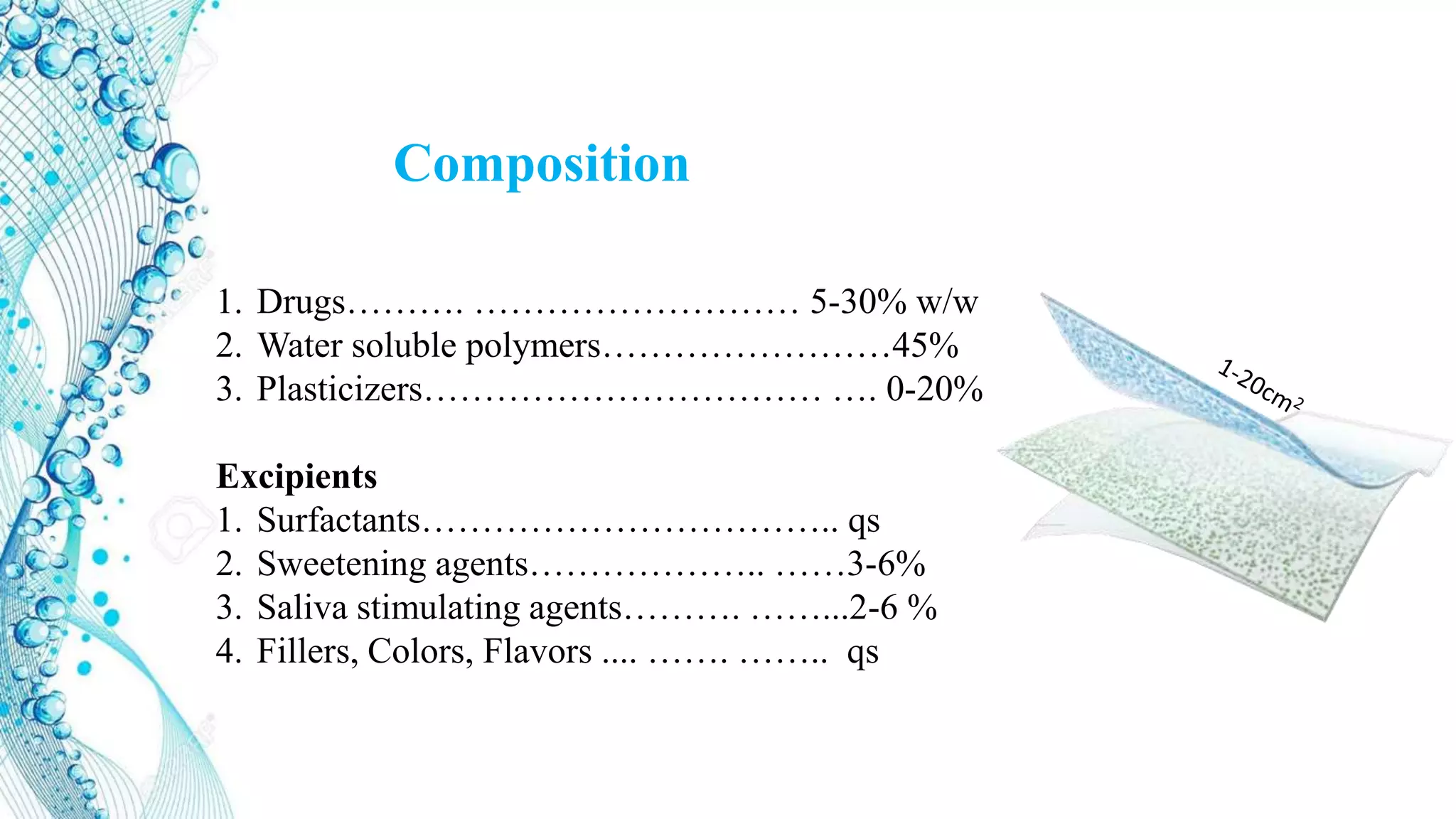
This document discusses emerging trends in alternative drug delivery systems, focusing on orally disintegrating films (ODFs). It provides information on:
