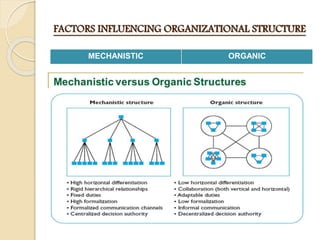
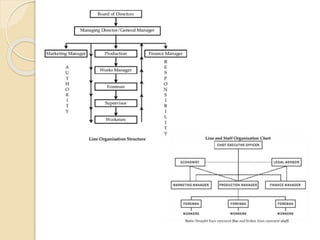
Organizational structure defines how tasks are divided and coordinated to help people work effectively. It is influenced by people, structure, technology, and the environment. Common structures include functional departmentalization by task, chain of command for authority, and centralization vs decentralization of decision-making. Organizational design depends on factors like size, strategy, environment, life cycle stage, and technology used. Structure impacts employee behavior but responses vary individually.