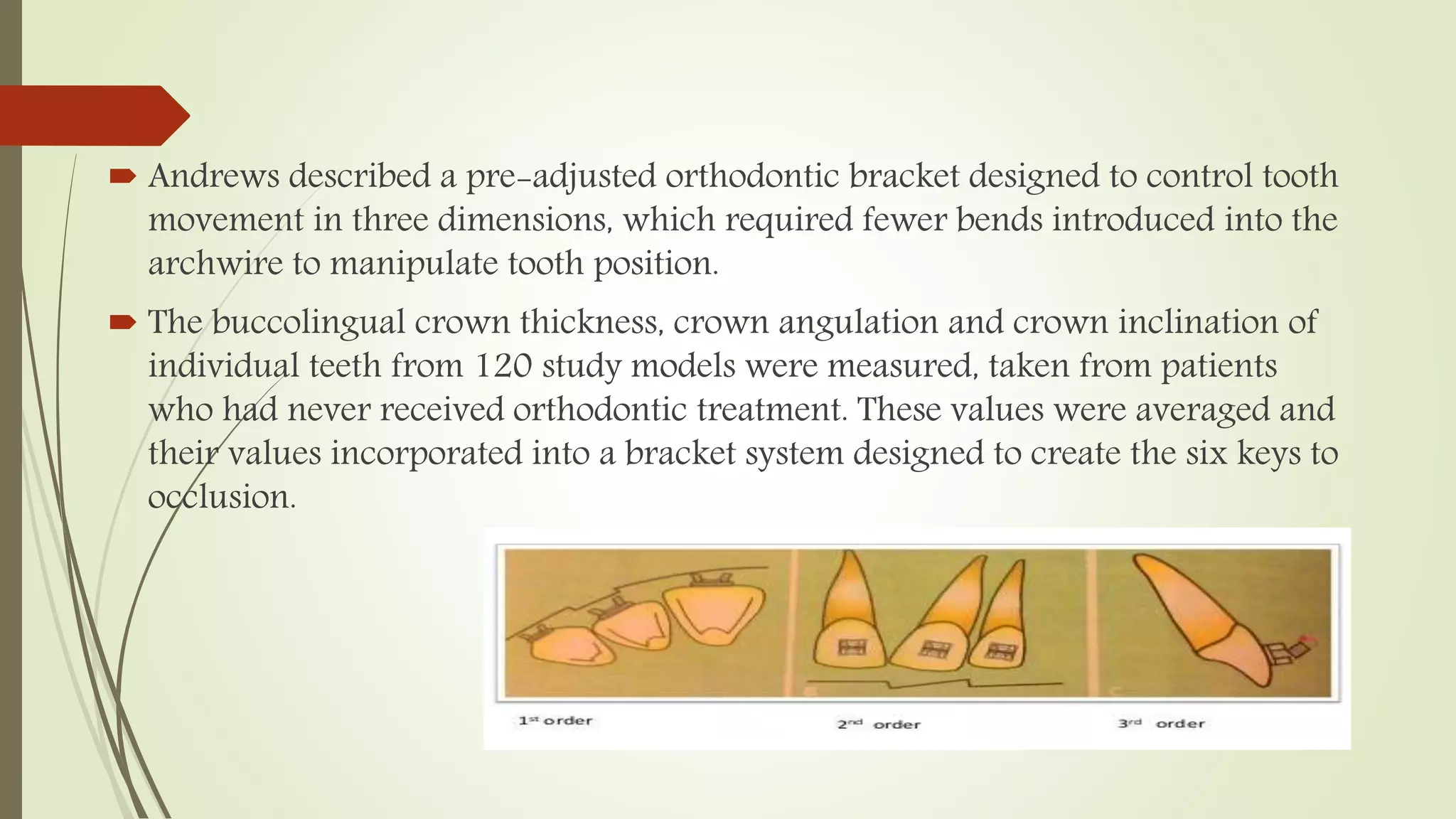
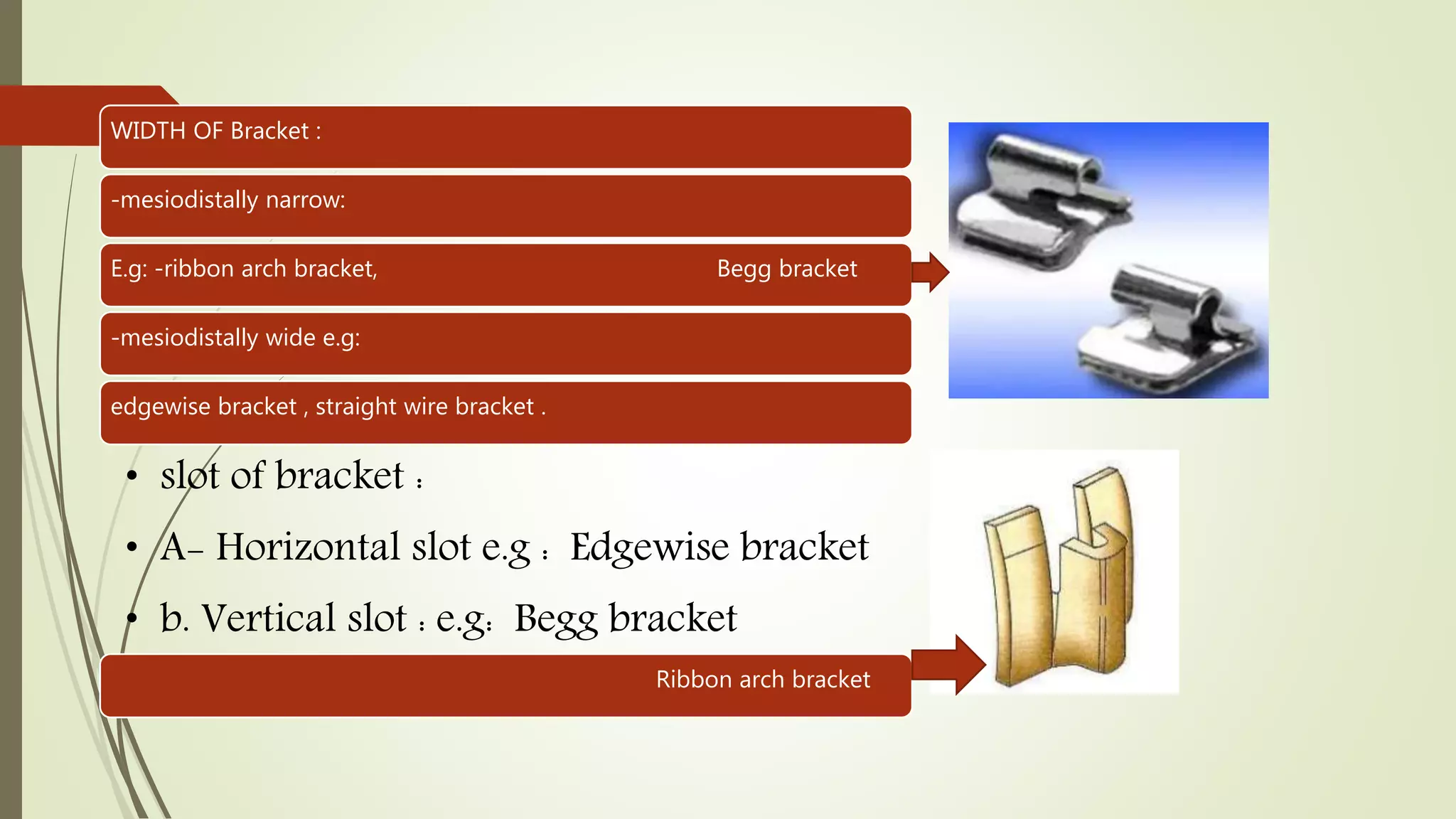
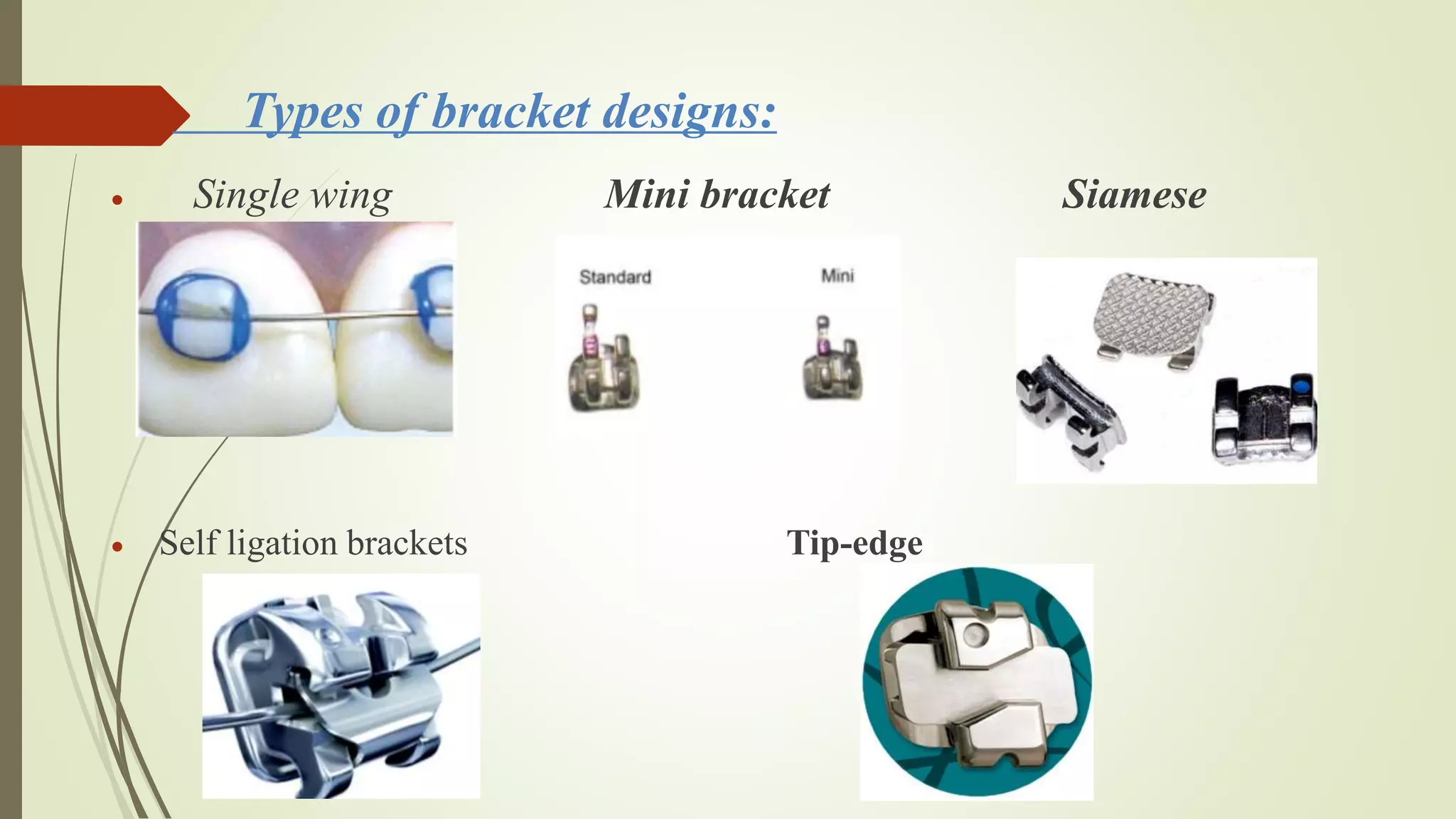
