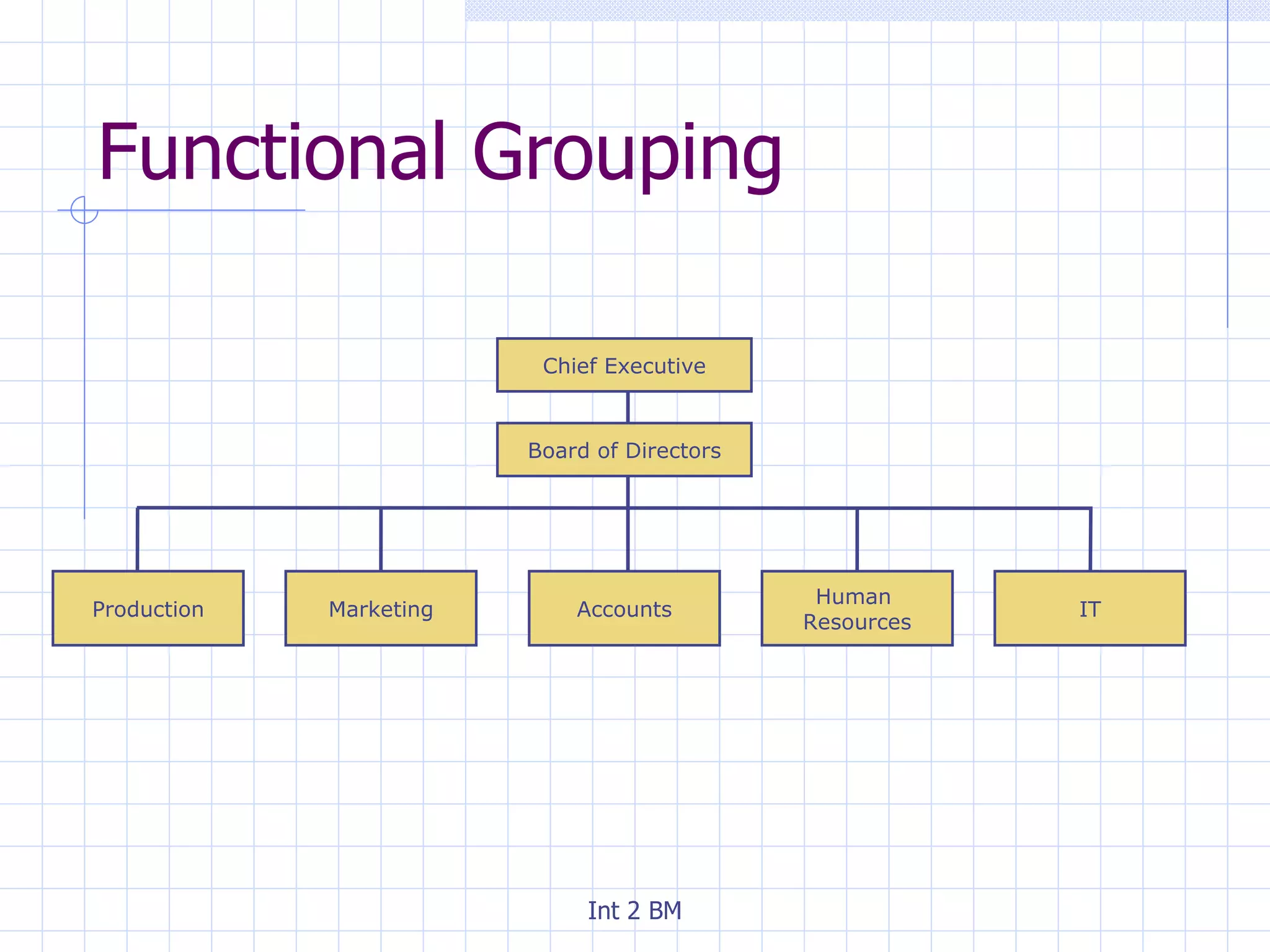
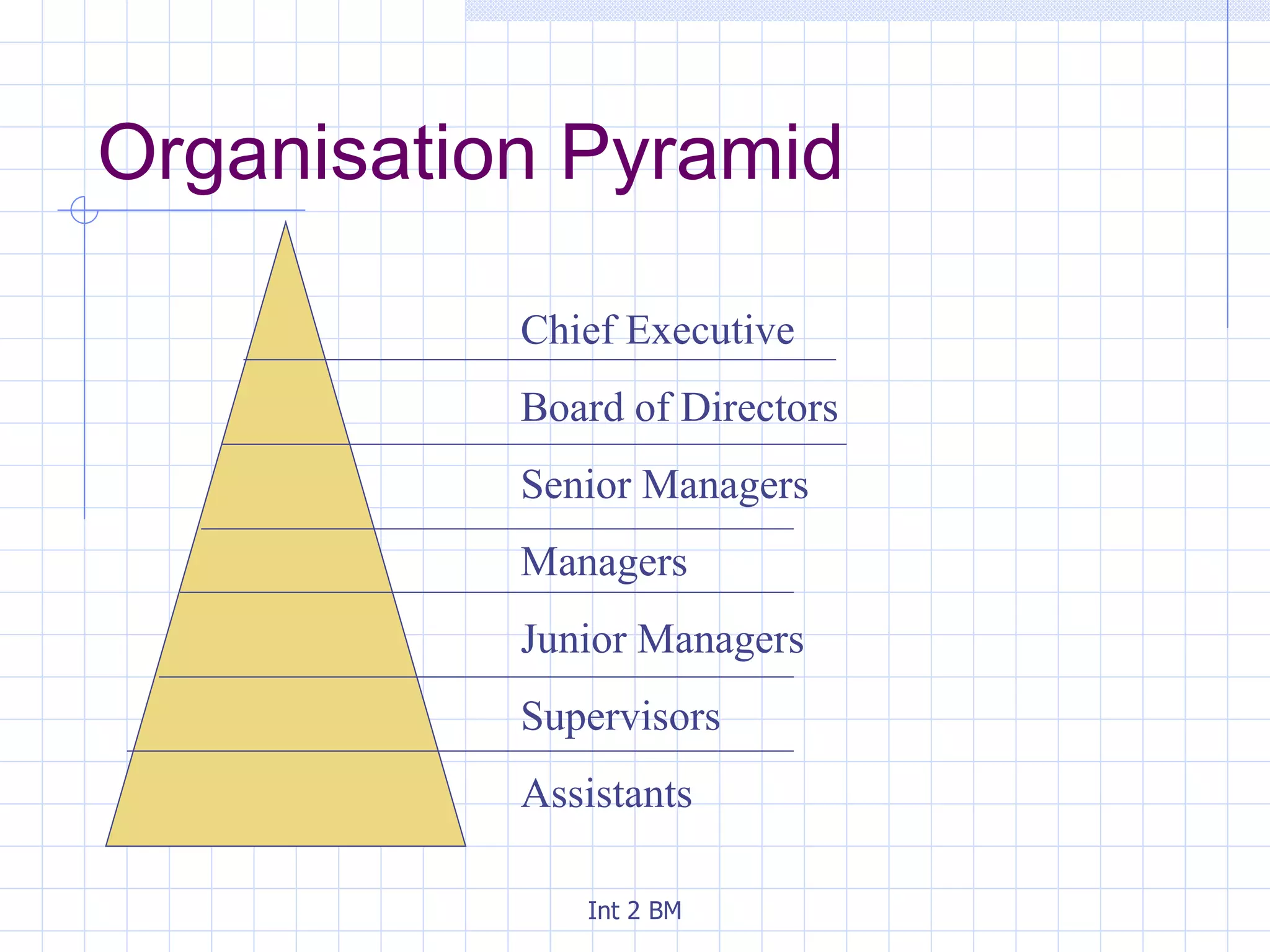
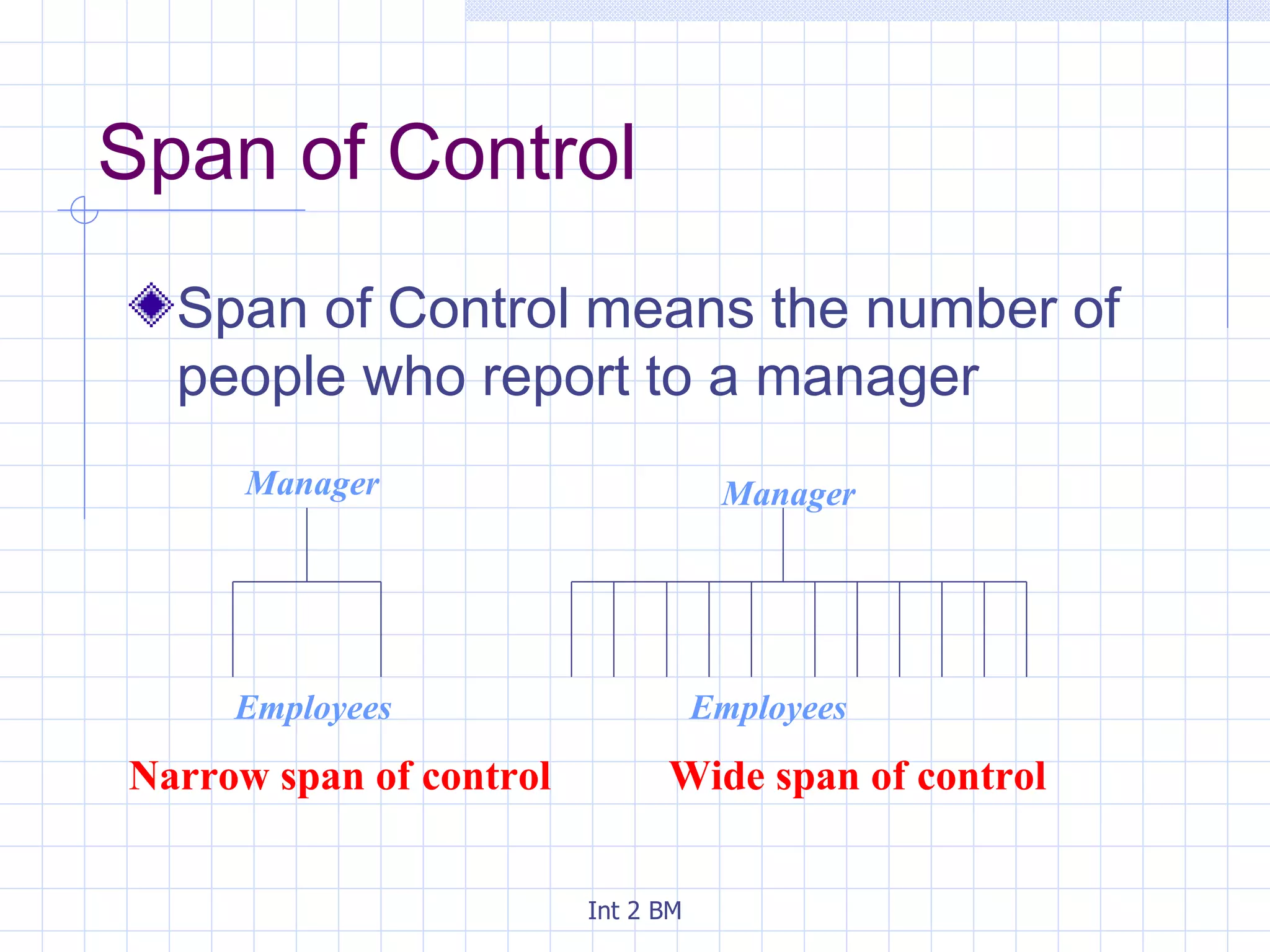
