This document discusses using carbon nanotubes for optical code division multiple access (OCDMA) systems. It first provides background on carbon nanotubes, including their unique electronic and optical properties. It then describes the basic architecture and working principle of OCDMA systems. The document focuses on analyzing how using carbon nanotubes can improve key communication parameters like data rate, bit error rate, and signal-to-noise ratio in OCDMA systems compared to silicon-based optical devices. It presents results showing carbon nanotubes enable ultra-high speed networks with terabits per second data rates and exceptional error rate performance.

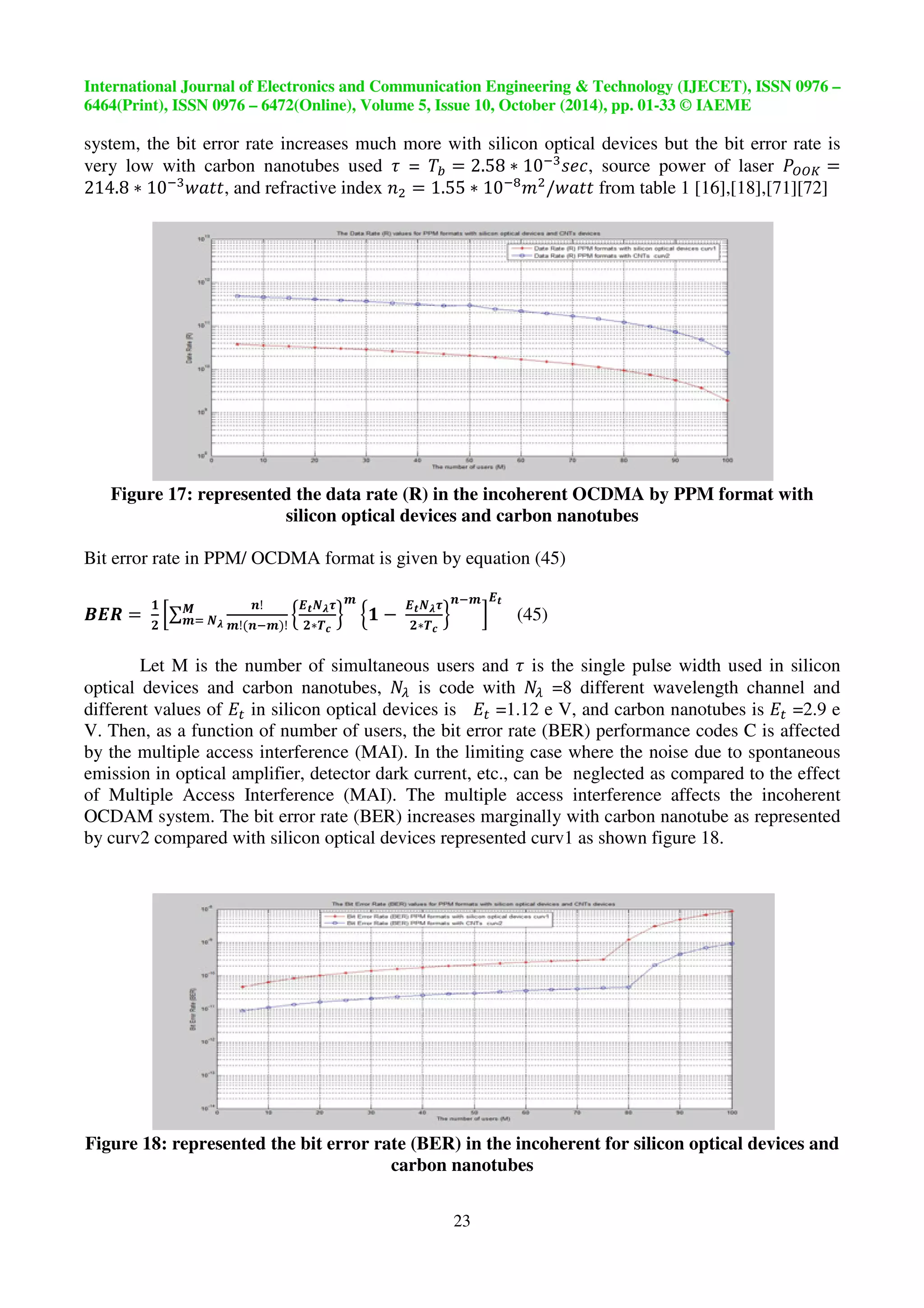
![International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering Technology (IJECET), ISSN 0976 –
6464(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6472(Online), Volume 5, Issue 10, October (2014), pp. 01-33 © IAEME
2
INTRODUCTION
Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs) were discovered by Sumio Iijima in NEC in Japan in the early 90s
[1].Carbon is the most important element of the periodic classification for human being. The six
electrons with two of them fill the first orbit as shown figure 1. The remaining four electrons fill the
second orbit as Diamond ( ) and Graphite ( ) as well as Sp hybrid orbital, responsible for
bonding structure of diamond, graphite, nanotubes, and fullerenes [3]. It has since become a
prominent material for an amazing breath of scientific and technological displines of ranging from
structural and material science to chemistry, biology, and electronics [2]. Carbon nanotubes are one
of most commonly mentioned building blocks of nanotechnology, with one hundred times the tensile
strength of steel, thermal conductivity better than all but the purest diamond and electrical
conductivity similar to copper but with the ability to carry much higher currents, they seem to be a
wonder material, thin cylinders of graphite. Graphite ( ) is made up layers of carbon atoms
arranged in a hexagonal lattice like chicken wire. Though the chicken wire structure itself is very
strong [4]. But let’s look at some of the different types of nanotubes and nanotube pretenders such as
One of major classification of carbon nanotubes is into Single – walled varieties (SWNTs), which
have a single cylindrical wall, and Multi-walled varieties (MWNTs), which have cylinders within
cylinders as shown in figure1 which illustrates all stages fabricated for carbon nanotubes (CNTs).
There are three parameters very important in carbon nanotubes (CNTs) as diameter, chirality angle,
and number of walls, and also has unique physical and chemical properties. There are two types for
fabrication first, chemical (chemical vapor deposition (CVD)) and second, other physical methods
(Arc discharge, Laser ablation).The graphite layer appears somewhat like a rolled up chicken wire
with a continuous unbroken hexagonal mesh and carbon molecules at the apexes of the hexagons [5].
They have two conduction bands and and two valence bands and, these are called Van
Hove Singularities observed in their electronic density of state (DOS) of these carbon nanotubes
(CNTs). The direct electronic band gap proportional to diameter for semiconducting carbon
nanotubes, while the direct band gap equal zero for metal carbon nanotubes so, they use in high
electrical current. It has typically have diameters range (1-2) nm for single walled nanotubes and (2-
25) nm for multi-walled nanotubes as well as the length of nanotubes may be (0.2 - 5) μm or some
centimeters, and the spacing distance between walls is 0.36nm. Here, a single wall nanotube is
prepared for optical proprieties applicable with optical system [6]. The potential applications of
carbon nanotubes have been attracting increasing attention from the photonics research community
[7]. It exhibits an exceptionally high third order optical nonlinearity and nonlinear saturable
absorption with ultrafast recovery time and broad bandwidth operation. Thus, carbon nanotubes are
becoming a key component towards the development of fiber lasers and nonlinear photonic
devices.They are making a more significant contribution towards the development of next generation
devises both from an academic and a commercial point of view. General rules have desired the
topology of the termination as a function of the Hamada indices (n, m). Carbon nanotubes can also
be opened ended, according to the integer n and m so, they may behave either semiconducting or
metallic.These calculations electronic structure for carbon nanotube shows about 1/3 of carbon
nanotube is metallic and 2/3 is semiconducting, depending on the nanotube diameter ( ) and chiral
angle (
). Another classification for carbon nanotubes depending on chiral vectors (](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opticalcodedivisionmultipleaccessusingcarbonnanotubessystem-141110054410-conversion-gate02/75/Optical-code-division-multiple-access-using-carbon-nanotubes-system-2-2048.jpg)

![International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering Technology (IJECET), ISSN 0976 –
6464(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6472(Online), Volume 5, Issue 10, October (2014), pp. 01-33 © IAEME
encode and decode the user’s data such that the optical channel can be shared, that is, we need to
develop the practical encoding and decoding techniques that can be exploited to generate and
recognize appropriate code sequences reliably [8]. Therefore, The OCDMA encoders and decoders
are the key components to implement OCDMA systems. In order to actualize the data
communications among multiple users based on OCDMA communication technology, one unique
codeword-waveform is assigned to each subscriber in an OCDMA network, which is chosen from
specific OCDMA address codes, and therefore, different users employ different address codeword-waveforms.
