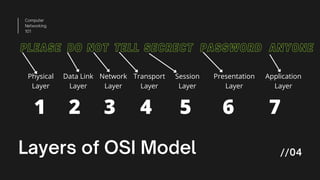
The document discusses the seven layers of the OSI model: Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, and Application layers. It provides a brief overview of the key functions and responsibilities of each layer, such as the Physical layer being responsible for the actual physical connection and converting signals to bits, the Data Link layer handling error control and flow control between nodes, and the Transport layer providing process to process delivery and error checking of data transmission.