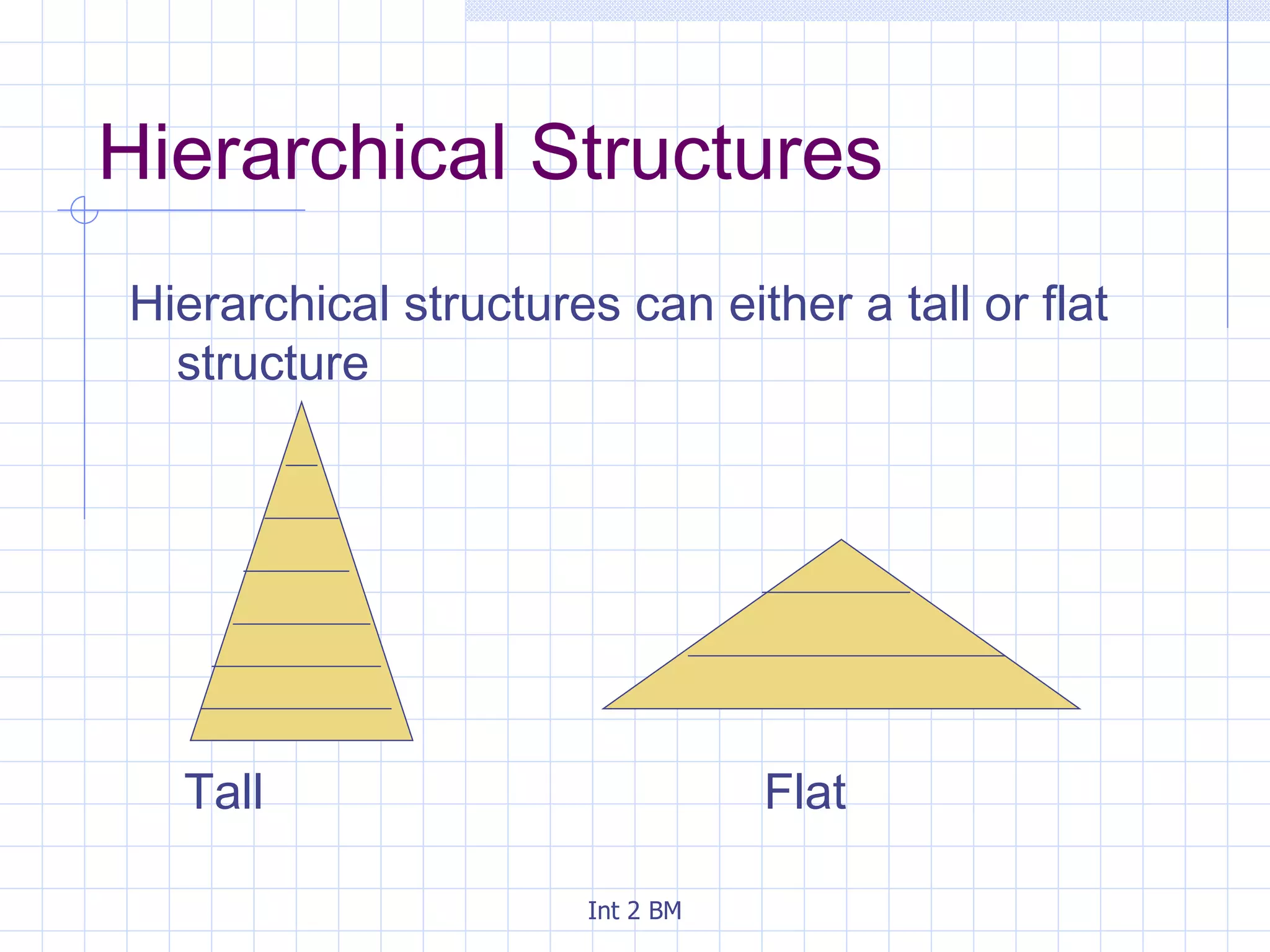
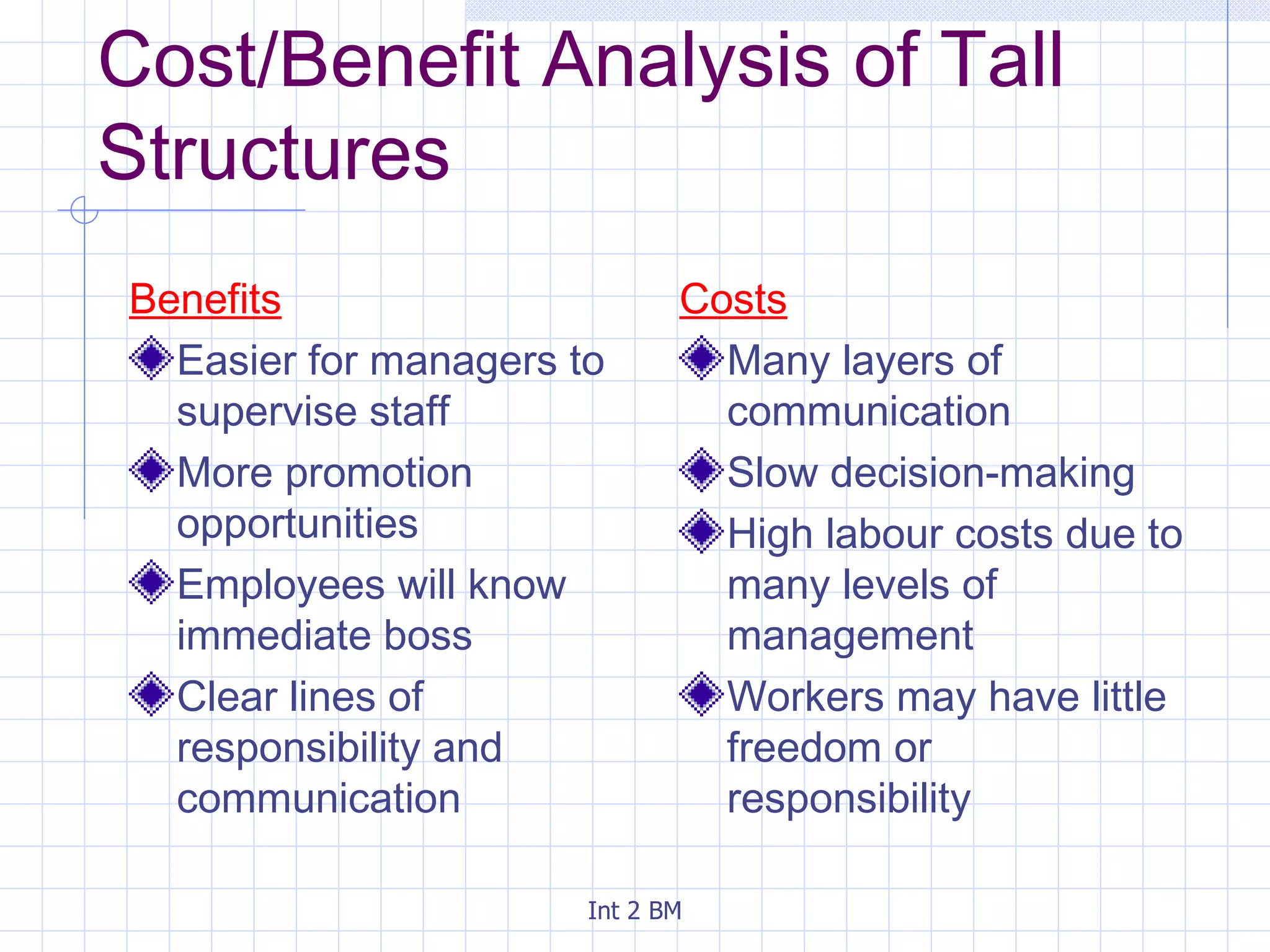
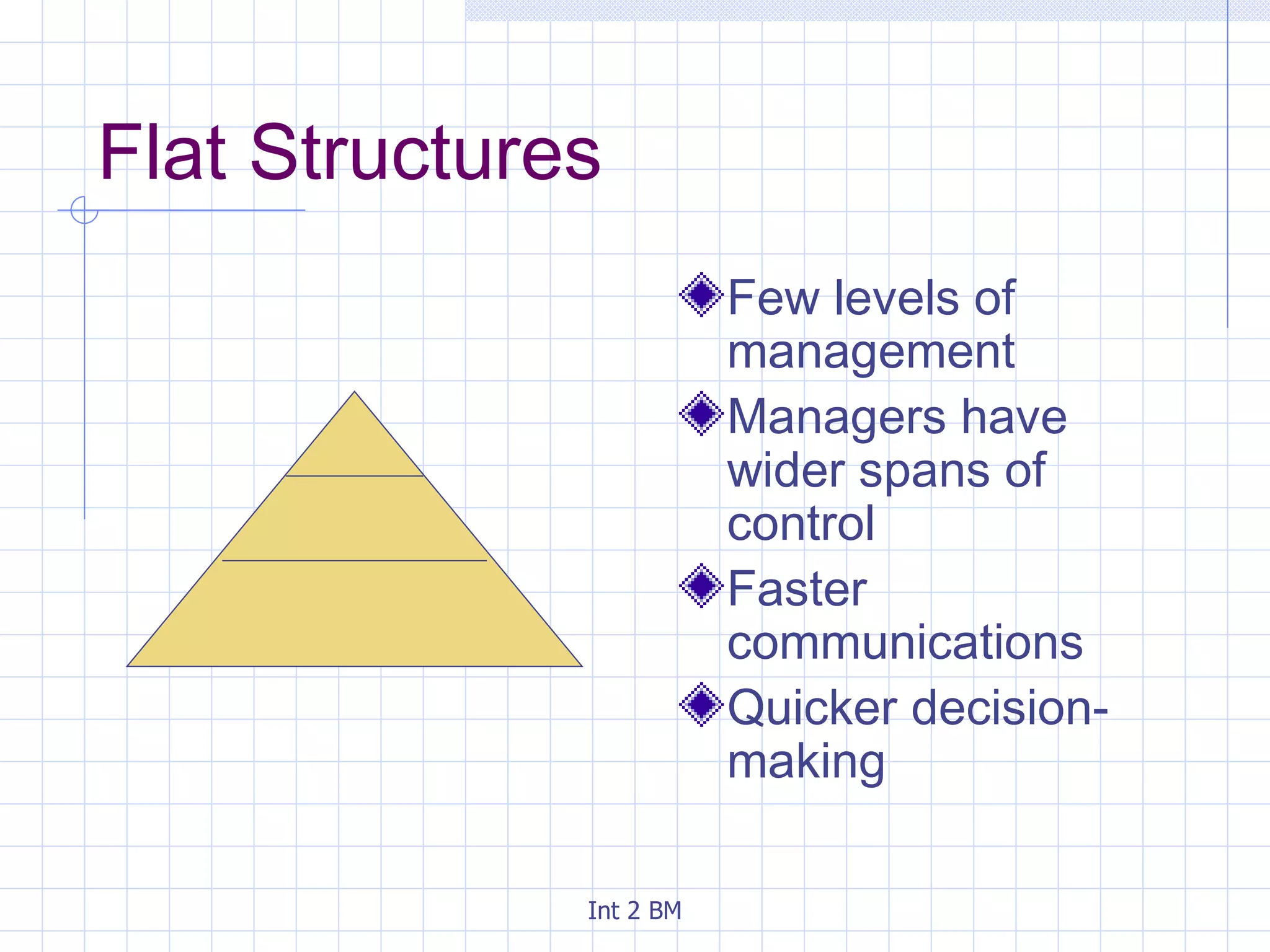