Figure 1: illustrates all stages fabricated for carbon nanotubes (CNTs) from carbon atoms,
graphite sheet, and rolled as form tube
Optical code division multiple access (OCDMA) technique is an attractive candidate for next
generation broadband access networks [9-10]. Basic architecture and working principle of an
OCDMA passive optical network (PON) network, in the OCDMA-PON network, the data are
encoded into pseudorandom optical code (OC) by the OCDMA encoder at the transmitter and
multiple users share the same transmission media by assigning different OCs to different users. At
the receiver, the OCDMA decoder recognizes the OCs by performing matched filtering, where the
auto-correlation for target OC produces high level output, while the cross-correlation for undesired
OC produces low level output. Finally, the original data can be recovered after electrical
thresholding. Due to the all optical processing for encoding/decoding, OCDMA has the unique
features of allowing fully asynchronous transmission with low latency access, soft capacity on
demand, protocol transparency, simplified network management as well as increased flexibility of
QoS control. In addition, since the data are encoded into pseudo-random OCs during transmission, it
also has the potential to enhance the confidentiality in the network [11- 15]. In an OCDMA network
using on-off keying pattern, the user’s data is transmitted by each information bit “1” which is
encoded into desired address codeword. However, the transmitter does not produce any optical
pulses when the information bit “0” is sent. In terms of the difference of signal modulation and
detection pattern, OCDMA encoders/decoders are roughly classified into coherent optical
encoders/decoders and incoherent optical encoders/decoders. The incoherent optical
encoders/decoders employ simple intensity-modulation/direct-detection technology and the coherent
optical en/decoders are based on the modulation and detection of optical signal phase. As global
network infrastructures expand to support various type of traffic, photonic networks are expected to
take an important role. The increasing demand for bandwidth forces network infrastructures to be
large capacity and reconfigurable [16]. The efficient utilization of bandwidth is a major design issues
for ultra-high speed photonic networks, also it increases data rate (R), and decreases bit error rate
(BER) so as to perform with improved signal to noise (SNR).The roots of OCDMA are found in
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opticalcodedivisionmultipleaccessusingcarbonnanotubessystem-141110054410-conversion-gate02/75/Optical-code-division-multiple-access-using-carbon-nanotubes-system-4-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering Technology (IJECET), ISSN 0976 –
6464(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6472(Online), Volume 5, Issue 10, October (2014), pp. 01-33 © IAEME
spread spectrum communication techniques. Spread spectrum was developed in the middle -1950s
mainly as a novel form of transmission overcoming the grid restrictions in radio bandwidth
allocations [17-21]. It is based on the idea of spreading the spectrum of the narrow band message
over a much wider frequency spectrum by means of digital codes [22-23].Within the category of
coherent systems, it is useful to further classify OCDMA systems based on the way in which phase
coding is applied to the optical signal field. Since optical phase can be manipulated in either the
frequency domain or the time domain, two types of coherent OCDMA systems are possible, as
Spectral Phase Coded Optical CDMA (SPC-OCDMA) and Temporal Phase Coded Optical CDMA
(TPC-OCDMA) [24-29]. Incoherent schemes use the simpler, more standard techniques of intensity
modulation with direct detection while
Figure 2: Schematic diagram of an OCDMA system
coherent schemes are based on the modulation and detection of optical phase The most common
approaches to incoherent OCDMA are based on spectral-amplitude coding, spatial coding, temporal
(time) spreading, and two-dimensional (2D) wavelength-hopping time-spreading (WHTS) [30-
37].The performance of any communication system is fundamentally limited by the available
bandwidth, the signal to noise ratio of received signal, and the codes used to relate the original
information to the transmitted signal. These limits inevitably lead to increased errors and
corresponding loss of information [16]. An OCDMA network is expected to be able to accommodate
many subscribers and simultaneous access users, and to have high date rate for each user and low bit
error rate [8]. However, since they are strongly associated with each other, optimized performance
analysis of network becomes an issue of multiple target function description, which is very complex.
Next generation of optical communication system may preferably incorporate carbon nanotubes
based devices so as to achieve much higher data rate up to Tb/s in comparison to present systems
using silicon optical devices giving data rate upto Gb/s. Besides, such systems with advanced energy
source power realize in much longer life Nevertheless, future requirements of ultrahigh speed
internet, video, multimedia, and advanced digital services, would suitably be met with incorporation
of carbon nanotubes based devices providing optimal performance. Two novel types of carbon
nanotubes (CNTs) based multiplexers. The new device is a solid – state transmission gate (t-gate)
multiplexer that uses carbon nanotube as channel in the Field Effect Transistor (FET) of both n- FET
and p- FET type. Because it has been shown that carbon nanotubes – based FET switches are reliable
and ultrafast responsivity using much less power than a silicon optical – based devices, and thus
support ultrahigh data rates to Tb/s for ultrahigh speed application networks. The new device will
consume less power than traditional t – gate multiplexer [38]. Nanotechnology is new field of
Research that cuts across many fields of electronics, chemistry, physics, and biology, that analyzes
and synthesize objects and structures in the nano-scale (
) such as nano particles, nanowires, and
carbon nanotubes (CNTs). Carbon nanotube is one of several cutting- edge emerging technologies
and very wide range of applications in many different streams of science and technology [39-46].
Here, we determine some of important parameter in this system as data rate (R) with Pulse Position
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opticalcodedivisionmultipleaccessusingcarbonnanotubessystem-141110054410-conversion-gate02/75/Optical-code-division-multiple-access-using-carbon-nanotubes-system-5-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering Technology (IJECET), ISSN 0976 –
6464(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6472(Online), Volume 5, Issue 10, October (2014), pp. 01-33 © IAEME
Modulation (PPM) formats, and bit error rate (BER) and also for On- OFF Keying (OOK) formats
on Incoherent OCDMA 2-D wavelength – hopping / time spread technique and coherent OCDMA
spectral phase encoding and temporal phase encoding for analysis and computing BER for silicon
optical devices and carbon nanotubes. Multiplexing technique is to increase the capacity of an optical
link beyond the limit available for serial transmission, a service provide can either install an
additional fiber or to use some form of multiplexing. Multiplexing allows multiple channels to be
transmitted simultaneously over a single optical fiber giving networkprovides access to the large
bandwidth capabilities of single fiber which can lead to increased throughput in the network without
laying additional fiber. Optical multiplexing can be achieved through multiplexing either in the time
domain, wavelength, or hybrid of both. Due to the large bandwidth (5GHz) and associated high bit
rates, the multiplexing process is beyond the capabilities of pure electronic methods and has to be
implemented optically as well. Code division multiple access (CDMA) is strong candidate for
creating effective multiple methods for the optical subscriber access network because of its
asynchronous access and code multiplexing [47].
ASSUMPTION SYSTEM AND SIMULATIONS
A single wall carbon nanotube (SWTN) can be described as a single layer of graphite crystal
that is rolled up into a seamless cylinder, one atom thick usually with a small number (perhaps 20 -
40) of atoms along the circumference and along length (micron) along the cylinder axis [49]. This
nanotube is specified by the chiral vector (](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opticalcodedivisionmultipleaccessusingcarbonnanotubessystem-141110054410-conversion-gate02/75/Optical-code-division-multiple-access-using-carbon-nanotubes-system-6-2048.jpg)

![(1)
Where n and m are two integers indices called Hamada integers, which often described by the
pair of indices (n, m) that denote the number of unit vectors n* and m* in the hexagonal
honeycomb lattice contained in this vector and where = = = *
=0.246nm,where = 0.142nm the c-c bond length and are graphite lattice vector ,which two
vectors real space vectors[2], [3],[48][49]. The chiral vector makes an angle (
) called the chiral
angle with the zigzag or direction.as figure 3. The vector connects two crystallographically
equivalent sites O and A on a two – dimensional (2D) graphene sheet where a carbon atom is located
at each vertex of the honeycomb structure [48]. The axis of the zigzag nanotube corresponds to
=
0, while the armchair nanotube axis corresponds to
= 30, and the chiral nanotube axis corresponds
to 0
30. The seamless cylinder joint of the nanotube is made by joining the line AB to the
parallel line OB in figure 3, in terms of the integer (n, m), the nanotube diameter ( ) is given by
equation (2).
5
!!