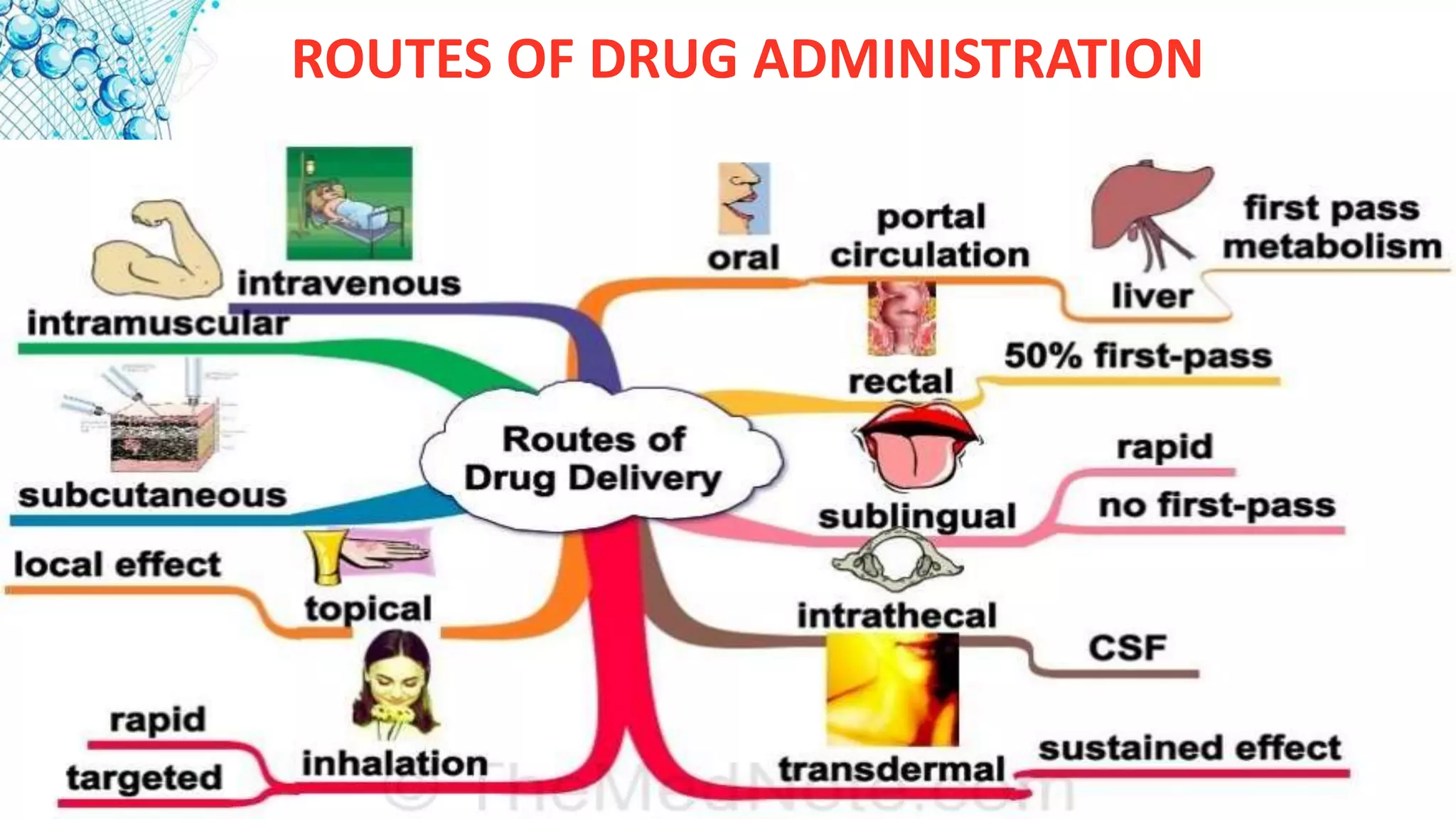
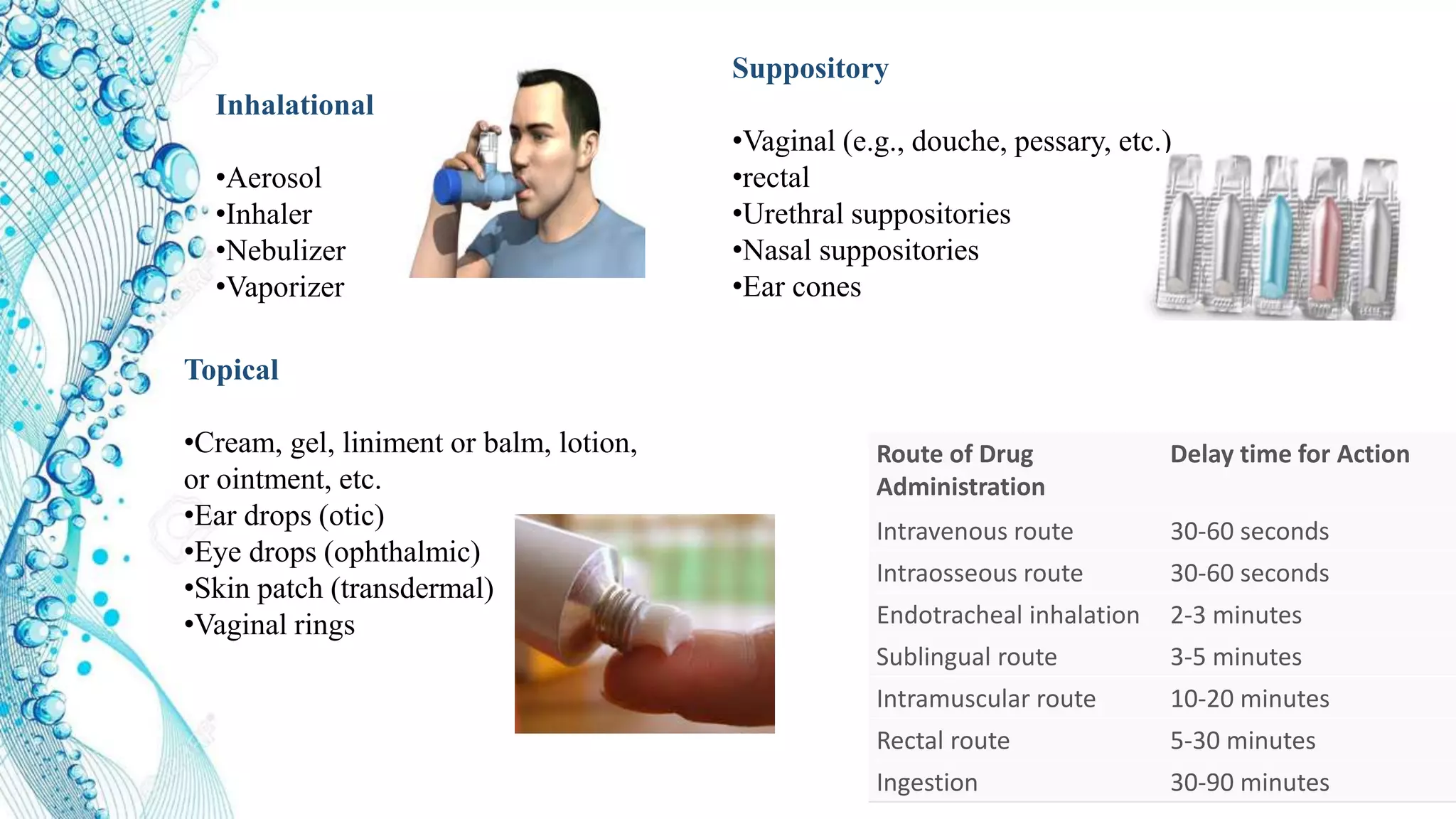
1. What drugs are and routes of drug administration