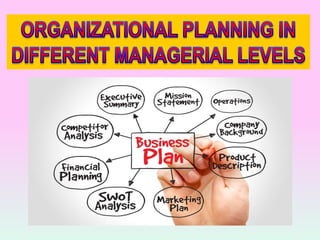
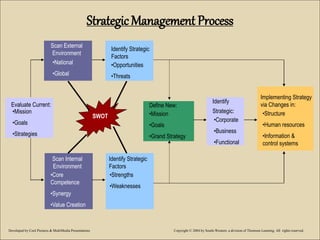
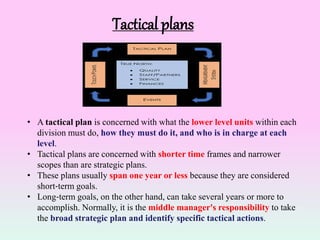
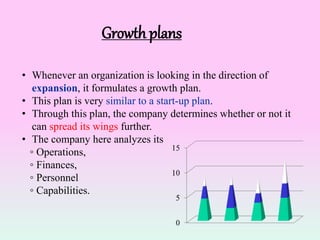
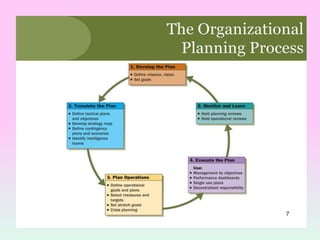
The document discusses various types of organizational plans. It defines a plan as a blueprint for attaining goals through allocating resources and scheduling actions. There are different levels of plans, including strategic plans that outline steps for the entire organization over 2-5 years, tactical plans for lower units over 1 year, and operational plans with specific measurable goals for departments. The planning process begins with developing a mission statement and strategic goals, then identifying internal/external factors in a SWOT analysis to define new missions, goals, and grand strategies. Lower levels then create compatible tactical and operational objectives to achieve the strategic plans.