#
(2)
The nearest – neighbor C-C distance 1.421 or 0.142 in graphite,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opticalcodedivisionmultipleaccessusingcarbonnanotubessystem-141110054410-conversion-gate02/75/Optical-code-division-multiple-access-using-carbon-nanotubes-system-8-2048.jpg)


![. The vectors K and K are obtained from the
relation
;L MN 3 OLN, where PQRS are the lattice vectors in real and reciprocal space
respectively. Form KK can be written as
T
G
'18 2 8 2 +-*:T
G')2 1 * 2 + (11)
Where , and , are the reciprocal lattice vectors of a two – dimensional graphene sheet
given by equation (5). The N wave vectors UK'U /V/W 1
+ give rise to N discrete k vectors
in the circumferential direction. For each of U discrete values of the circumferences wave vectors a
one – dimensional electronic energy band appears, whereas each U gives rise to 6 branches in the
phonon dispersion relations [48]. A nanotube (n,m) is formed by rolling a graphite sheet along the
chiral vector](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opticalcodedivisionmultipleaccessusingcarbonnanotubessystem-141110054410-conversion-gate02/75/Optical-code-division-multiple-access-using-carbon-nanotubes-system-15-2048.jpg)

![International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering Technology (IJECET), ISSN 0976 –
6464(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6472(Online), Volume 5, Issue 10, October (2014), pp. 01-33 © IAEME
can be obtained: zigzag (n, 0), armchair (n, m), n= m, and chiral (n, m), where nm0, they are (17,
0), (15, 0), (12, 5), (16, 2), (10, 10), and (11, 11). The lattice constant and intertube spacing are
required to generate a SWNT bundle, and MWNT, the most experimental measurements and
theatrical calculations, agree that on average the C-C bond length and intertube ' HI+
[49]. Thus, equations (1) and (2) can be used to model various tube structures and interpret
experimental observation. They now consider the energetics or stability of nanotubes; strain energy
caused forming a SWNT from a graphite sheet is proportional to
+ ghi .T`-
0 fjdk 'T`-
+ (12)
8
XY
per tube or
XY
Z per atom [3].
Typical experimentally observed SWNT diameter is between (0.6 nm – 2.0 nm) while smaller
(0.4nm) or larger (3.0nm). In simplest model [3], the electronic properties of a nanotube derived
from the dispersion relation of a graphite sheet with the wave vectors (K[/ K), [3], [7].
]^T_/ T`a bcde f ghi'(T_-
Where lmis the nearest neighbor – hopping parameter and a lattice constant (ln = 2.5eV-
3.0eV) from different sources and a=0.246nm. When the graphite is rolled over to form a nanotube,
a periodic boundary condition is imposed along the tube circumference or the C directions. This
condition quantizes the two – dimensional wave vector k = (K[/ K) along this direction. The k
satisfies k.c=2op are allowed where q is an integer. This leads to the following condition at which
metallic conductance occurs as equation (13)
(n - m) = q metallic or (2n + m) = 3q (13)
Semiconducting
The top half of the energy curve corresponds to the conduction o energy band while the
bottom half corresponds to the valence o energy band. The conduction and valence band come into
contact at the six corners (high symmetry points k) in the Brillouin zone, implying that 2D graphite
is a zero – gap semiconductor, when s=0, the valence and conduction band become symmetric a ball
E=qrs this is given by equation (12) and lm = 2.9 eV. The positive sign is for the conduction band
and the negative one for the valence band. In contrast to Si, which is an indirect band gap
semiconductor and asymmetric band structures for electron and holes, grapheme has symmetric
conduction and valence bands. The energy valleys are located at the corners of the Brillouin zones,
which are usually referred as the Fermi points. The basis vectors in the reciprocal lattices,S. The
periodic boundary condition imposed along the circumference direction restricted the wave vectors
to
k.c = 2oq (14)
where k is an allowed wave vector and q is integer which is the quantum number [50] – [58]. The
conductance for SWNT, a SWNT rope, or MWNT given by equation (15)
t tu v .wZ](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opticalcodedivisionmultipleaccessusingcarbonnanotubessystem-141110054410-conversion-gate02/75/Optical-code-division-multiple-access-using-carbon-nanotubes-system-18-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering Technology (IJECET), ISSN 0976 –
6464(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6472(Online), Volume 5, Issue 10, October (2014), pp. 01-33 © IAEME
R= 6.5*
ohm [24]. The knowledge of this limit (which only depends on the communication
channel) allows evaluating the performance of the system, and finding the guidance to its
improvement. In particular, for a linear communication channel with additive noise, and a total
signal power constraint at the input, the fundamental limit to the information capacity is given by the
celebrated Shannon formula [16],[ 37].
9
|B@}~
€
] (16)
Where W is the channel bandwidth, ‚u is the average signal power, and ‚ƒ is the average
noise power. In comparison, the standard On- Off Keying (OOK) procedure where the information
in encoded via a “ train” of nonoverlapping pulses – with the presence of the pulse in a given time
corresponding to “1” and it’s absence to “0”, leads to the transmission bit rate (data bit rate R) of one
bit per time slot. To avoid the interference of pulses from the adjacent slots, the size of the time slot
is generally chosen to be no less than the pulse width („), leading to the transmission rate up to
…
bit/sec. Since the corresponding bandwidth is on order of
…
, OOK algorithm performance is by a
factor of †‡ˆ'‰Š‹+ less than the fundamental limit. However, the representation of the fundamental
limit to the information capacity in the standard form of equation (16) is unsuitable for applications
to fiber – optical systems, as it was obtained based on the assumption of linearity of the
communication channel, while modern fiber optics systems operate in a substantially nonlinear
regime to improve the performance. Since the optical transmission lines or devices must satisfy very
strict requirements for bit error rate (BER) (
E@
Œ+/ to use optical fiber for longest distance
and also use integrated circuit from silicon but when the using integrated circuit from silicon does
not support its work enough to transmission rate between these devices and optical fiber has largest
bandwidth to transport most information but it needs the optical devices to support that use here the
new device called carbon nanotubes (CNTs) preferably of the type Single Walled Carbon nanotubes
(SWNTs) to get better improved performance of the system such devices are called biological
device and can be used with human bodies that means it uses in small length maximum 1 centimeter
so they cannot be used like fiber or optical fiber cable but they can also be used in manufacturing
integrated optical circuits like encoder and decoder for optical signal, also mode locked lasers which
have highest efficiency for energy and transferring optical signal with optical code division multiple
access (OCDMA) to develop communication system from increasing data bit rate and to improve the
SNR in the system. For OOK modulation format, the slot length is equal to the length of a frame.
Assuming that both the chip time E {H
Ž?C and throughput are held fixed, the code
length is given by equation (17) [27] [37].
‘
@’““R
”m•Z–
–‘
@’‚‚v
D (17)
Where M indicates the number of possible slots within a PPM time frame and Pu
H
denotes the throughput in bits/chip time. At the receiving end, the data are restored by the
OOK/PPM chip – level optical receiver. Since the chip – level receiver are dependent on the number
of photons (optical energy) per chip in the received frame when it uses silicon optical devices the
optical source power is {Hxx
—99, whereas when it uses carbon nanotubes the optical source
power is J
IH
—99. That means when we use the carbon nanotubes devices the consumed
power is very low. Here, the time duration of time slot E˜ H
n sec or nanosecond in
silicon optical devices, but the time duration E˜ JH{
?C or femtosecond in carbon](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opticalcodedivisionmultipleaccessusingcarbonnanotubessystem-141110054410-conversion-gate02/75/Optical-code-division-multiple-access-using-carbon-nanotubes-system-21-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering Technology (IJECET), ISSN 0976 –
6464(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6472(Online), Volume 5, Issue 10, October (2014), pp. 01-33 © IAEME
11
] -j¡jcd
:8
¢H£¤¥
:8
(18)
where q• the energy band gap for semiconductor which has two conduction bands and two
valence bands as shown in figure 5 which illustrates how to work with two van hove singularities ,
with Fermi energy lm JHxCž. If (2n+m) = 3q ¦ , the carbon nanotubes would be 2/3
semiconductor from equation (13). The Kinetic energy (qœ) form the lowest subband is determine by
the minimum value given by equation (20)
Figure 5: illustrates two van hove singularities in semiconductor carbon nanotubes
MjH§
(:8
(19)
Where is the diameter of the carbon nanotube the energy output for CNTs are given by
equations (20)
]'M8+ b(-j¡jcd
eT8
'
¨ + (20)
(:8
And
]d b(-j¡jcd
(21)
Where qm is energy gap with normal temperature for graphite. Subsequently from equations
(20) and (21) we get equation (20) for ]d©8 , the output energy band gap.
]d©8 ]'T8+
]d
(22)
The output energy band gap for carbon nanotubes depends on doping the electron density of
states in during fabrication and expressed by equation (23).