including oral, parenteral, suppository, inhalational, and topical.
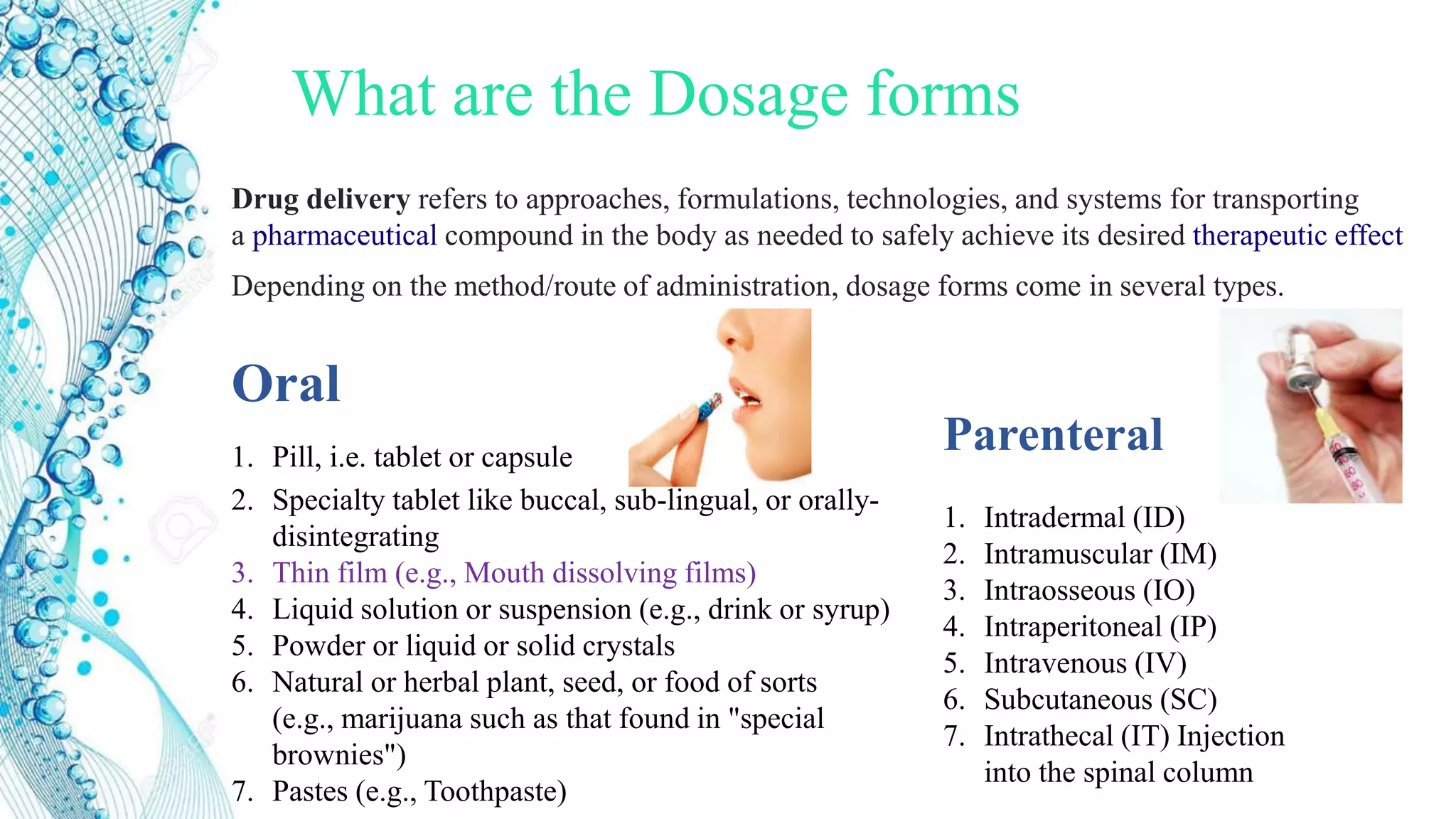
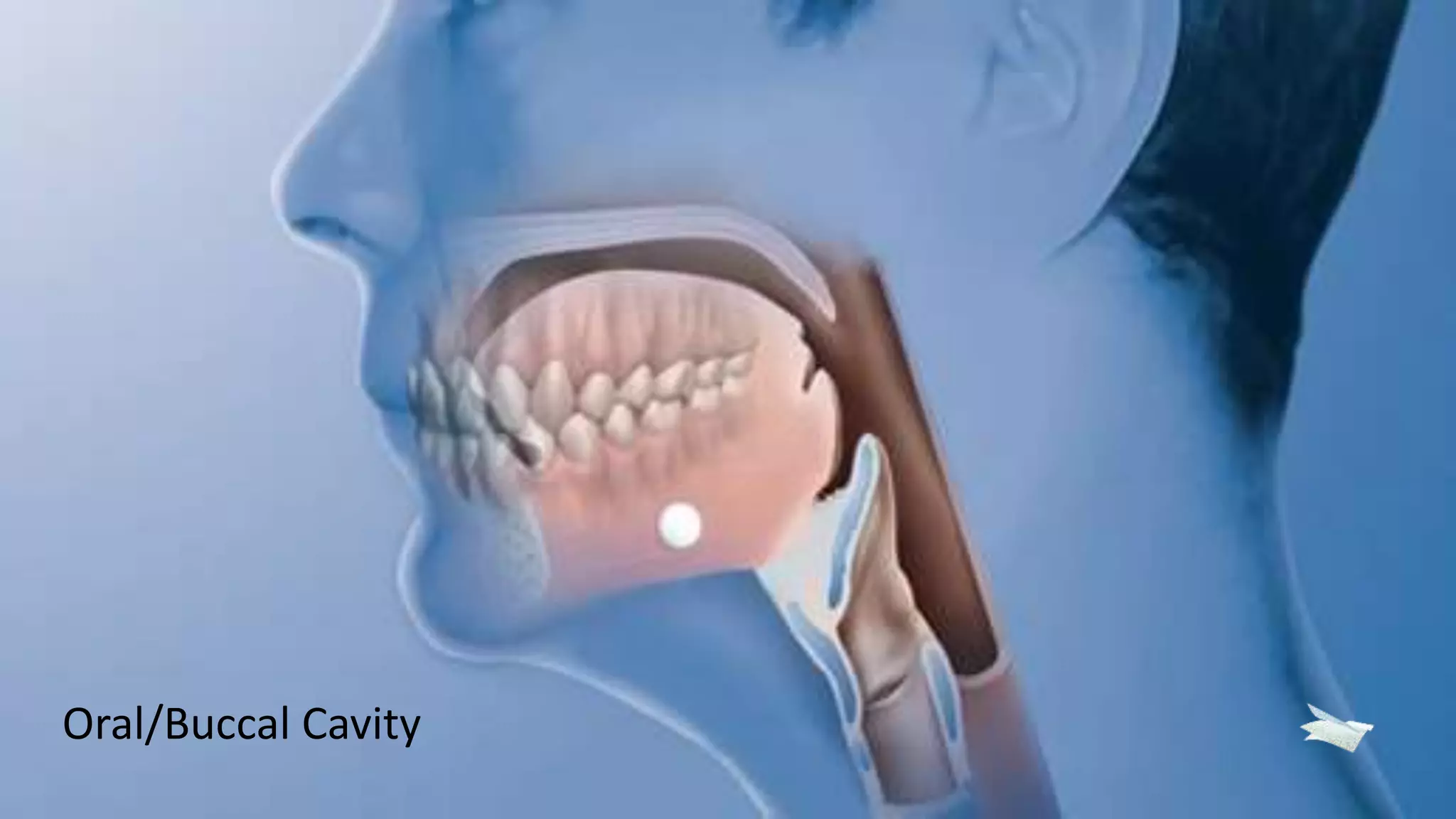
