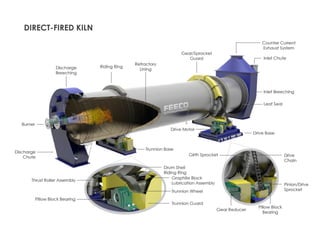
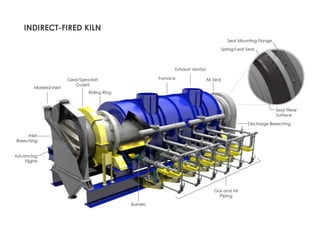
Rotary kilns are advanced thermal processing tools utilized for chemical reactions and physical changes in solid materials through high temperatures, with applications in industries such as mineral roasting, waste incineration, and catalyst activation. They can be either direct-fired or indirect-fired, influencing the processing environment and material behavior. As a versatile technology, rotary kilns are critical to various industrial processes and continually see new applications and developments.