ª']T+ £
(3-j¡jcd
]'T8+
e]'T8+'
]
¨ +
(23)
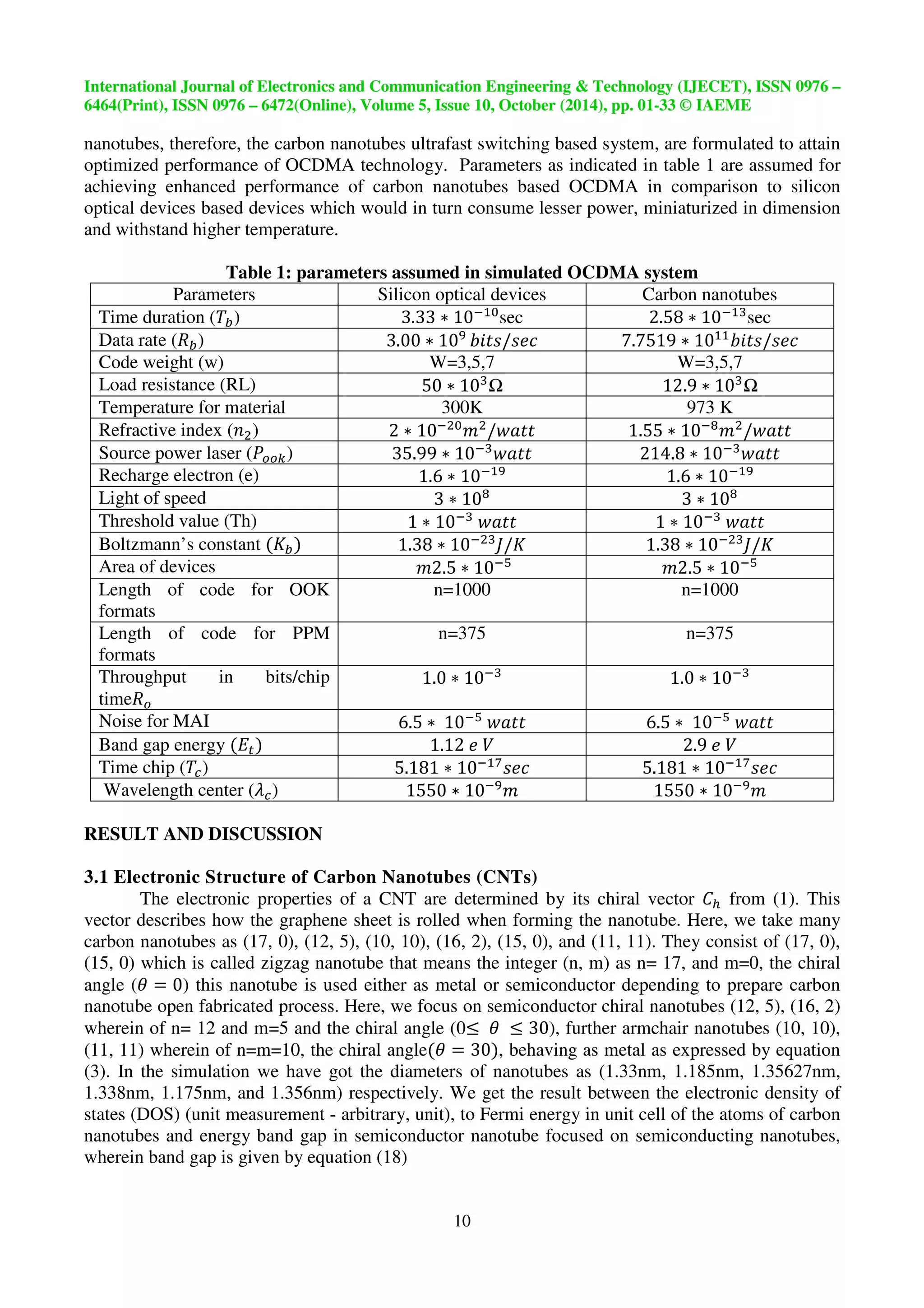
From the equations 20, 21, 22, 23 has got results as shown in figure 6 a and b has been
obtained which calculated is nanotubes the energy band gap has positive as well as negative values,
that is the carbon nanotubes show very high symmetry in (a) and (b) of figure 6 which illustrate (17,
0), (12, 5), (15, 0), and (16, 2) for energy gap has two van hove two conduction bands (/ )
and two valence bands () symmetries in both side positive and negative in energy gap](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opticalcodedivisionmultipleaccessusingcarbonnanotubessystem-141110054410-conversion-gate02/75/Optical-code-division-multiple-access-using-carbon-nanotubes-system-24-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering Technology (IJECET), ISSN 0976 –
6464(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6472(Online), Volume 5, Issue 10, October (2014), pp. 01-33 © IAEME
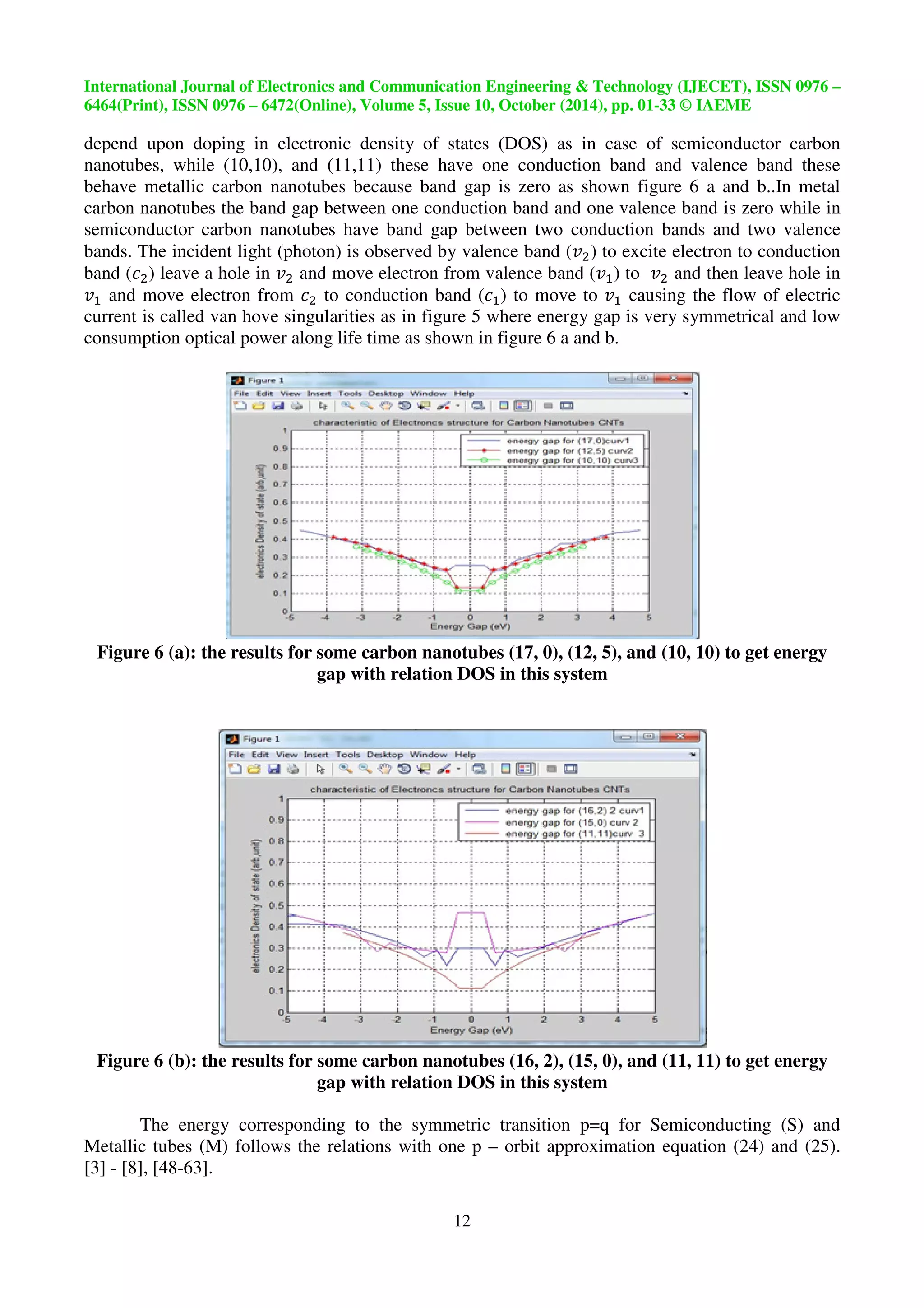
depend upon doping in electronic density of states (DOS) as in case of semiconductor carbon
nanotubes, while (10,10), and (11,11) these have one conduction band and valence band these
behave metallic carbon nanotubes because band gap is zero as shown figure 6 a and b..In metal
carbon nanotubes the band gap between one conduction band and one valence band is zero while in
semiconductor carbon nanotubes have band gap between two conduction bands and two valence
bands. The incident light (photon) is observed by valence band () to excite electron to conduction
band () leave a hole in and move electron from valence band () to and then leave hole in
and move electron from to conduction band () to move to causing the flow of electric
current is called van hove singularities as in figure 5 where energy gap is very symmetrical and low
consumption optical power along life time as shown in figure 6 a and b.