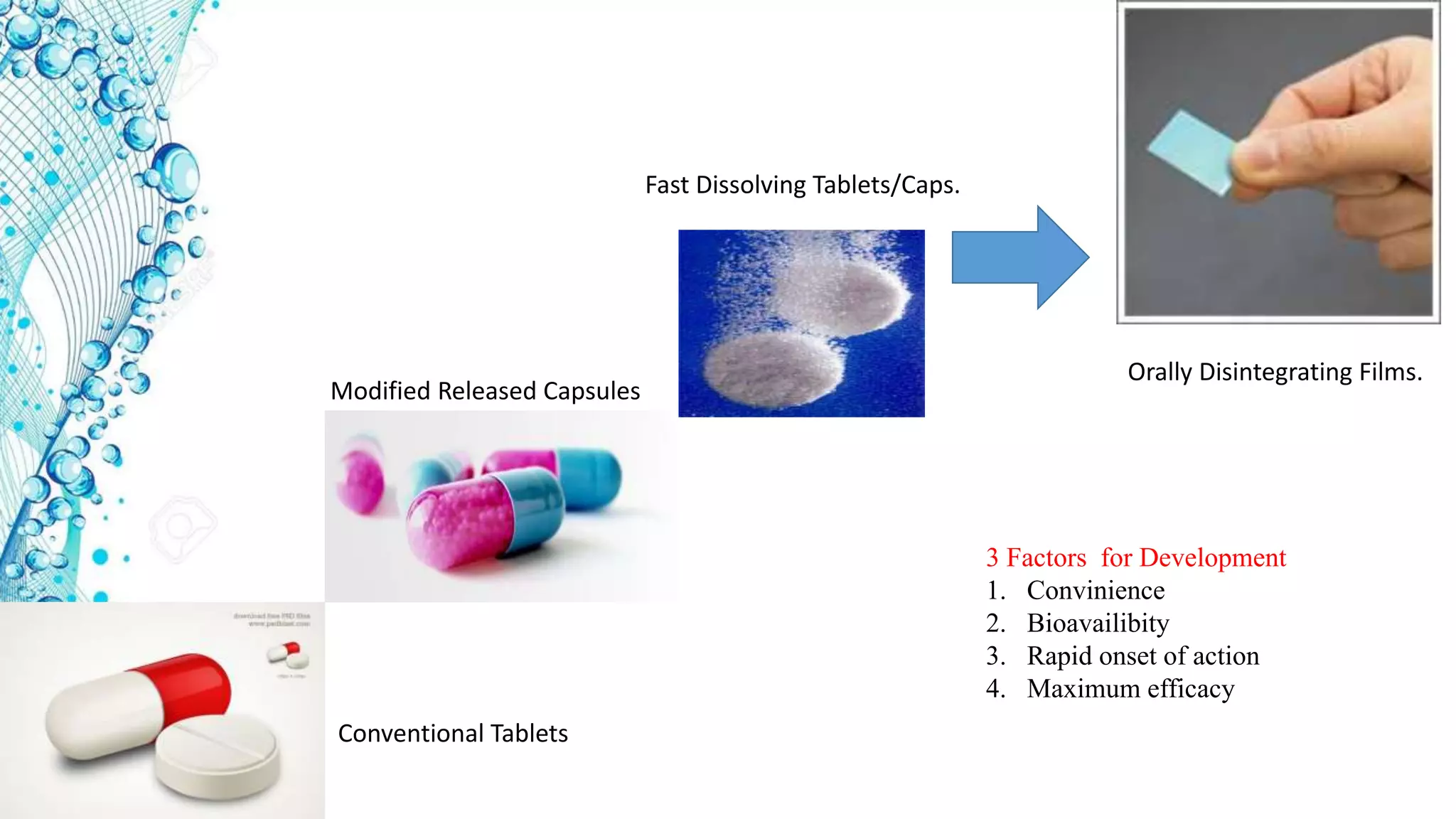
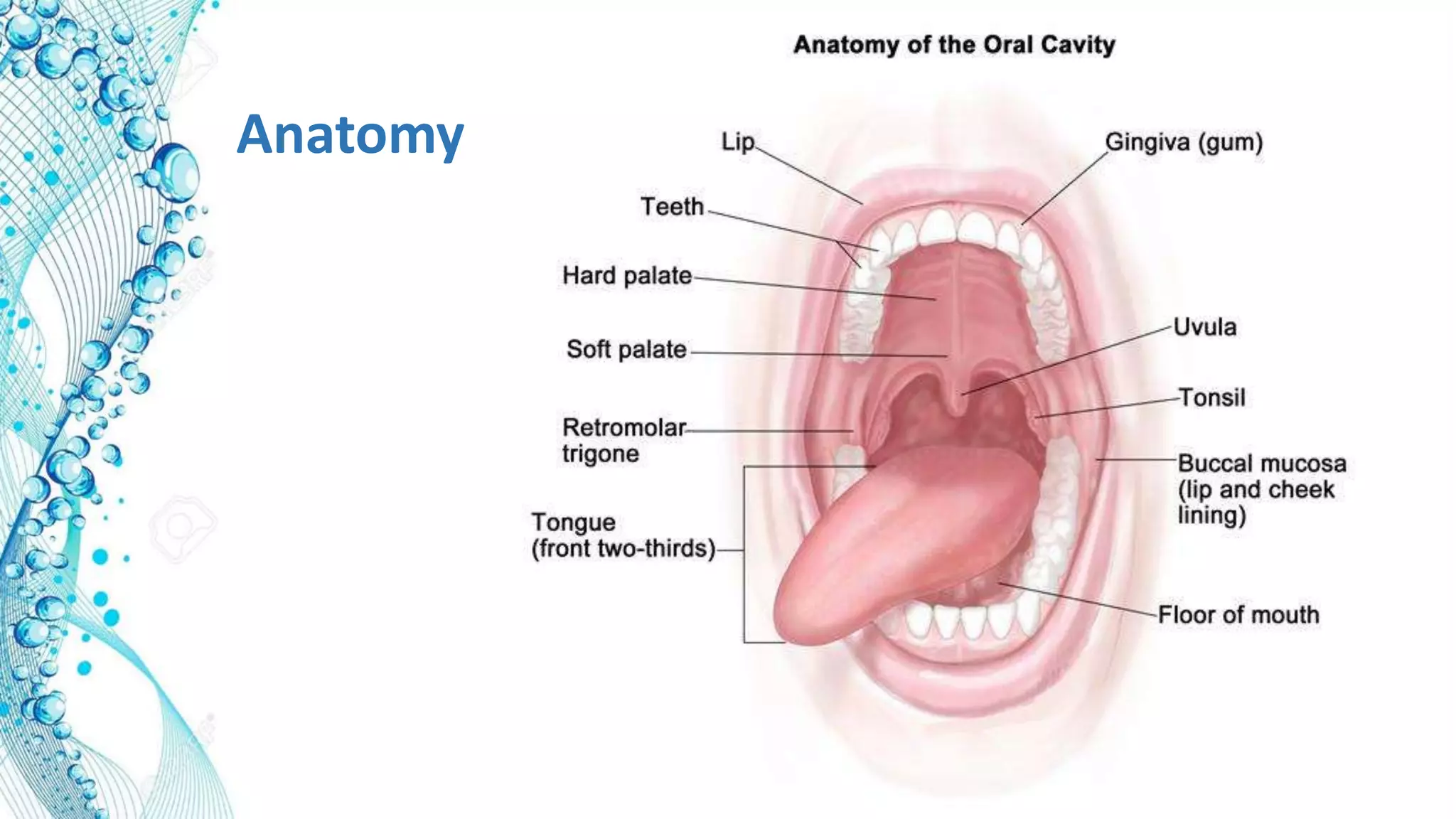
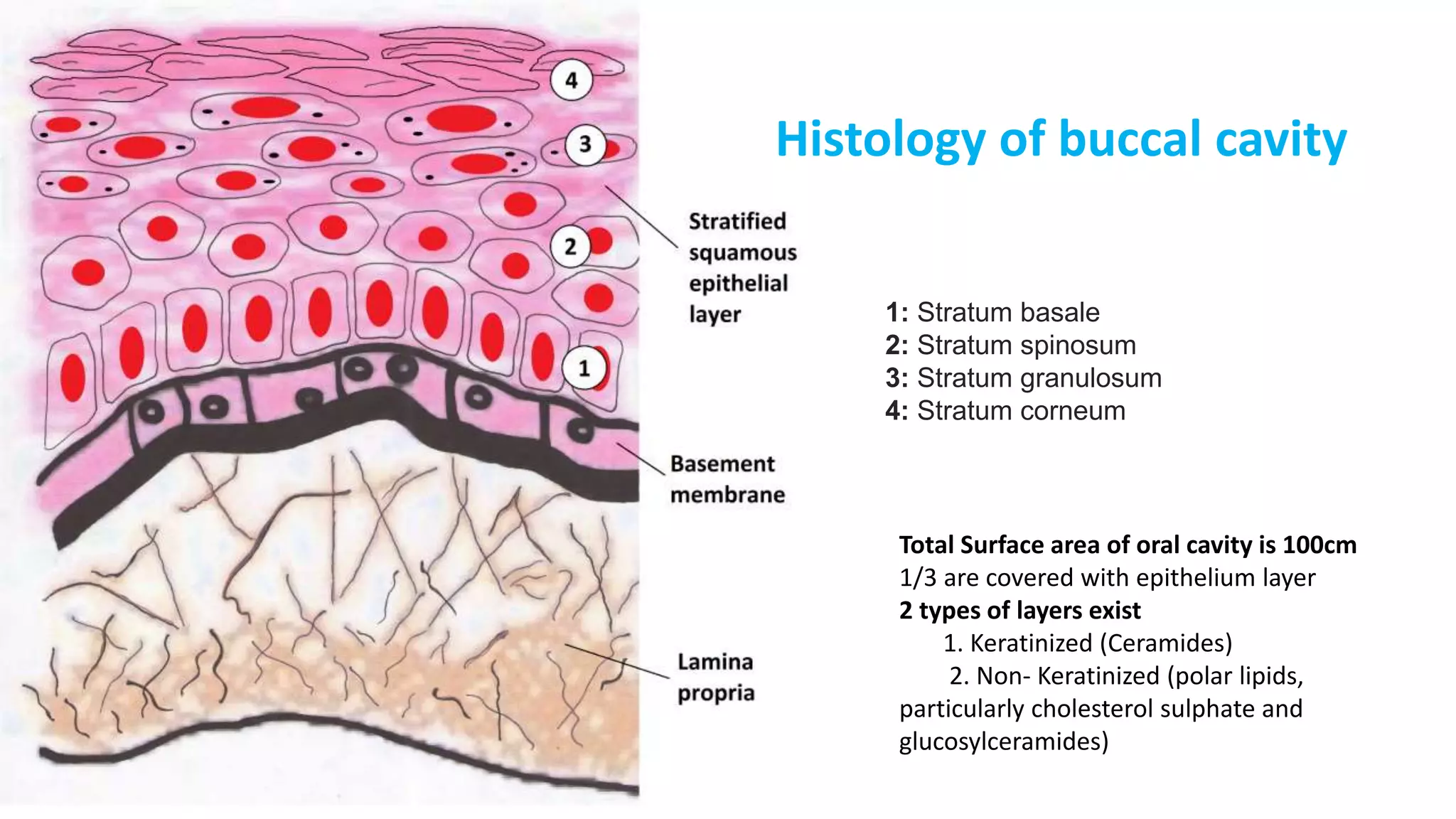
