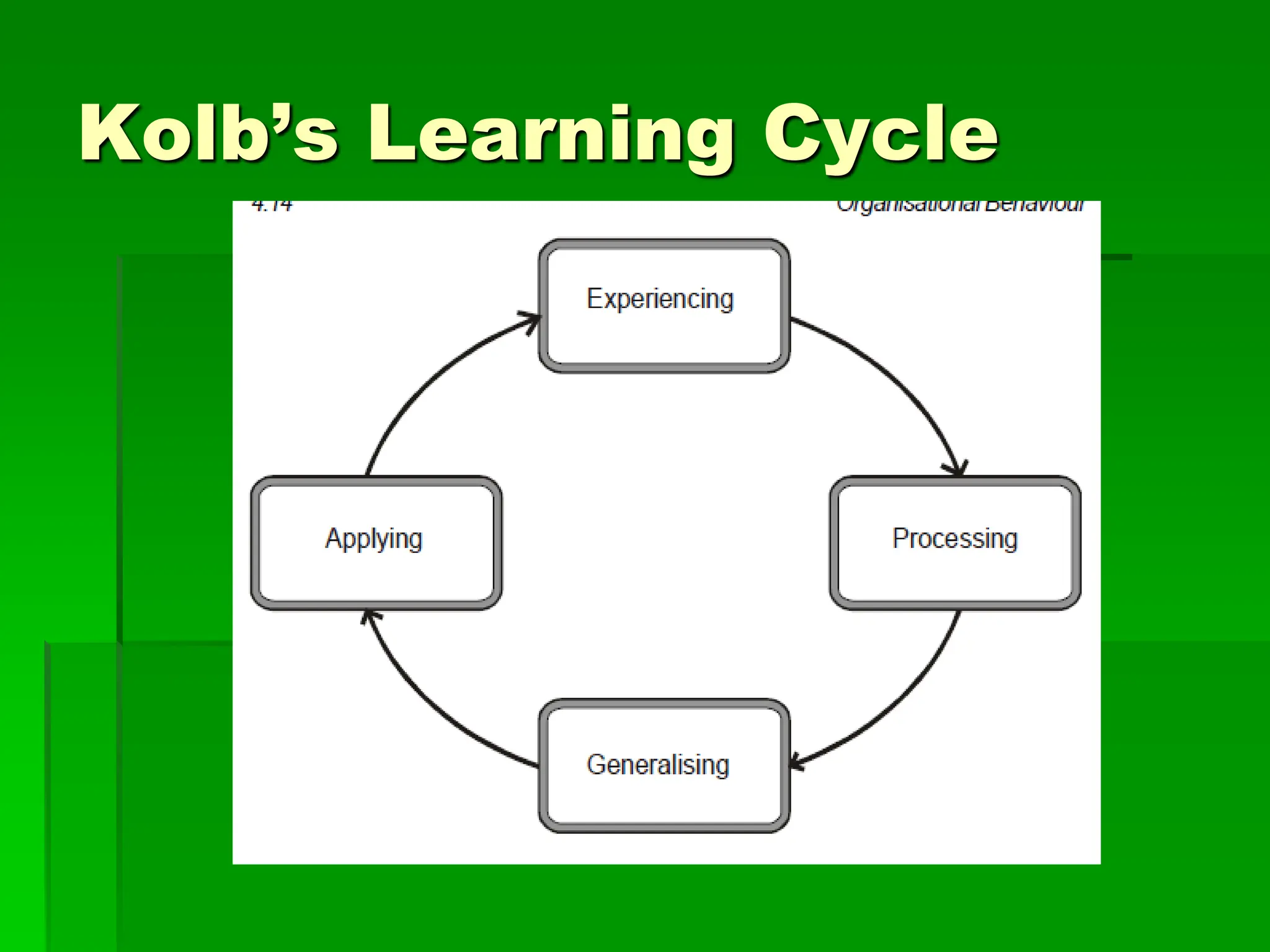
The document discusses learning in organizational behavior. It defines learning as a relatively permanent change in behavior resulting from experience or practice. Several theorists define learning differently, such as a process of acquiring new behaviors, or changes in knowledge, skills, and attitudes. Key aspects of learning include reinforcement, different learning theories, and its application in organizations. Learning plays a vital role in organizational behavior as employees must continuously learn and update their skills through training.