Figure 6 (a): the results for some carbon nanotubes (17, 0), (12, 5), and (10, 10) to get energy
gap with relation DOS in this system
Figure 6 (b): the results for some carbon nanotubes (16, 2), (15, 0), and (11, 11) to get energy
gap with relation DOS in this system
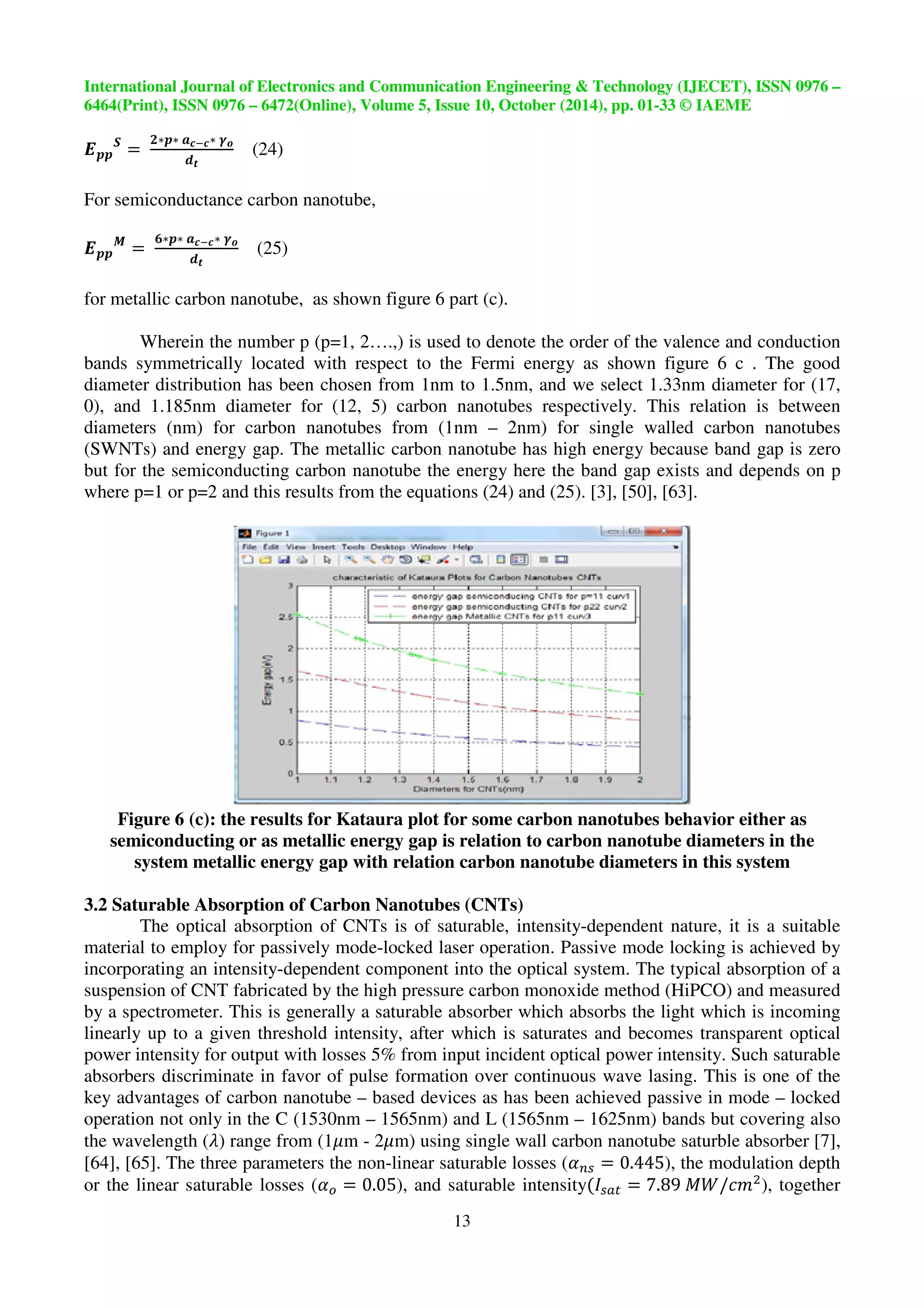
The energy corresponding to the symmetric transition p=q for Semiconducting (S) and
Metallic tubes (M) follows the relations with one p – orbit approximation equation (24) and (25).
[3] - [8], [48-63].
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opticalcodedivisionmultipleaccessusingcarbonnanotubessystem-141110054410-conversion-gate02/75/Optical-code-division-multiple-access-using-carbon-nanotubes-system-25-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering Technology (IJECET), ISSN 0976 –
6464(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6472(Online), Volume 5, Issue 10, October (2014), pp. 01-33 © IAEME
13
]««
¬ «-j¡jcd
:8
(24)
For semiconductance carbon nanotube,
]««
®«-j¡jcd
:8
(25)
for metallic carbon nanotube, as shown figure 6 part (c).
Wherein the number p (p=1, 2….,) is used to denote the order of the valence and conduction
bands symmetrically located with respect to the Fermi energy as shown figure 6 c . The good
diameter distribution has been chosen from 1nm to 1.5nm, and we select 1.33nm diameter for (17,
0), and 1.185nm diameter for (12, 5) carbon nanotubes respectively. This relation is between
diameters (nm) for carbon nanotubes from (1nm – 2nm) for single walled carbon nanotubes
(SWNTs) and energy gap. The metallic carbon nanotube has high energy because band gap is zero
but for the semiconducting carbon nanotube the energy here the band gap exists and depends on p
where p=1 or p=2 and this results from the equations (24) and (25). [3], [50], [63].
Figure 6 (c): the results for Kataura plot for some carbon nanotubes behavior either as
semiconducting or as metallic energy gap is relation to carbon nanotube diameters in the
system metallic energy gap with relation carbon nanotube diameters in this system
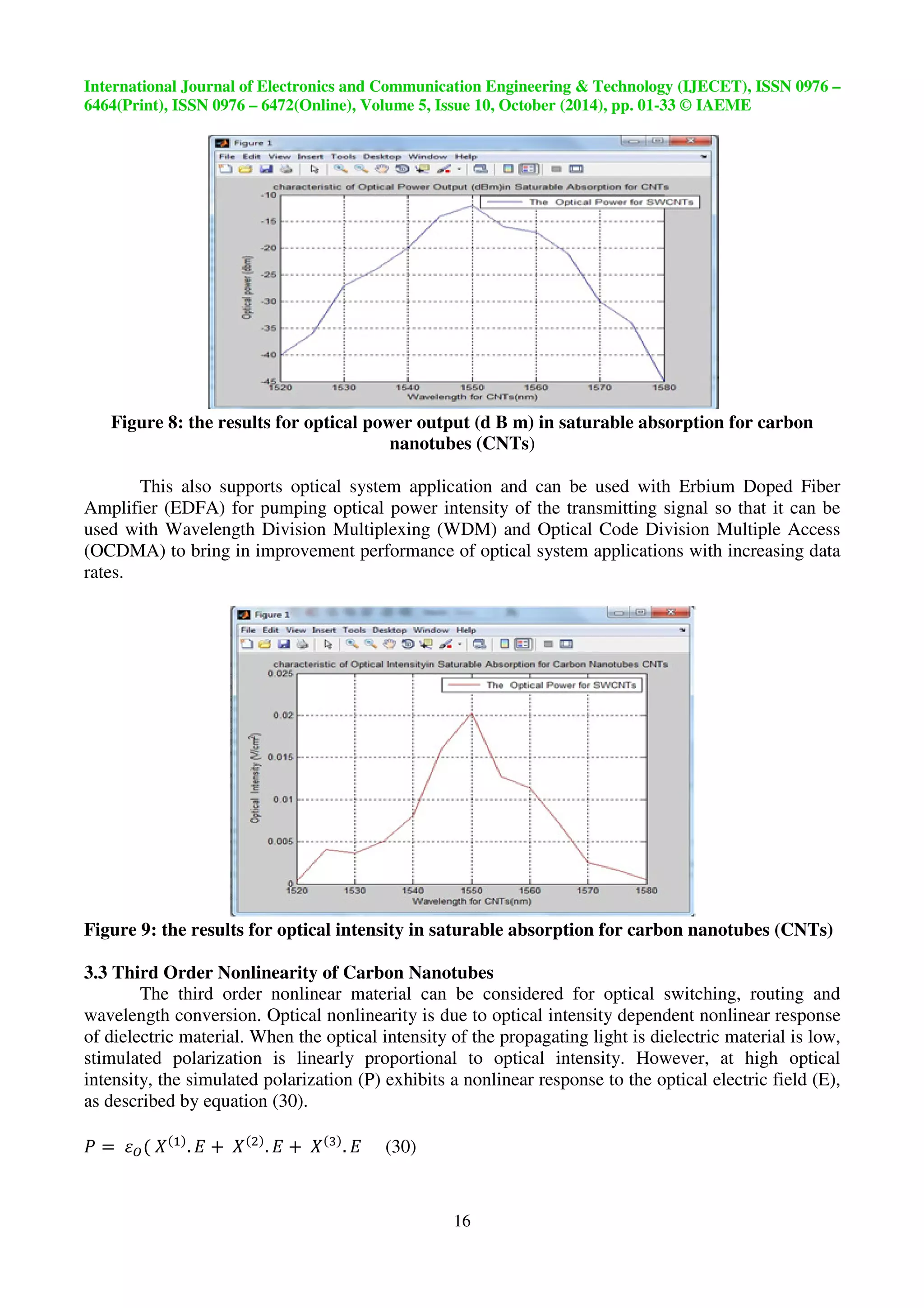
3.2 Saturable Absorption of Carbon Nanotubes (CNTs)
The optical absorption of CNTs is of saturable, intensity-dependent nature, it is a suitable
material to employ for passively mode-locked laser operation. Passive mode locking is achieved by
incorporating an intensity-dependent component into the optical system. The typical absorption of a
suspension of CNT fabricated by the high pressure carbon monoxide method (HiPCO) and measured
by a spectrometer. This is generally a saturable absorber which absorbs the light which is incoming
linearly up to a given threshold intensity, after which is saturates and becomes transparent optical
power intensity for output with losses 5% from input incident optical power intensity. Such saturable
absorbers discriminate in favor of pulse formation over continuous wave lasing. This is one of the
key advantages of carbon nanotube – based devices as has been achieved passive in mode – locked
operation not only in the C (1530nm – 1565nm) and L (1565nm – 1625nm) bands but covering also
the wavelength (Ÿ) range from (1Um - 2Um) using single wall carbon nanotube saturble absorber [7],
[64], [65]. The three parameters the non-linear saturable losses (¯°r HII{), the modulation depth
or the linear saturable losses (¯m H{), and saturable intensity'±r6 šHxv|™), together](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opticalcodedivisionmultipleaccessusingcarbonnanotubessystem-141110054410-conversion-gate02/75/Optical-code-division-multiple-access-using-carbon-nanotubes-system-26-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering Technology (IJECET), ISSN 0976 –
6464(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6472(Online), Volume 5, Issue 10, October (2014), pp. 01-33 © IAEME
response time (²= 1.85 ps) give us the location of the applicability of carbon nanotubes for passive
mode locking applications.