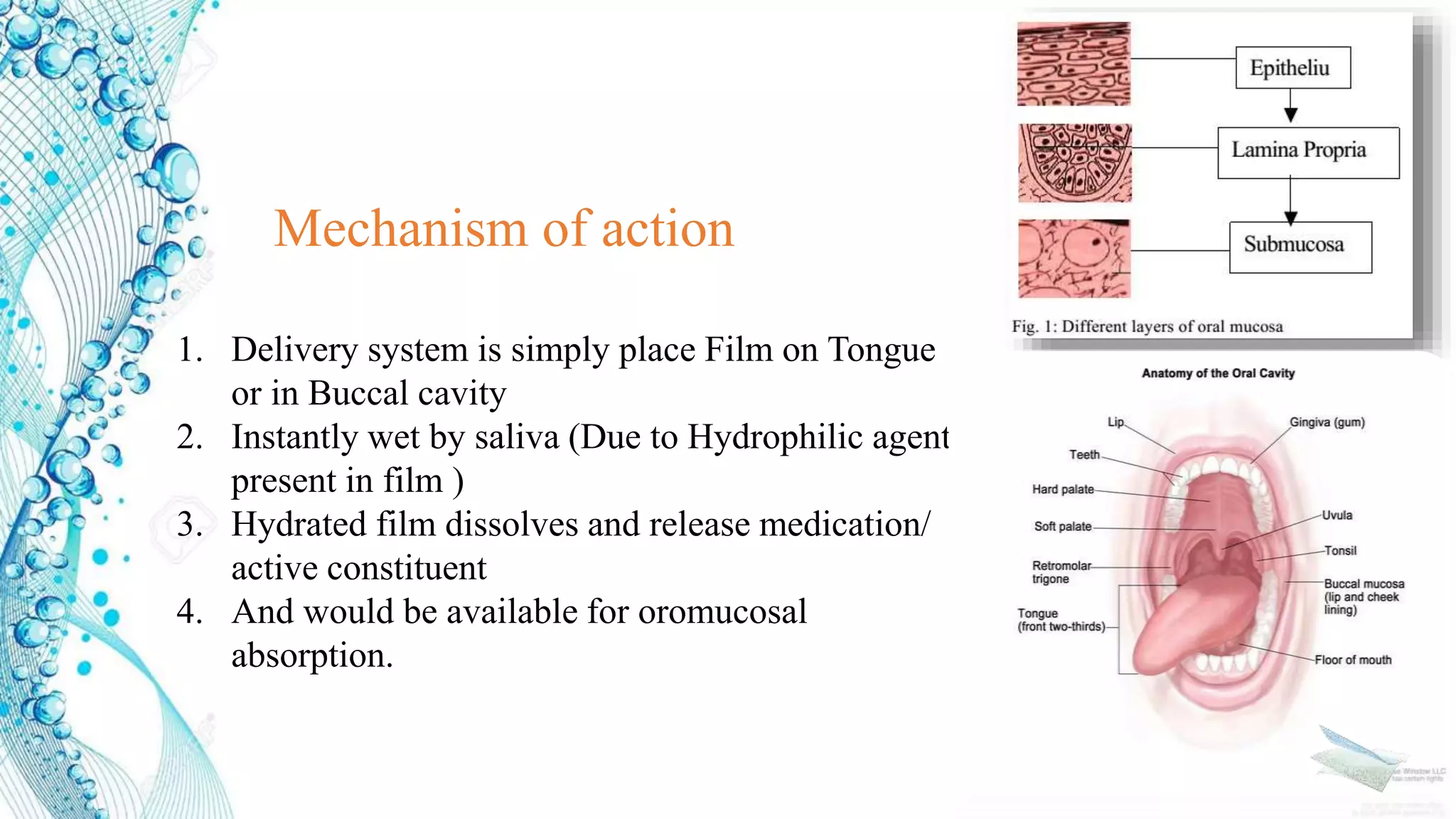
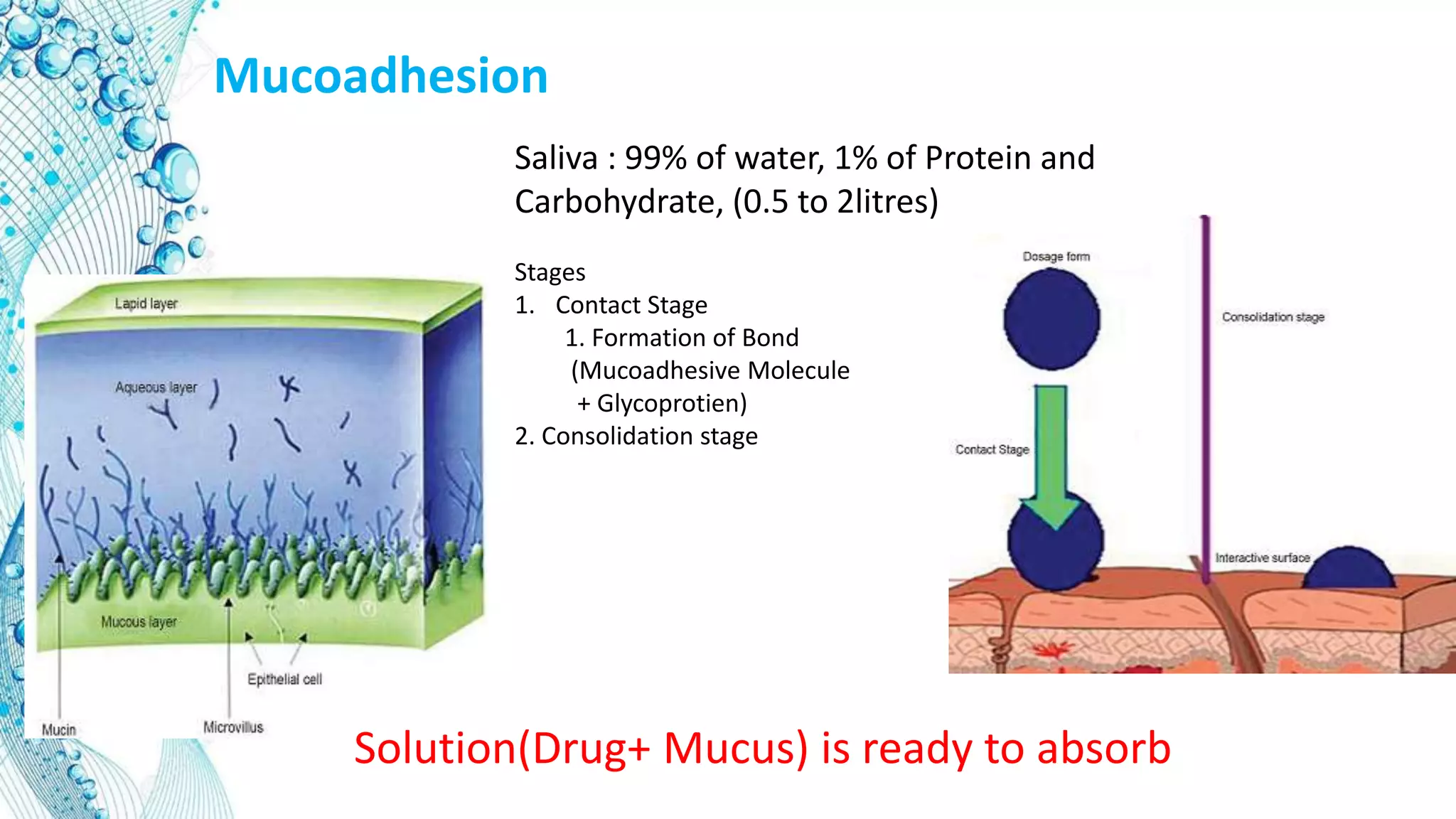
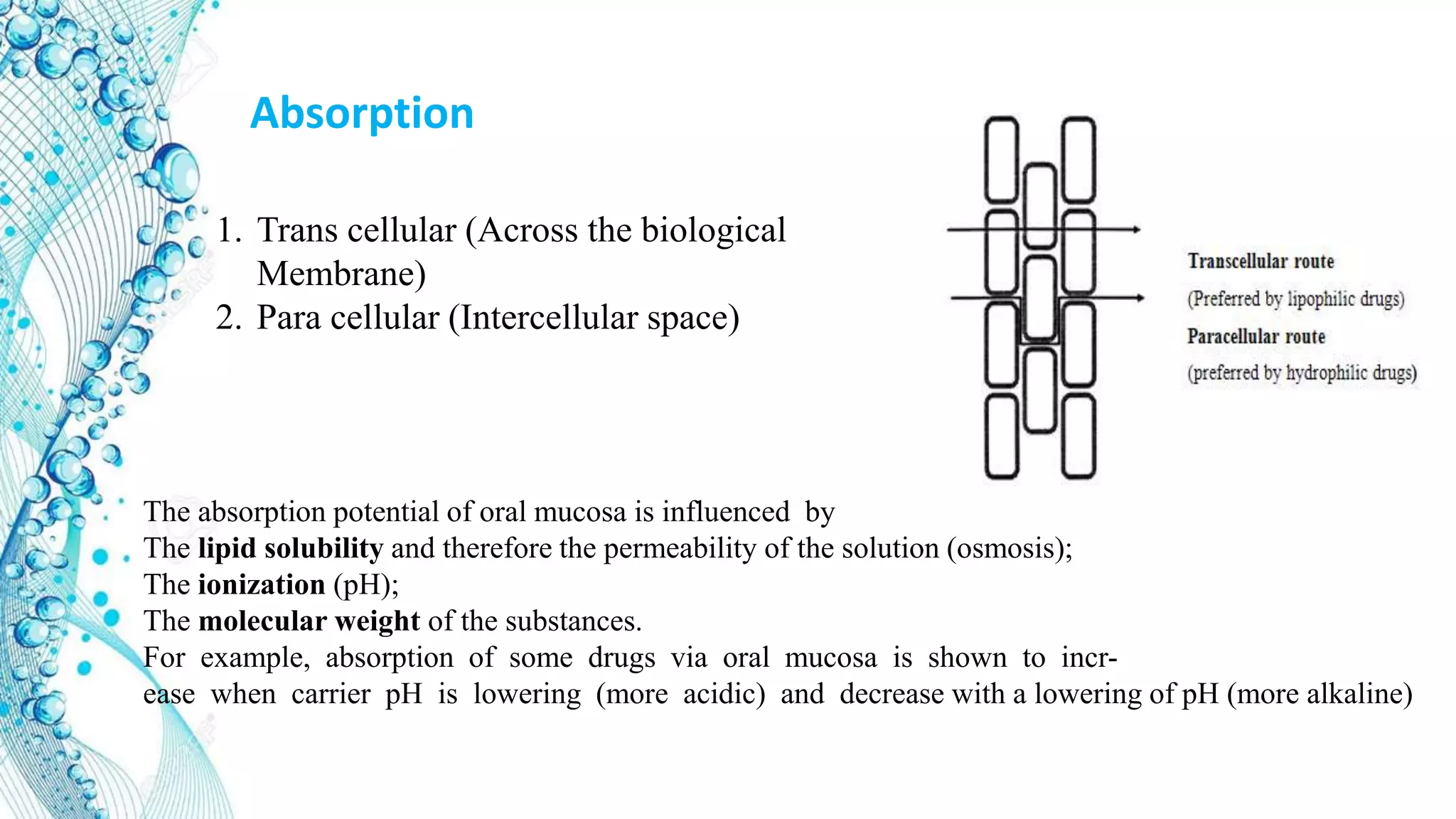
2. Details on oral dosage forms including pills, liquids, and thin films. It describes the mechanism of action for ODFs including mucoadhesion and absorption.
