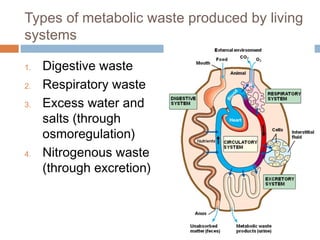
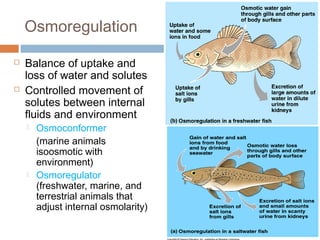
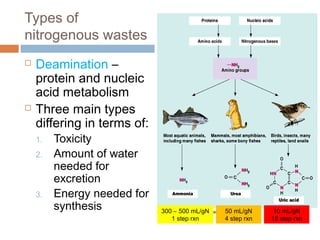
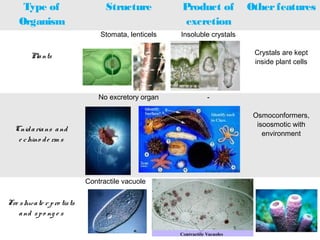
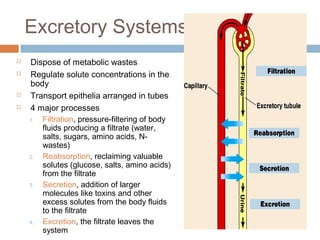
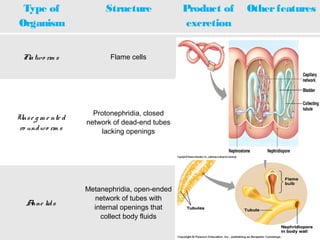
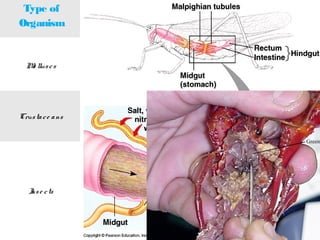
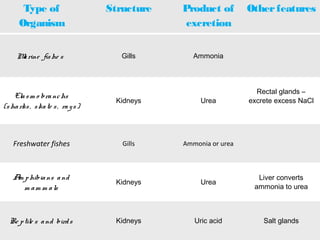
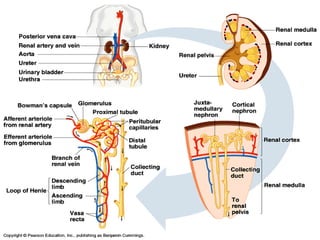
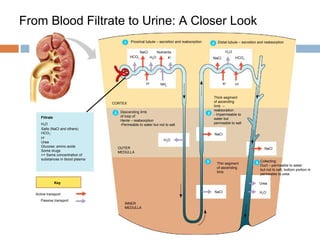
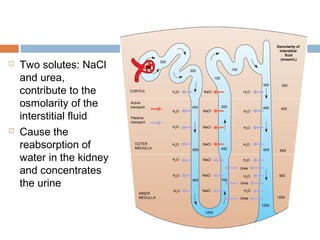
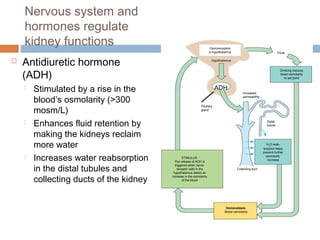
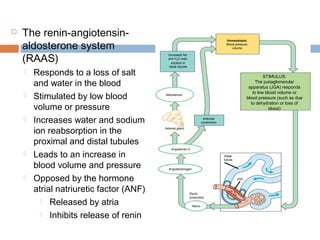
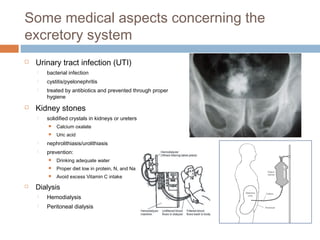
This document discusses osmoregulation and excretion in animals. It describes how different organisms produce nitrogenous waste and regulate water and solute levels. The mammalian kidney is highlighted, with nephrons filtering blood to form urine via selective reabsorption and secretion. Key parts of the nephron work together to concentrate urine by actively transporting water and solutes like urea and NaCl. Hormones like ADH and aldosterone help the kidney regulate water and salt levels in response to osmolarity and blood pressure changes. The functions of the kidney are vital for homeostasis and common disorders like kidney stones and infections are also outlined.