¯'±+ ³€
14
´! µ
µ¶·Y
¯°r (26)
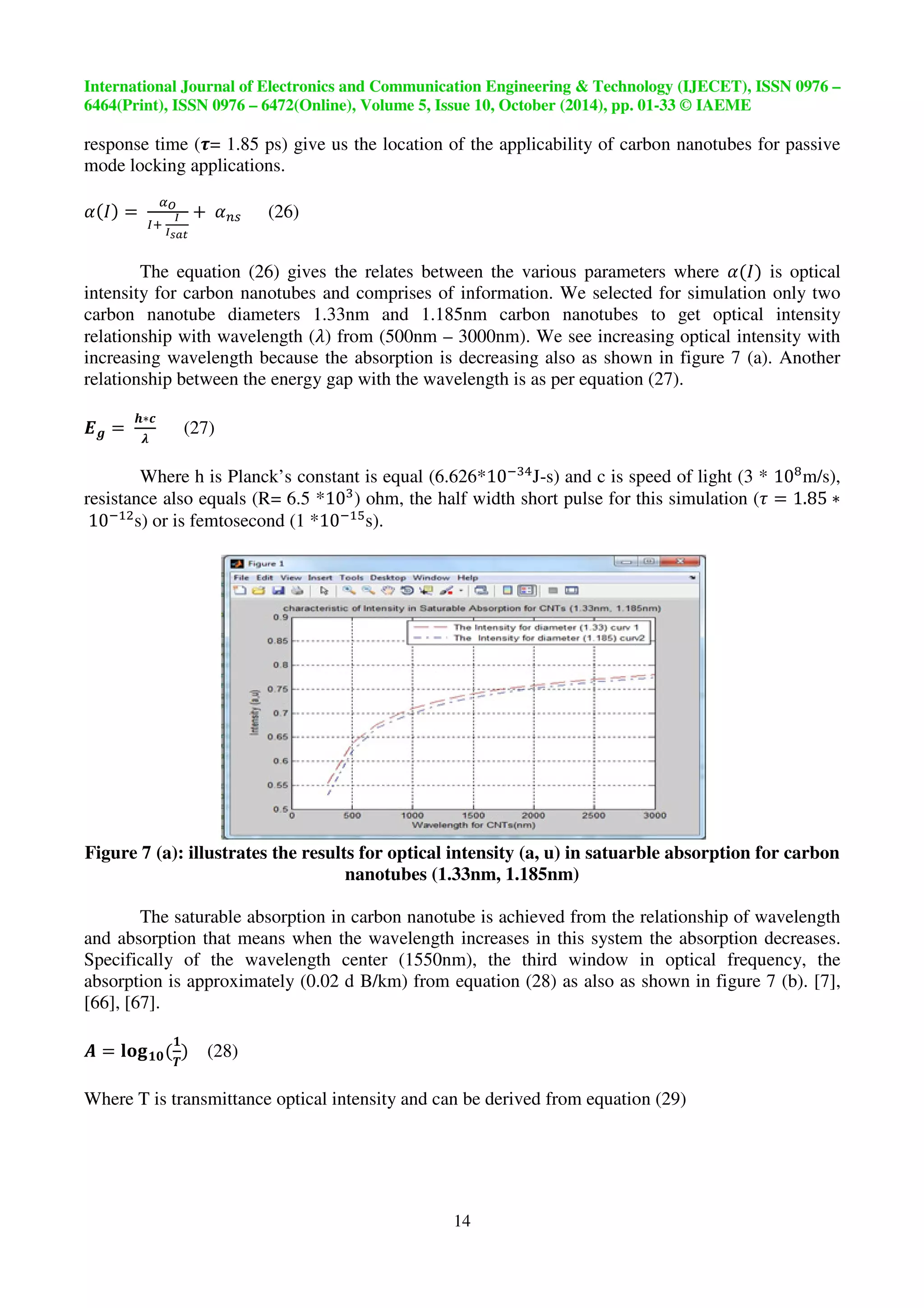
The equation (26) gives the relates between the various parameters where ¯'±+ is optical
intensity for carbon nanotubes and comprises of information. We selected for simulation only two
carbon nanotube diameters 1.33nm and 1.185nm carbon nanotubes to get optical intensity
relationship with wavelength (Ÿ) from (500nm – 3000nm). We see increasing optical intensity with
increasing wavelength because the absorption is decreasing also as shown in figure 7 (a). Another
relationship between the energy gap with the wavelength is as per equation (27).
] ¸j
¹
(27)
Where h is Planck’s constant is equal (6.626*
4J-s) and c is speed of light (3 *
›m/s),
resistance also equals (R= 6.5 *
) ohm, the half width short pulse for this simulation („
H{
s) or is femtosecond (1 *
Œs).
Figure 7 (a): illustrates the results for optical intensity (a, u) in satuarble absorption for carbon
nanotubes (1.33nm, 1.185nm)
The saturable absorption in carbon nanotube is achieved from the relationship of wavelength
and absorption that means when the wavelength increases in this system the absorption decreases.
Specifically of the wavelength center (1550nm), the third window in optical frequency, the
absorption is approximately (0.02 d B/km) from equation (28) as also as shown in figure 7 (b). [7],
[66], [67].
º »h¼¢'
7+ (28)
Where T is transmittance optical intensity and can be derived from equation (29)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opticalcodedivisionmultipleaccessusingcarbonnanotubessystem-141110054410-conversion-gate02/75/Optical-code-division-multiple-access-using-carbon-nanotubes-system-27-2048.jpg)


![International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering Technology (IJECET), ISSN 0976 –
6464(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6472(Online), Volume 5, Issue 10, October (2014), pp. 01-33 © IAEME
Where Á'+/ Á'+/ Á'+ correspond to the linear, the second order nonlinear, and third
order nonlinearity susceptibility respectively. It has been reported that some types of carbon
nanotubes present a highÁ'+, however, there is not much active research on exploiting this property.
On the other hand, the high values of Á'+ calculated theatrically and experimentally are of great
interest. There refractive index in carbon nanotubes can be described by equation (31). [49] - [66].
17
* (
£* ;¤Â___
'(+
(31)
Where Re stands for the real part the optical field is assumed to polarized so that only is components
Á[[[
'+
, (n=m
) is refractive index in free space (air). We have another equation to get
refractive index to get from simple equation (32)
* j
Ã
(32)
Where v is the optical frequency if we take wavelength (1550 nm) that means'
H{
›
| ¨ ) is high. The third order susceptibility of carbon single walled nanotube from Z-Scan
spectroscopy was estimated for the same. Á[[[
'+
can be expressed by equation (33)
Â___
'(+ ';¤Â(+ '¿)Â(+ (33)
Where ;¤Â( f
(3 *d j Äd ½*k is real part of Á'+ ; (Åm H{
+, and ¿)Â'(+
(3 *d j Äd ½*k ¹is the imaginary part ofÁ'+. The values of real and imaginary part of Á'+
are being of the carbon single wall nanotubes, the vacuum permittivity (Åm). The nonlinear
relationship between the average electrical fields inside materials (D) and the incoming optical (E)
field, nonlinear effects is defined the tensor of optical susceptibility x, which is the transformation
matrix of the incoming E vector to get the result polarization (P) vector inside materials given by
equation (34)
Æ Ä¾~Â'+ ] ghi'Dz+ Â' + ] jdk 'Dz+ Â'(+ ]( jdk('Dz+È (34)
We get another expression given by equation (35).