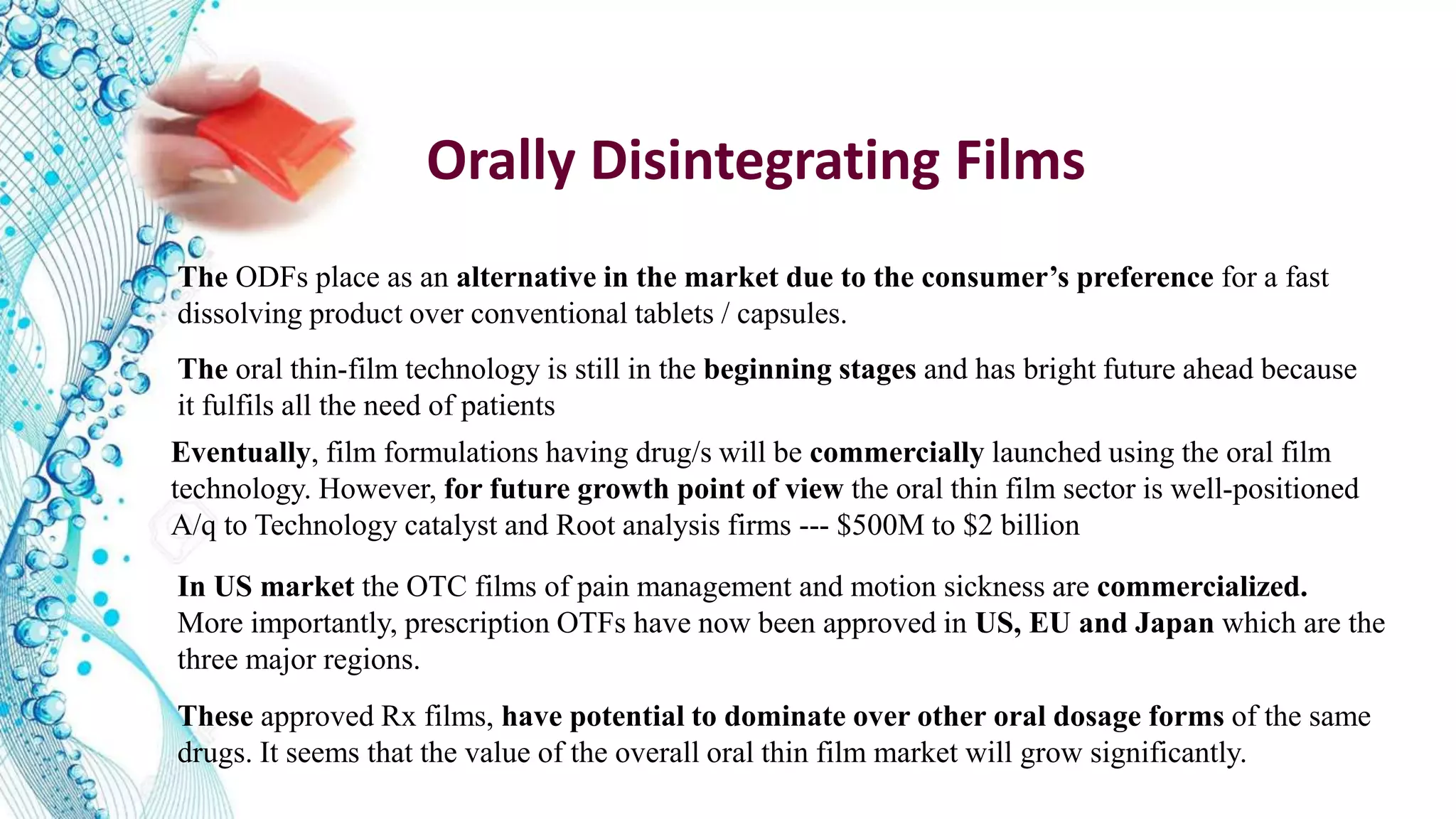
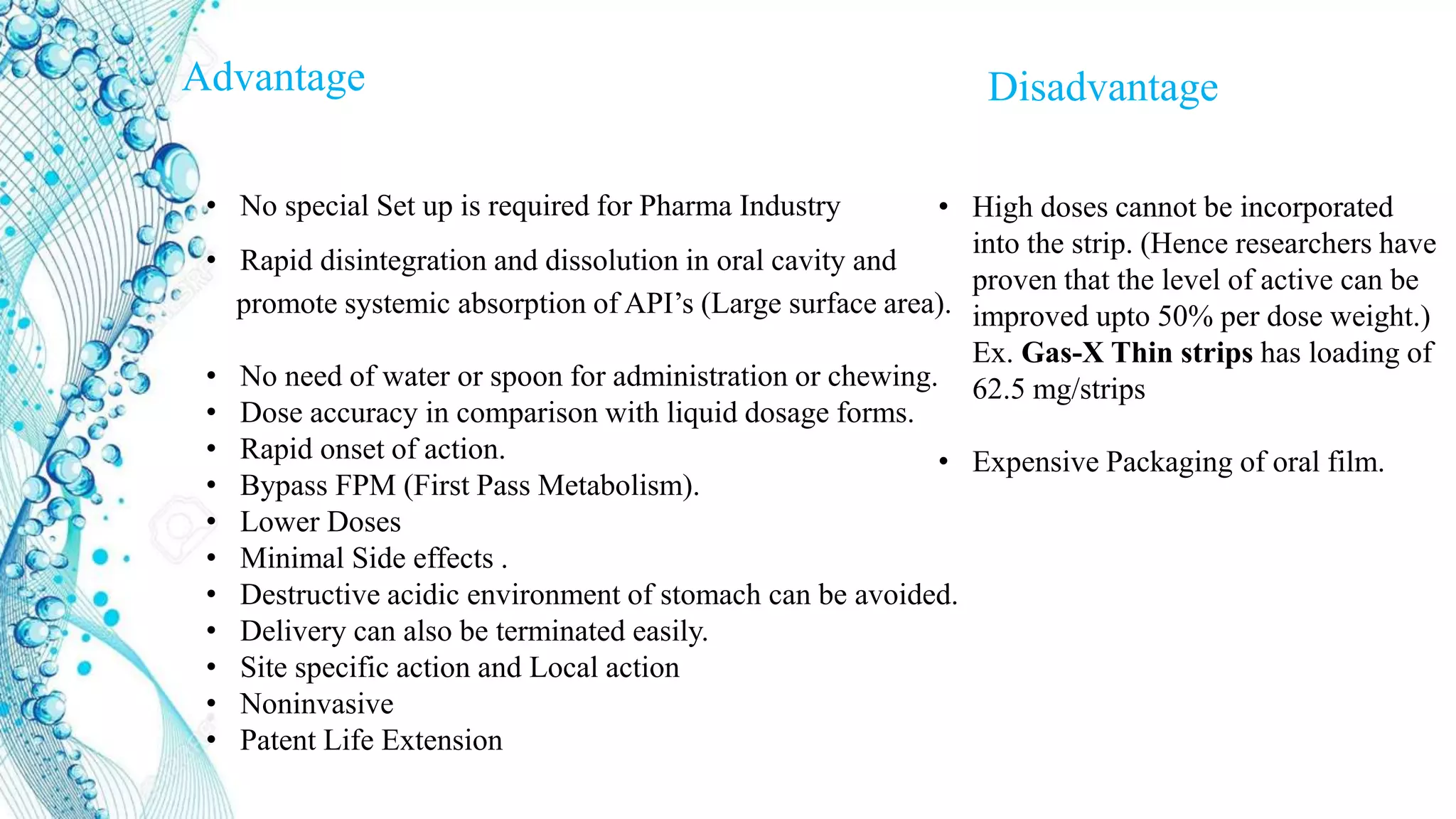
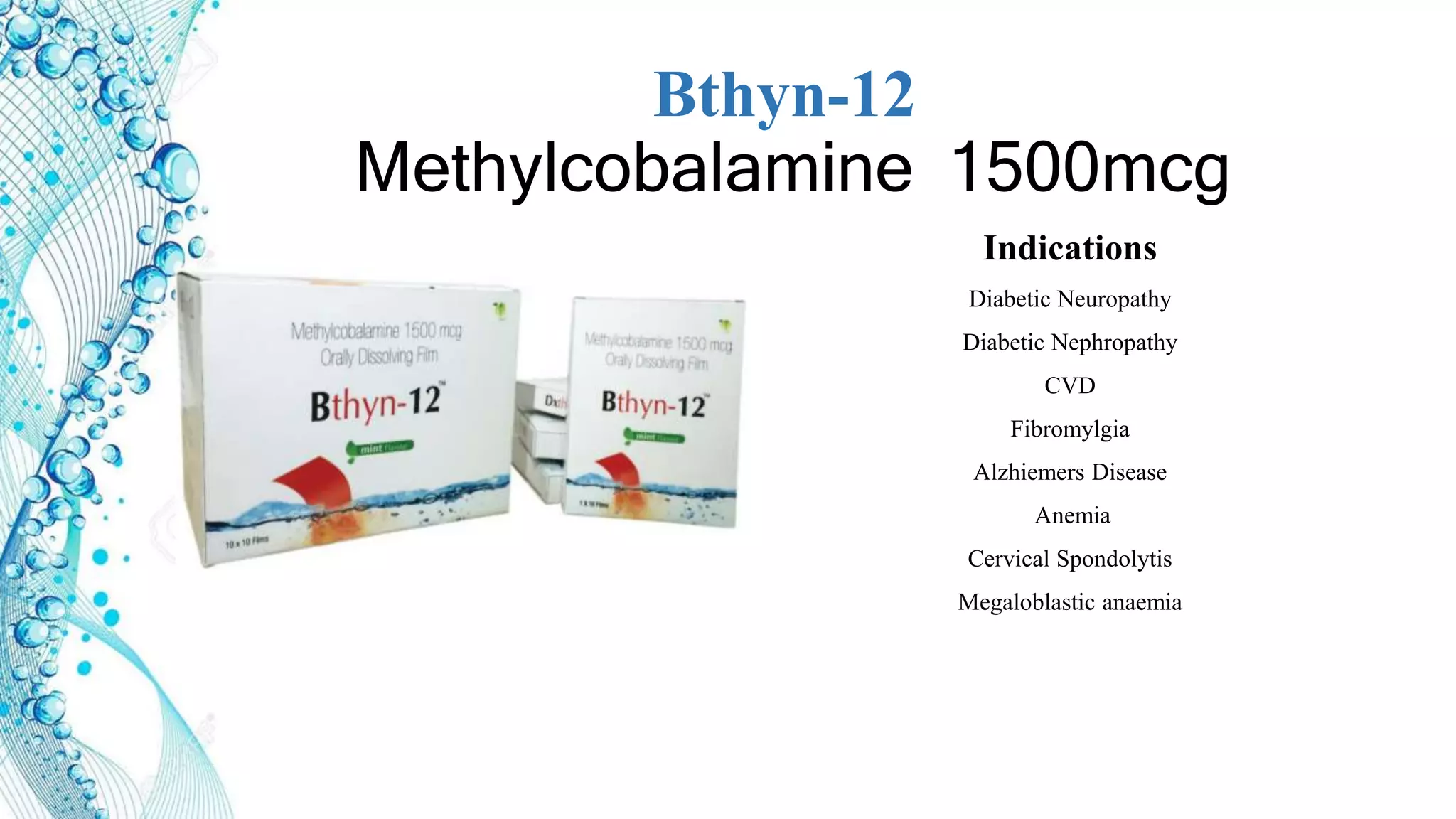
3. Advantages of ODFs include rapid onset, bypassing first pass metabolism, and improved patient compliance compared to other dosage forms. Example products incorporating drugs into ODFs are mentioned.