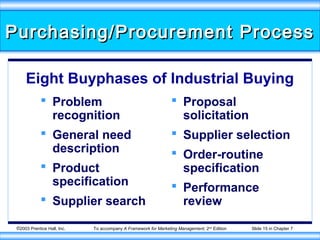
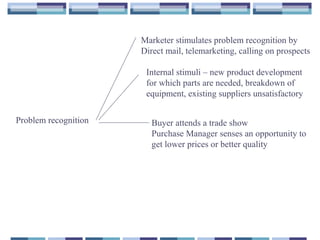
This document summarizes key concepts about organizational buying and the business buying process. It discusses how organizational buying differs from consumer buying, including that business markets have fewer and larger buyers that are geographically concentrated. It also outlines the different buying situations organizations face, including straight rebuys, modified rebuys, and new tasks. Additionally, it identifies the various roles in organizational buying centers and the environmental, organizational, interpersonal, and individual influences that impact business buying decisions. Finally, it provides an overview of the typical steps in the business purchasing/procurement process.