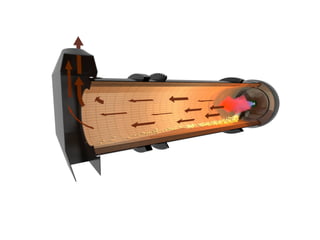
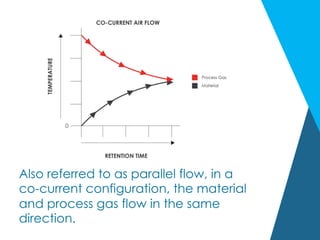
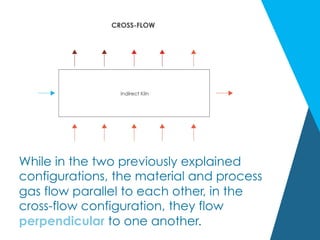
The document discusses various air flow configurations in rotary kilns, essential for effective thermal processing. It describes co-current, counter-current, and cross-flow designs, highlighting their advantages and applications based on material properties and processing goals. Understanding these configurations is crucial for optimizing kiln design to enhance efficiency and output.