Æ ~
ľ Â' + ] .ľ Â'+ ] (
f ľ Â'(+ ](0 jdkDz
Äd ] jdkDz
Äd Â( ]( jdkÇ²È (35)
According equation (34) and (35) we can get new equation (36)
Æ_ ½ ] ½*k ] + * ]( (36)
We can get results for optical polarization intensity in third order nonlinearity for carbon
nanotubes the maximum optical intensity between wavelengths (1540nm – 1550nm) for single wall
nanotube by equation (36) as shown in figure 10 (a).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opticalcodedivisionmultipleaccessusingcarbonnanotubessystem-141110054410-conversion-gate02/75/Optical-code-division-multiple-access-using-carbon-nanotubes-system-30-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering Technology (IJECET), ISSN 0976 –
6464(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6472(Online), Volume 5, Issue 10, October (2014), pp. 01-33 © IAEME
Figure 10 (a): explains optical polarization intensity in third order nonlinearity for carbon
nanotubes (CNTs) also single wall nanotubes (SWNTs)
The optical intensity in third order nonlinearity we get maximum in wavelength center at
(1550 nm), the third window in optical systems and covers large bandwidth to support optical
integrated electronic circuit to work in optical frequencies to improve performance for optical system
application as shown figure 10 part (b). The relationship between the potential V (E) and the
electrical field (E) will be symmetrical given by equation (37)
18
¥']+ 1~.
0 ½ ] .
(0 * ]( .
f0 * ]fÈ (37)
The symmetrical potential of the material under the influence of an incoming signal optical E
field implies that the material is contrast electrical that electron polarization in positive and negative
direction as shown figure 10 part (c). The optical potential in third order nonlinearity the ultrafast
optical switches to get approximately (1.85 ps) or few femtosecond (ˇˇ 10
15), fast relaxation
process in the order of 100s of femtoseconds combined with an extremely high nonlinear coefficient
can be observed in real carbon nanotubes devices in fabricated optical integrated circuit in ultra large
scale integrated circuits (ULSI). It is also very high third nonlinear and ultrafast respond times [7],
[68], [69].
Figure 10 (b): explains optical power intensity in third order nonlinearity for carbon
nanotubes (CNTs) also single wall nanotubes (SWNTs)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opticalcodedivisionmultipleaccessusingcarbonnanotubessystem-141110054410-conversion-gate02/75/Optical-code-division-multiple-access-using-carbon-nanotubes-system-31-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering Technology (IJECET), ISSN 0976 –
6464(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6472(Online), Volume 5, Issue 10, October (2014), pp. 01-33 © IAEME
Figure 10 (c): explains optical potential in third order nonlinearity for carbon nanotubes
(CNTs) also single wall nanotubes (SWNTs).
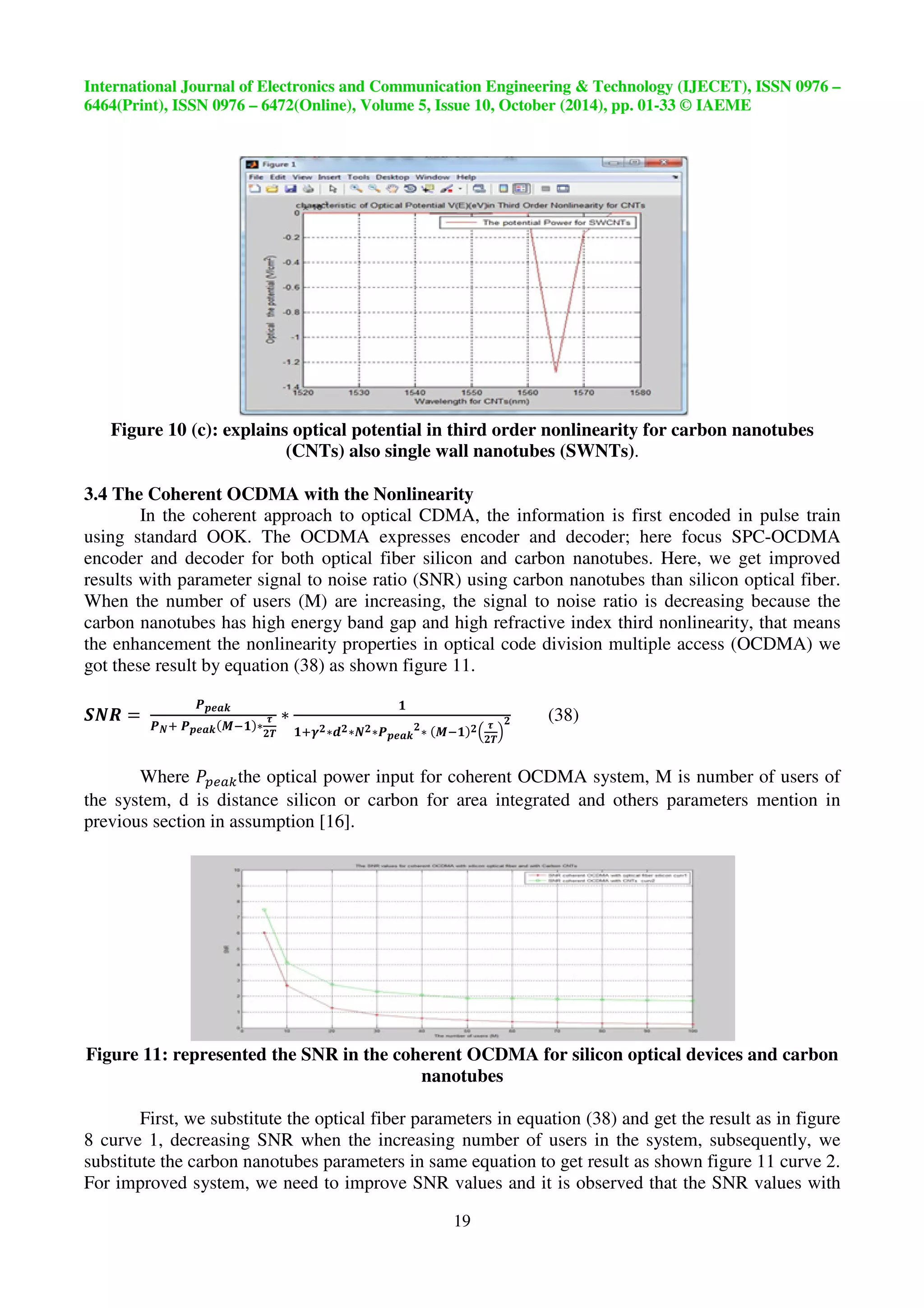
3.4 The Coherent OCDMA with the Nonlinearity
In the coherent approach to optical CDMA, the information is first encoded in pulse train
using standard OOK. The OCDMA expresses encoder and decoder; here focus SPC-OCDMA
encoder and decoder for both optical fiber silicon and carbon nanotubes. Here, we get improved
results with parameter signal to noise ratio (SNR) using carbon nanotubes than silicon optical fiber.
When the number of users (M) are increasing, the signal to noise ratio is decreasing because the
carbon nanotubes has high energy band gap and high refractive index third nonlinearity, that means
the enhancement the nonlinearity properties in optical code division multiple access (OCDMA) we
got these result by equation (38) as shown figure 11.
19
¬G; Æ«¤-T
ÆG!Æ«¤-T'+ ²
7
!c : G Æ«¤-T
'+ . ²
70
(38)
Where ‚sw6œthe optical power input for coherent OCDMA system, M is number of users of
the system, d is distance silicon or carbon for area integrated and others parameters mention in
previous section in assumption [16].
Figure 11: represented the SNR in the coherent OCDMA for silicon optical devices and carbon
nanotubes
First, we substitute the optical fiber parameters in equation (38) and get the result as in figure
8 curve 1, decreasing SNR when the increasing number of users in the system, subsequently, we
substitute the carbon nanotubes parameters in same equation to get result as shown figure 11 curve 2.
