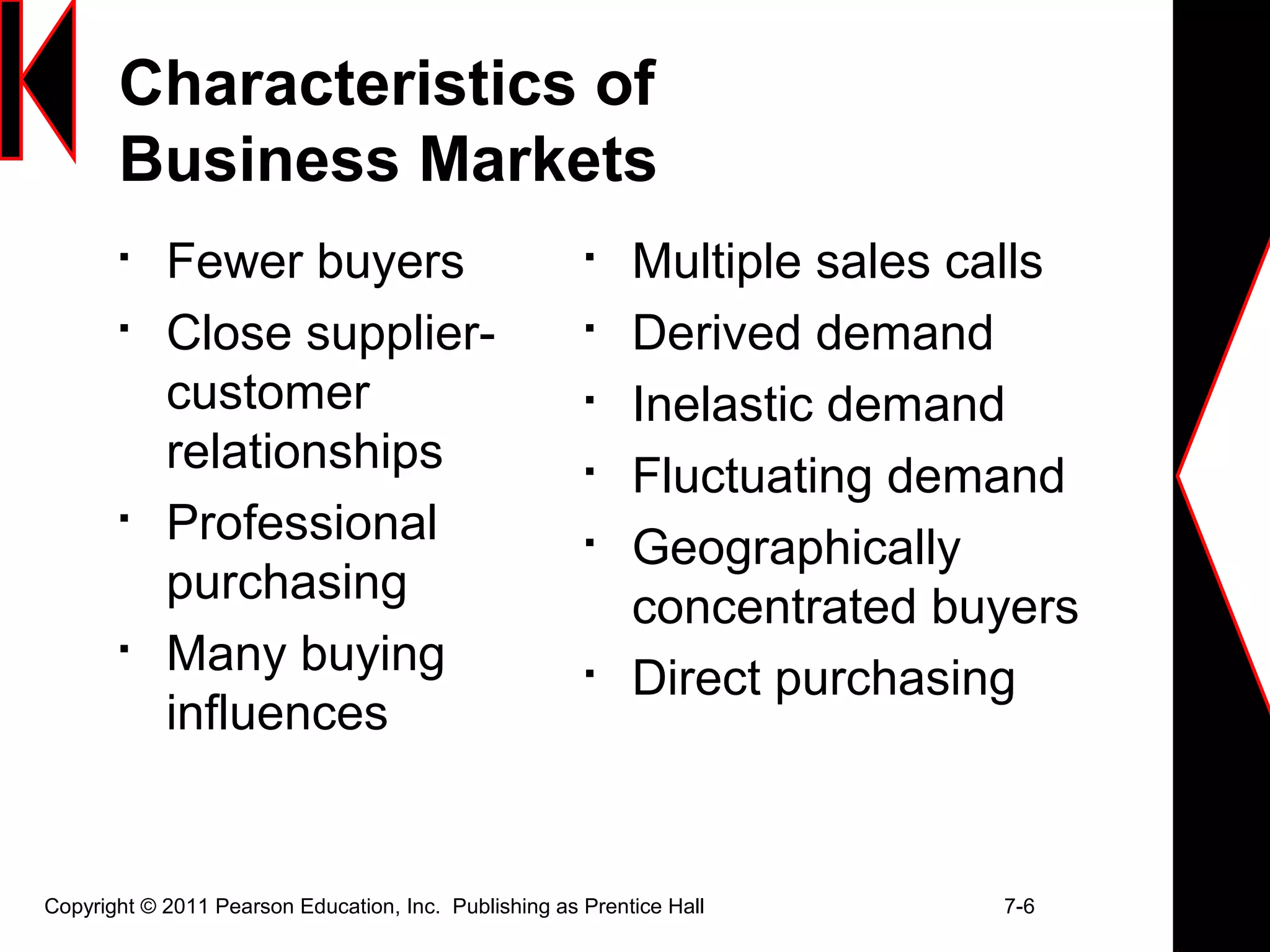
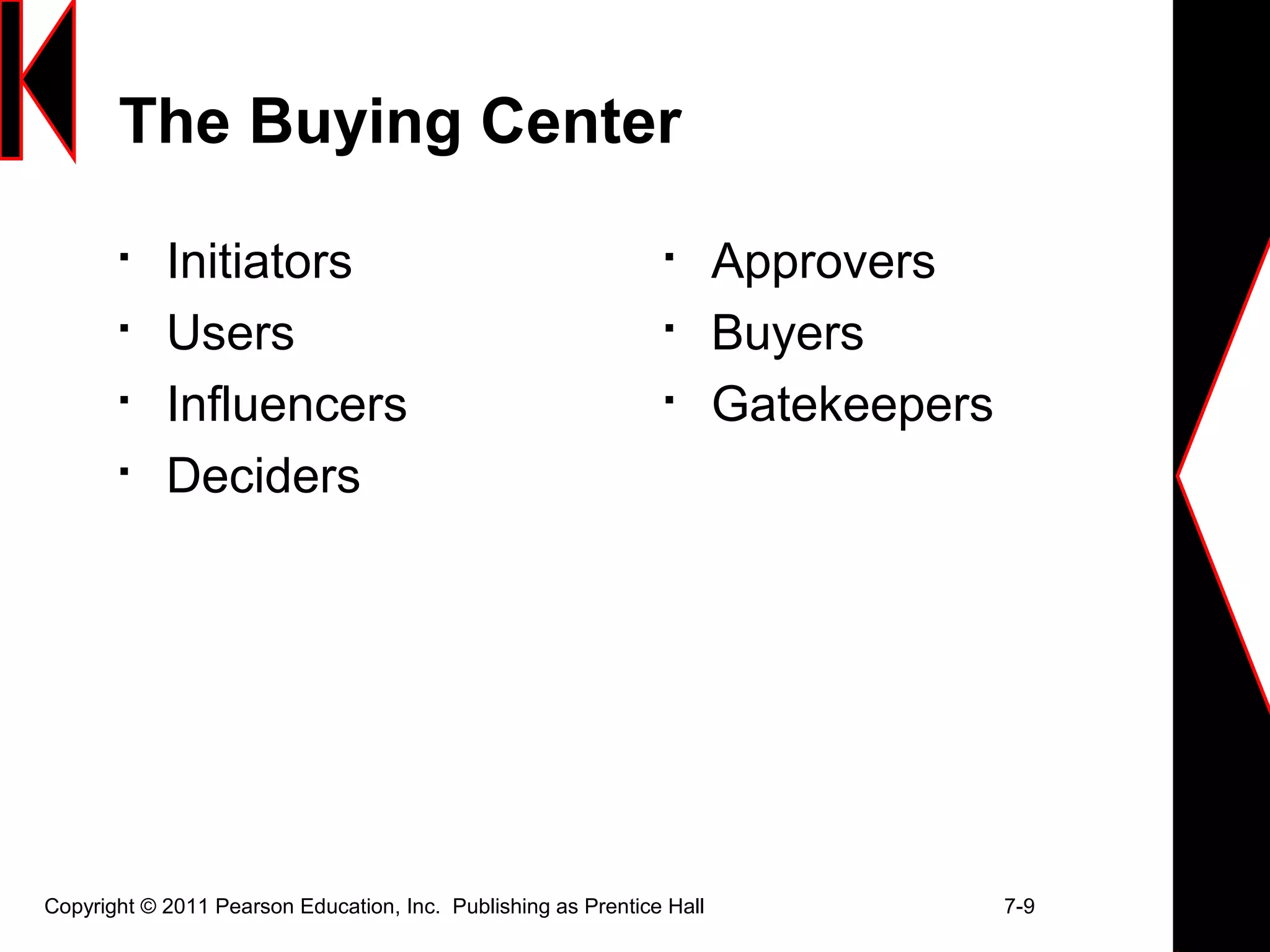
This document discusses analyzing business markets and organizational buying. It begins by asking chapter review questions about the nature of business markets, buying situations, and the business-to-business buying process. The document then defines organizational buying and discusses characteristics of business markets, different buying situations, and the various roles that make up the buying center. It also outlines the stages in the buying process and methods for researching customer value and building buyer-seller relationships. Finally, it briefly discusses institutional markets and repeats the chapter review questions.