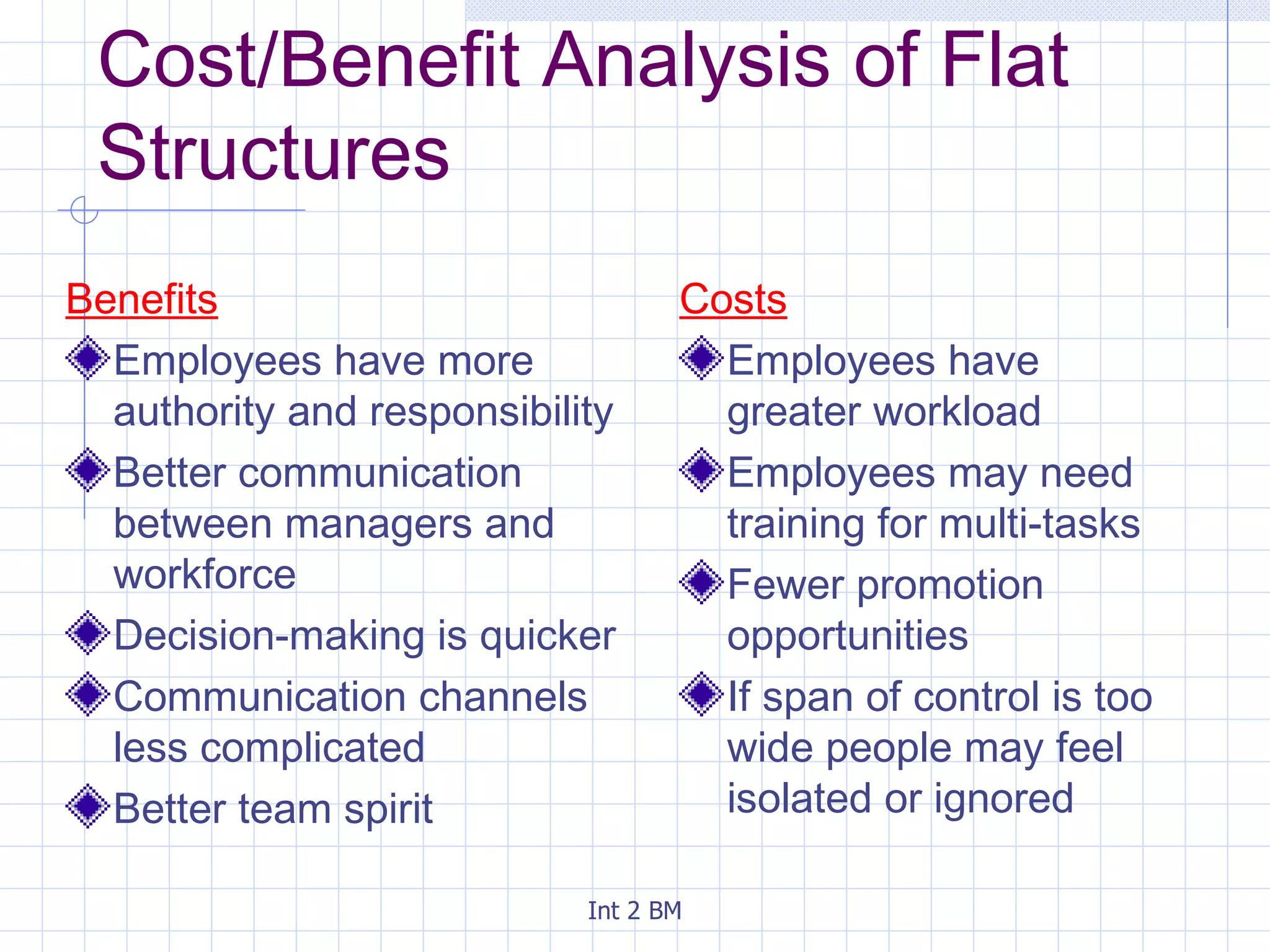
An organization is a group of people working towards defined goals and objectives. Organizations typically have functional groupings where staff with similar skills and expertise perform similar jobs, such as marketing, finance, and human resources. There are two main types of organizational structures - hierarchical and flat. Hierarchical structures have many levels of management and narrow spans of control, while flat structures have few levels of management and wider spans of control. The optimal structure depends on factors like the organization's size, technology used, and staff skills.