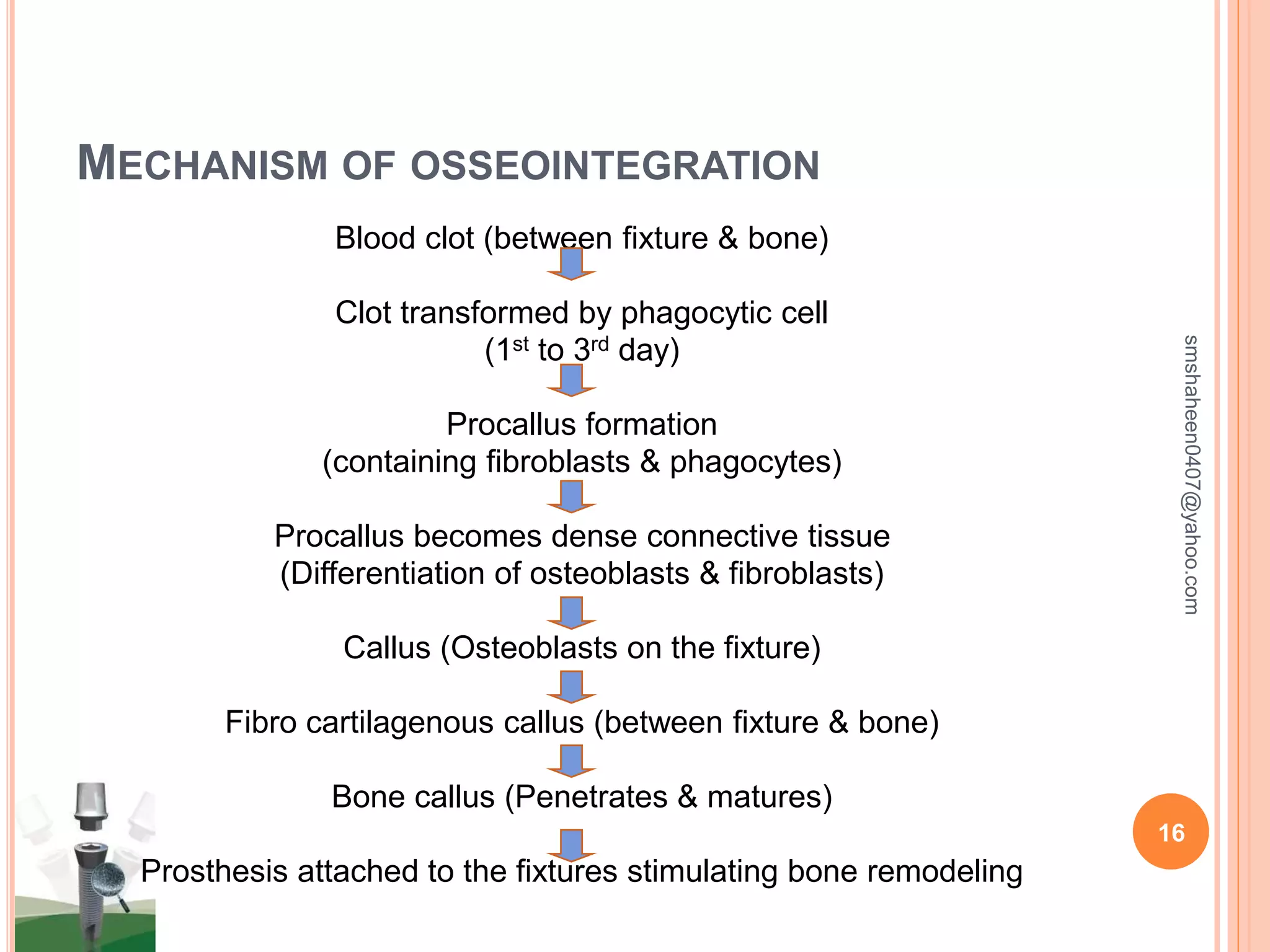
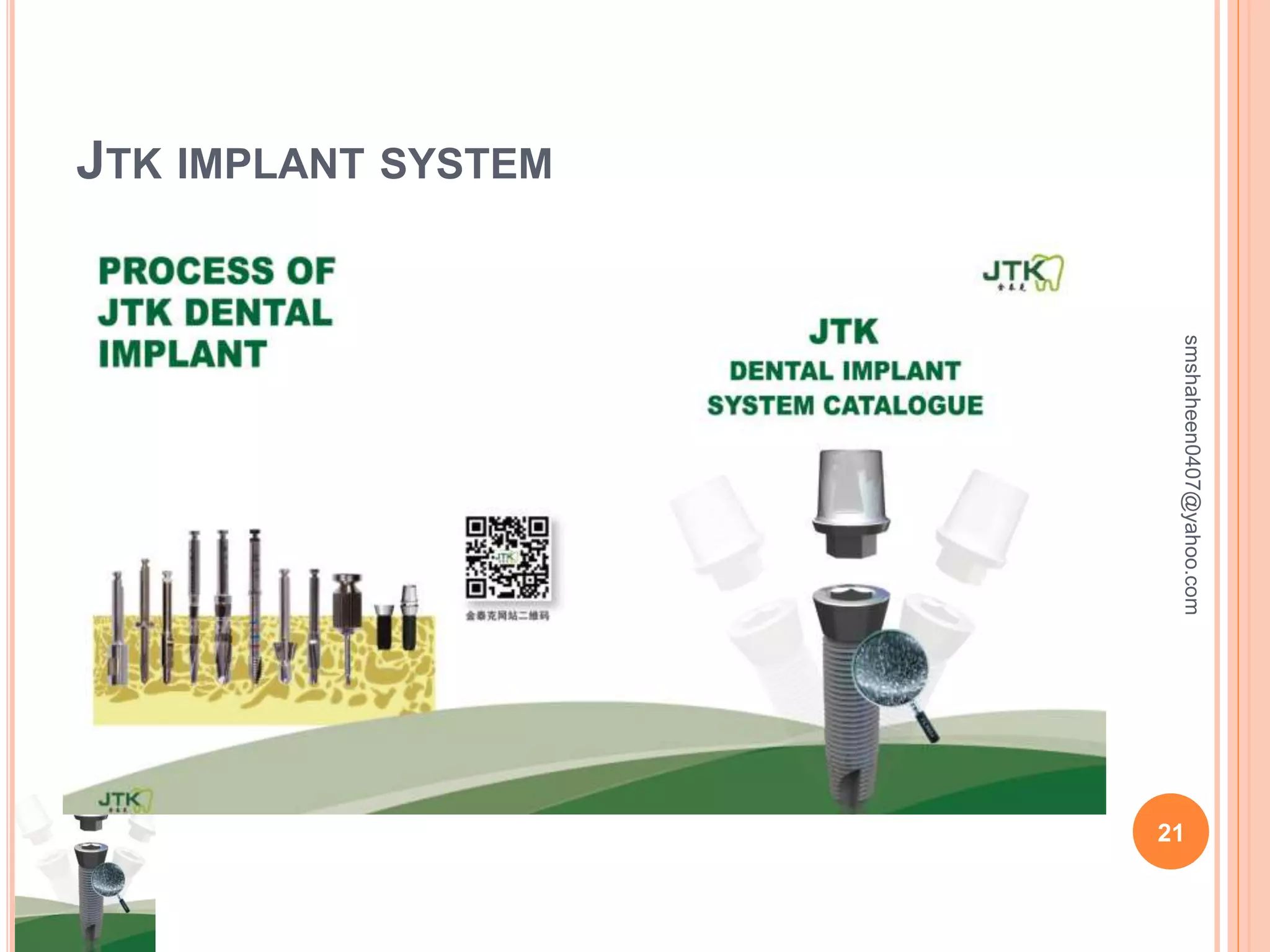
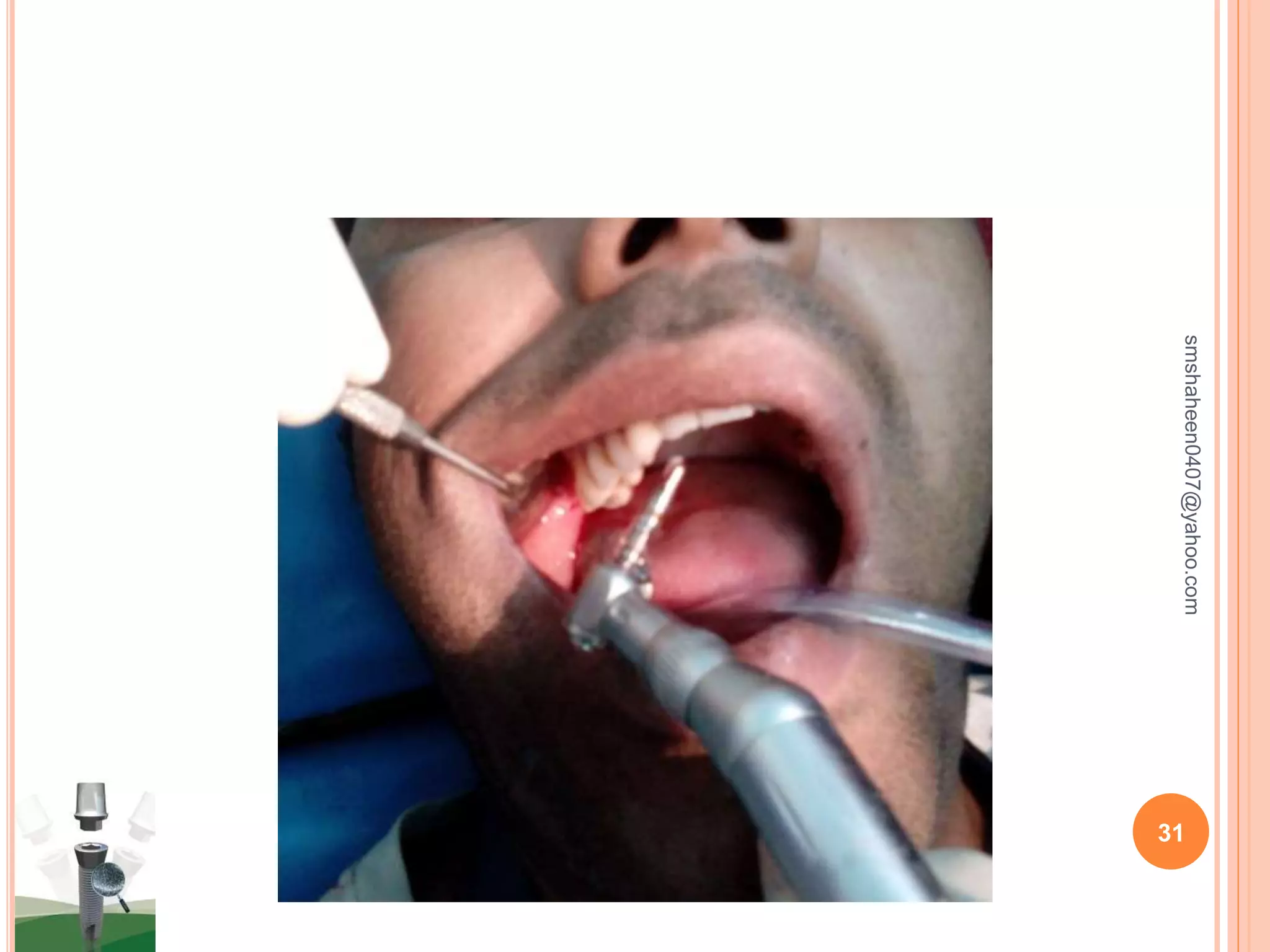
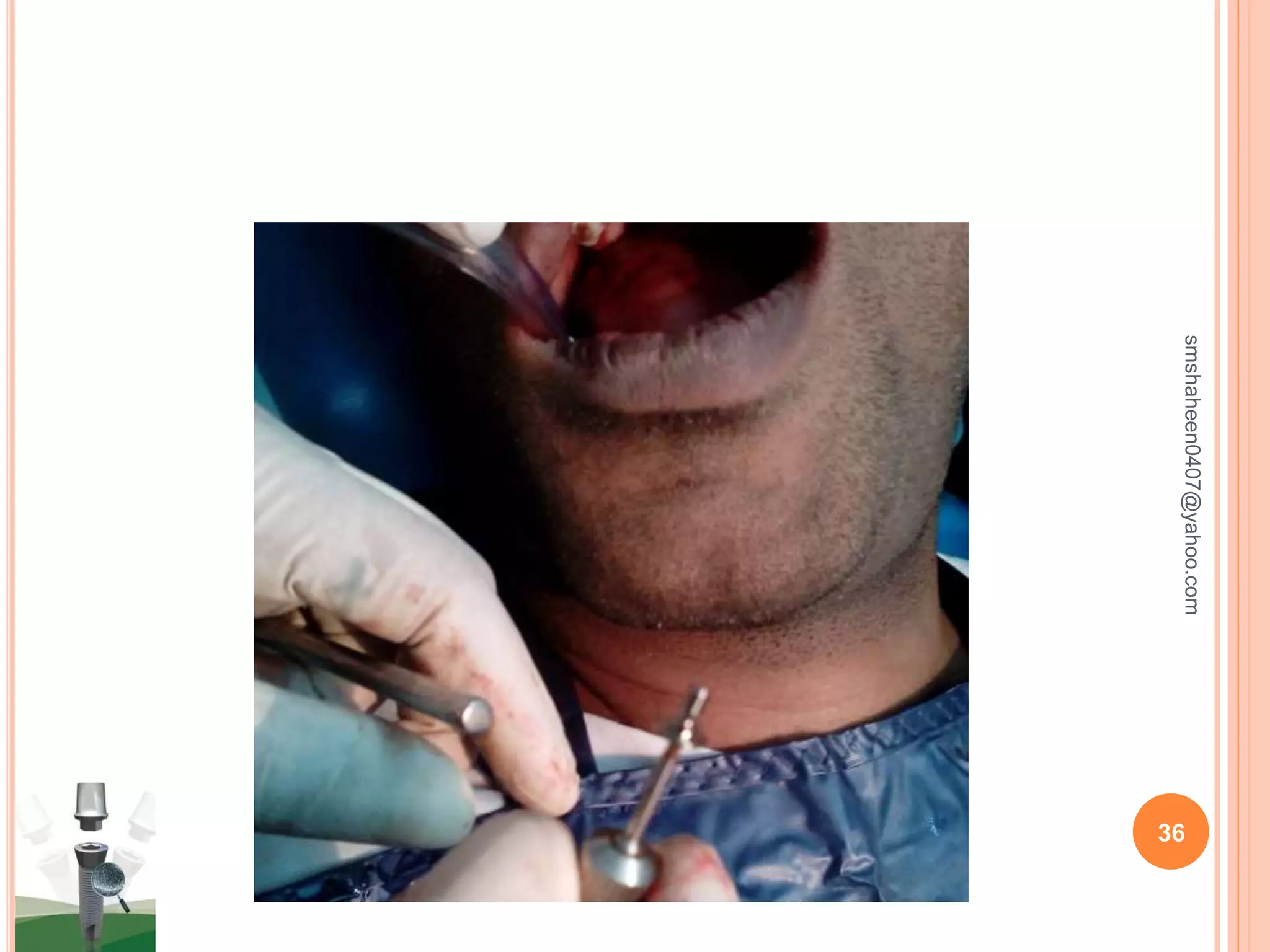
The document discusses osseointegrated dental implants. It describes osseointegration as direct bone anchorage to an implant that can support a prosthesis. The history of dental implants is covered, with Dr. Per-Ingvar Branemark pioneering the field in the 1950s and developing the concept of osseointegration. Key factors for successful osseointegration include the implant material, design, surgical procedure, and healing period. The document also outlines structures of implants, success rates, biological considerations, and the clinical procedure for dental implant placement and restoration.