For improved system, we need to improve SNR values and it is observed that the SNR values with](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opticalcodedivisionmultipleaccessusingcarbonnanotubessystem-141110054410-conversion-gate02/75/Optical-code-division-multiple-access-using-carbon-nanotubes-system-32-2048.jpg)
![International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering Technology (IJECET), ISSN 0976 –
6464(Print), ISSN 0976 – 6472(Online), Volume 5, Issue 10, October (2014), pp. 01-33 © IAEME
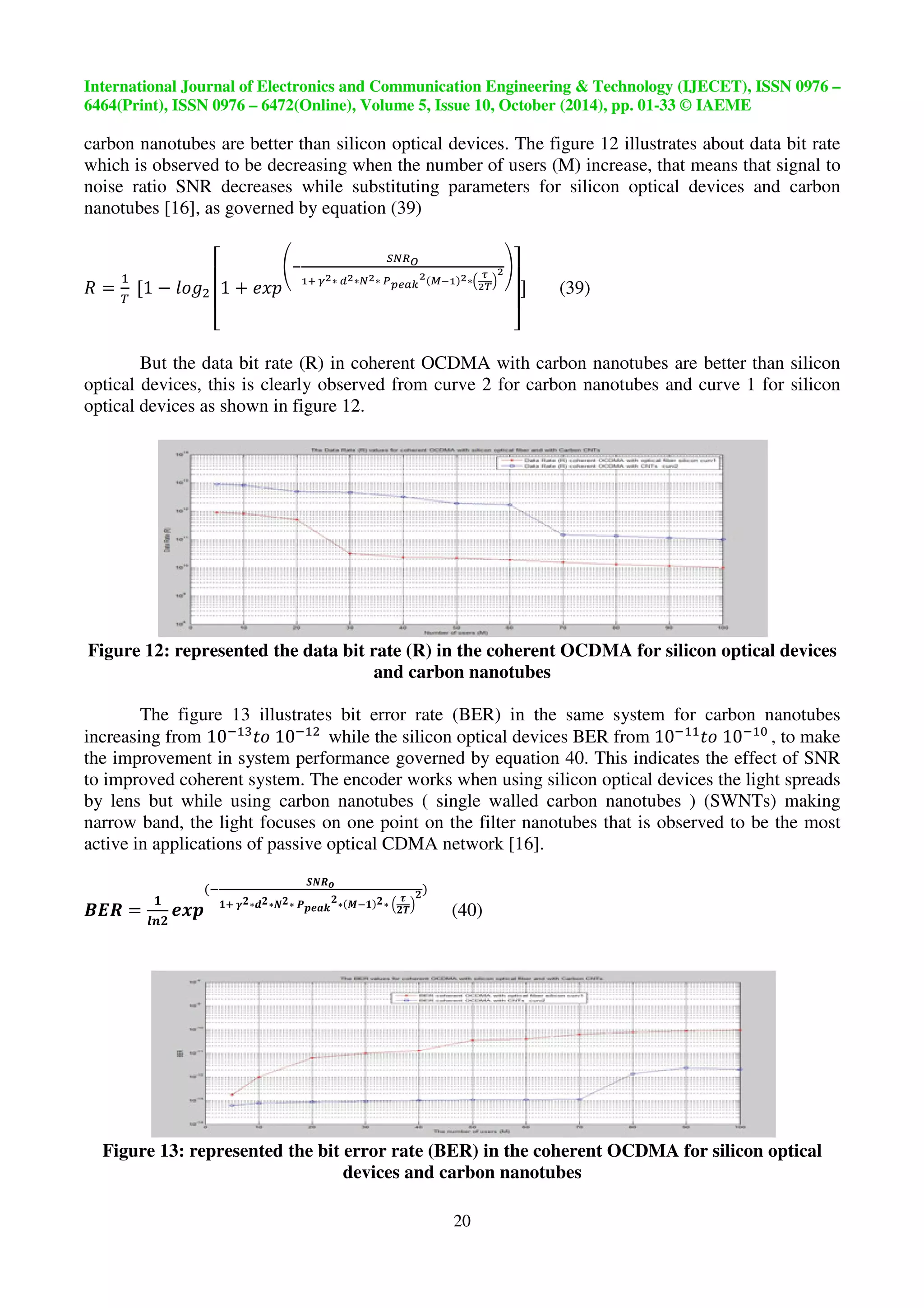
carbon nanotubes are better than silicon optical devices. The figure 12 illustrates about data bit rate
which is observed to be decreasing when the number of users (M) increase, that means that signal to
noise ratio SNR decreases while substituting parameters for silicon optical devices and carbon
nanotubes [16], as governed by equation (39)
20
P
É~
1 B@}
Ê Ë Ë Ì
CÍ
Î ÏЀ
ÑÒÓZÔZZÕÖ×·Ø
Z'Ù¡Ñ+Z. Ú
ZÜ
ZÛ0
Ý Þ Þ ß
È (39)
But the data bit rate (R) in coherent OCDMA with carbon nanotubes are better than silicon
optical devices, this is clearly observed from curve 2 for carbon nanotubes and curve 1 for silicon
optical devices as shown in figure 12.
Figure 12: represented the data bit rate (R) in the coherent OCDMA for silicon optical devices
and carbon nanotubes
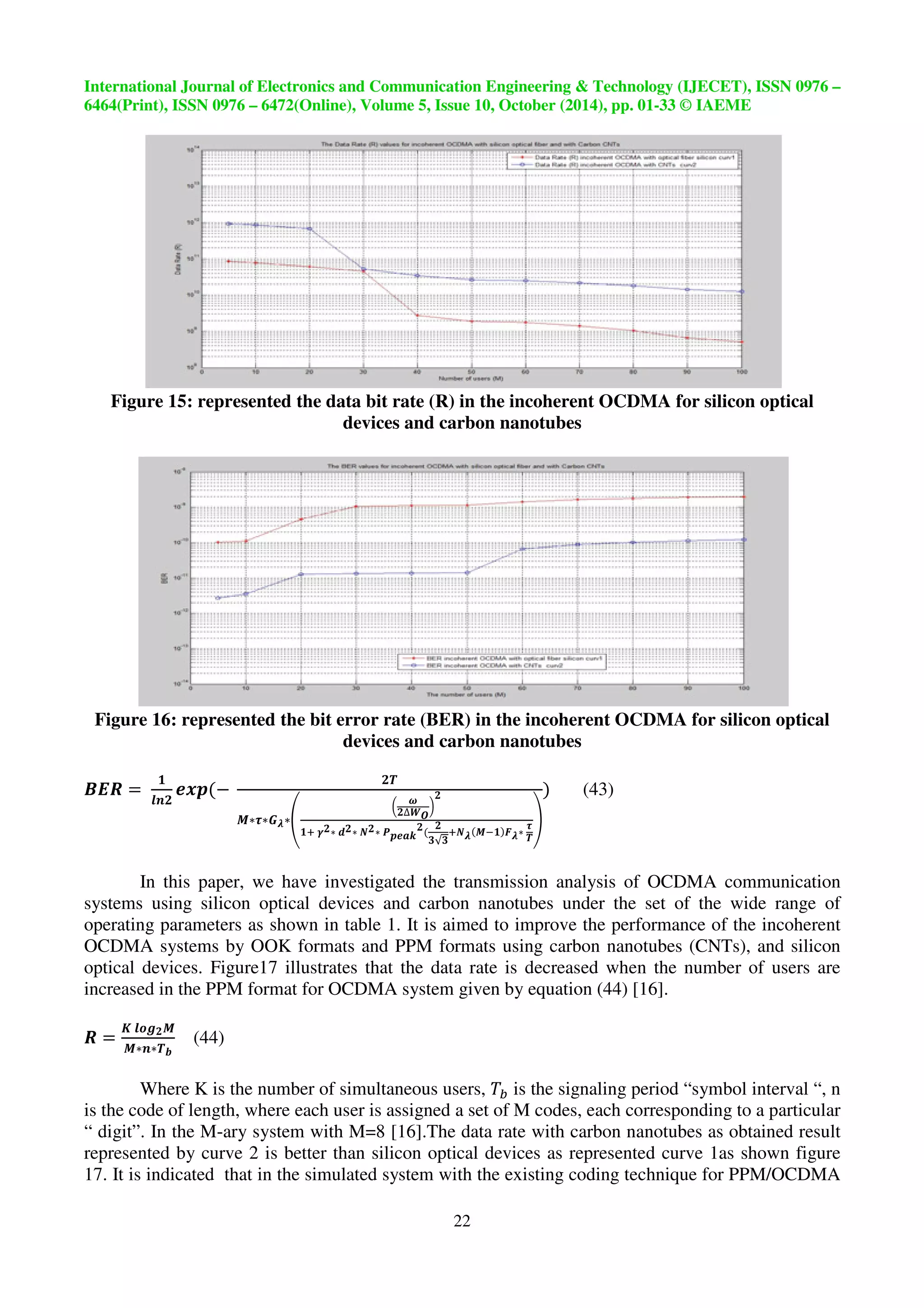
The figure 13 illustrates bit error rate (BER) in the same system for carbon nanotubes
increasing from
9@
while the silicon optical devices BER from
9@
n, to make
the improvement in system performance governed by equation 40. This indicates the effect of SNR
to improved coherent system. The encoder works when using silicon optical devices the light spreads
by lens but while using carbon nanotubes ( single walled carbon nanotubes ) (SWNTs) making
narrow band, the light focuses on one point on the filter nanotubes that is observed to be the most
active in applications of passive optical CDMA network [16].
à];
' ¬G;d
Òc : G Æ«¤-T
á* ¤_«
'¡+ . ²
+
70
(40)
Figure 13: represented the bit error rate (BER) in the coherent OCDMA for silicon optical
devices and carbon nanotubes](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/opticalcodedivisionmultipleaccessusingcarbonnanotubessystem-141110054410-conversion-gate02/75/Optical-code-division-multiple-access-using-carbon-nanotubes-system-33-2048.jpg)