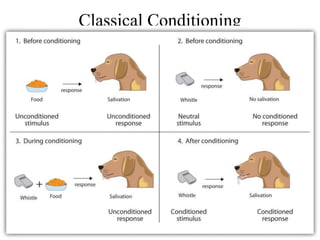
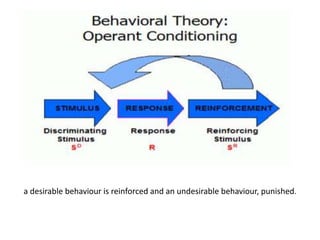
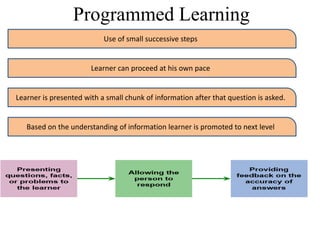
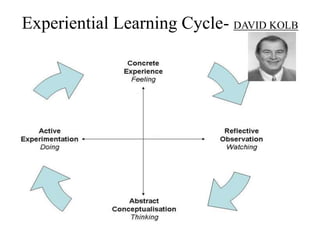
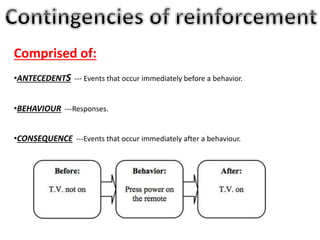
The document discusses learning and reinforcement approaches including classical conditioning, operant conditioning, social learning, and cognitive learning. It describes key theorists like Ivan Pavlov, B.F. Skinner, and Albert Bandura. Bandura's social learning theory explains how observation, imitation, and modeling influence learning. The document also discusses barriers to learning at the individual, group, and organizational levels and different methods of programmed learning like linear programming.