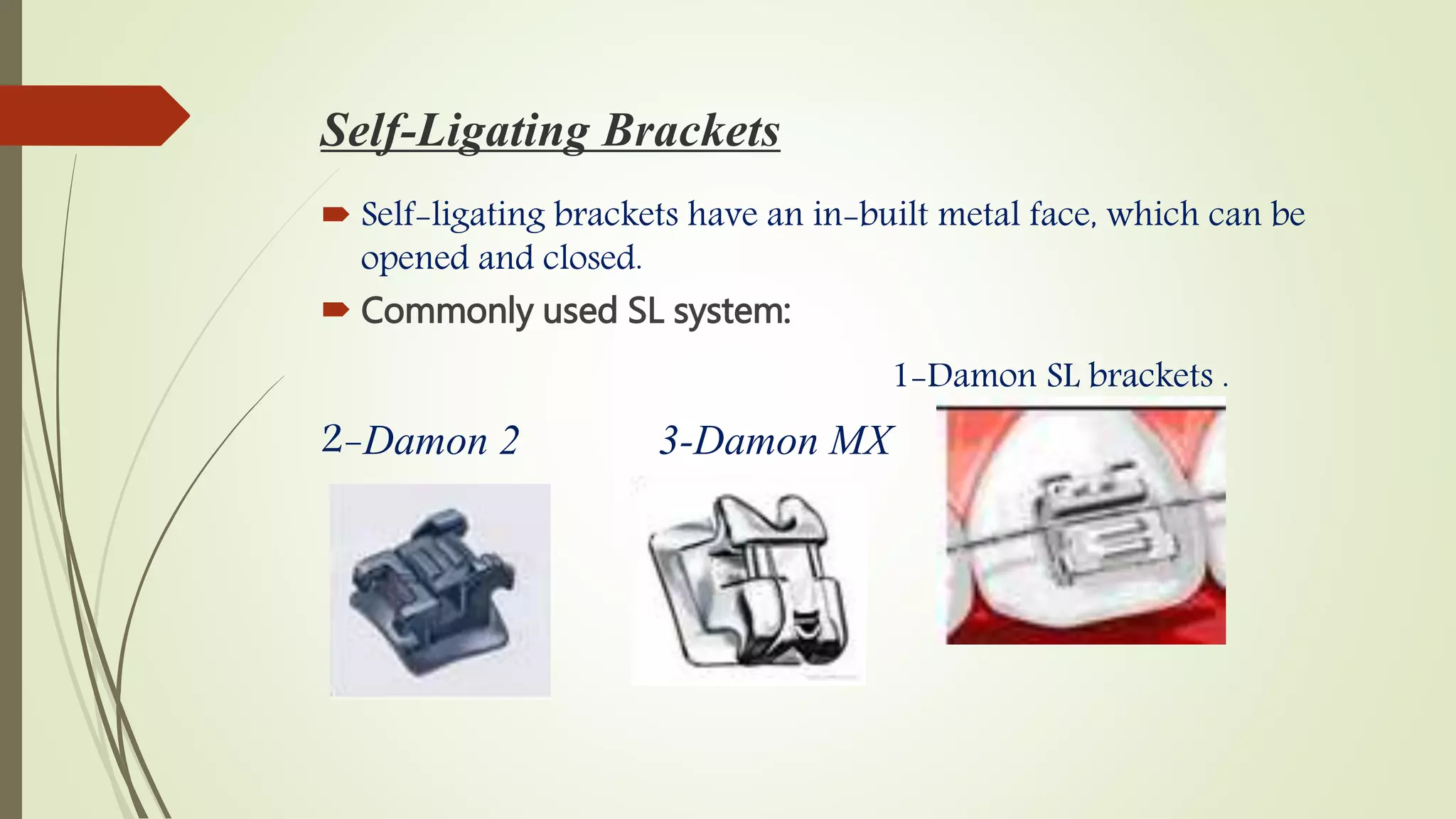
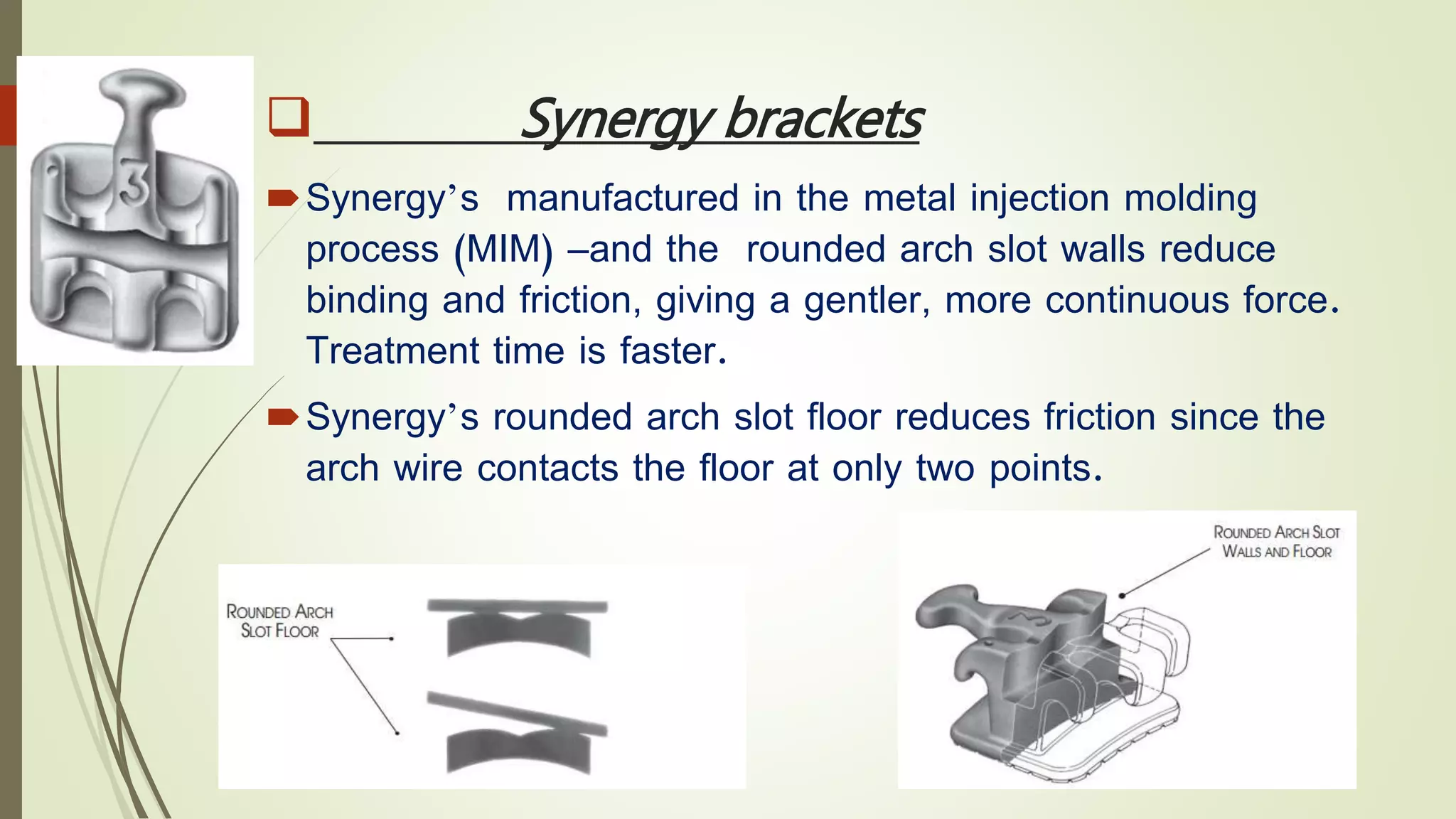
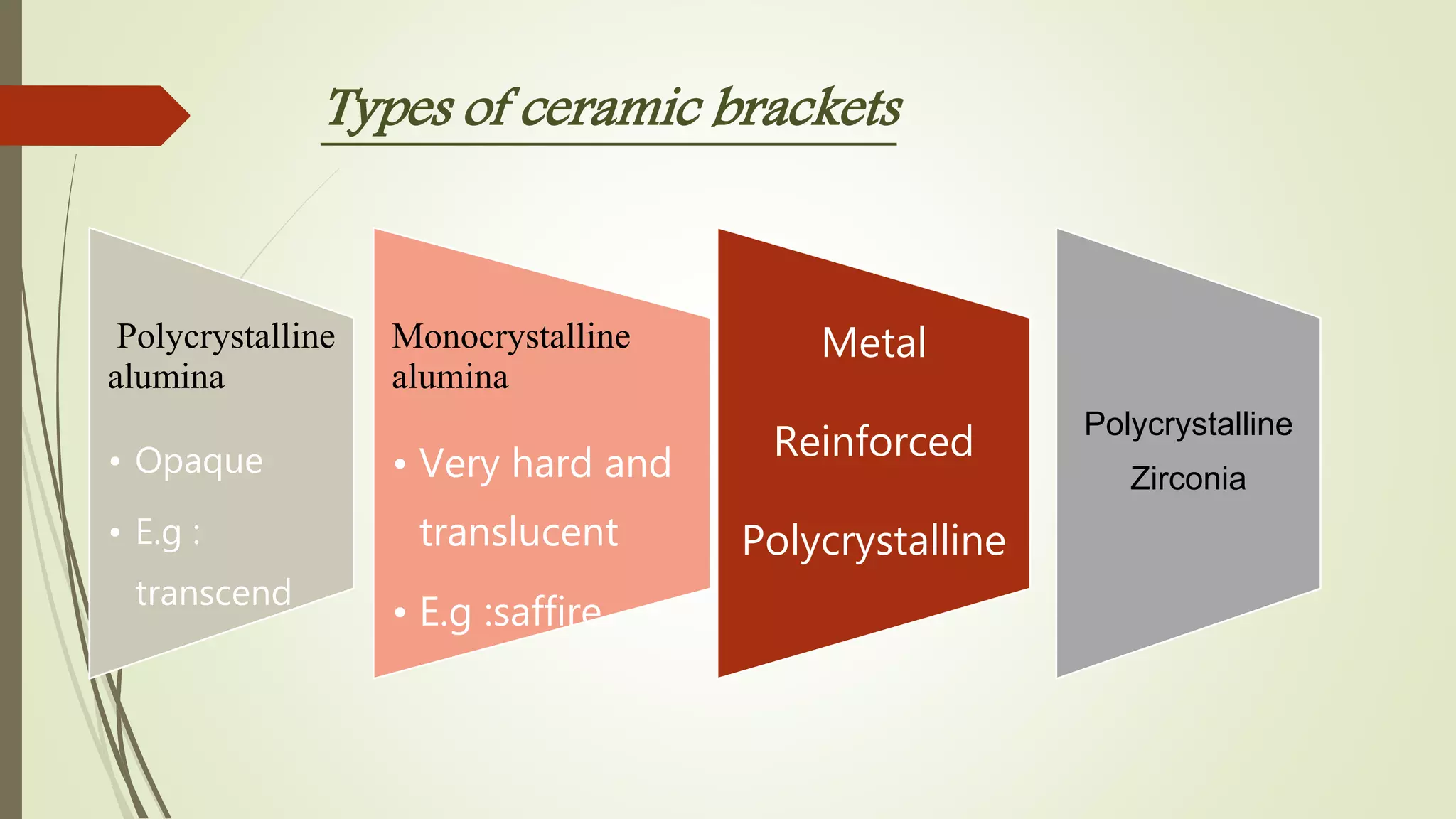
Orthodontic brackets are components bonded to teeth that transfer force from archwires to move teeth into proper alignment and function. There are various bracket designs that differ in material, size, shape, and prescription. The development of pre-adjusted edgewise brackets aimed to directly guide teeth into normal occlusion with fewer bends in the archwire. However, individual variations still require some adjustments to achieve ideal positioning. Modern bracket types include self-ligating, ceramic, and lingual systems that offer enhanced aesthetics, mechanics, or patient comfort.