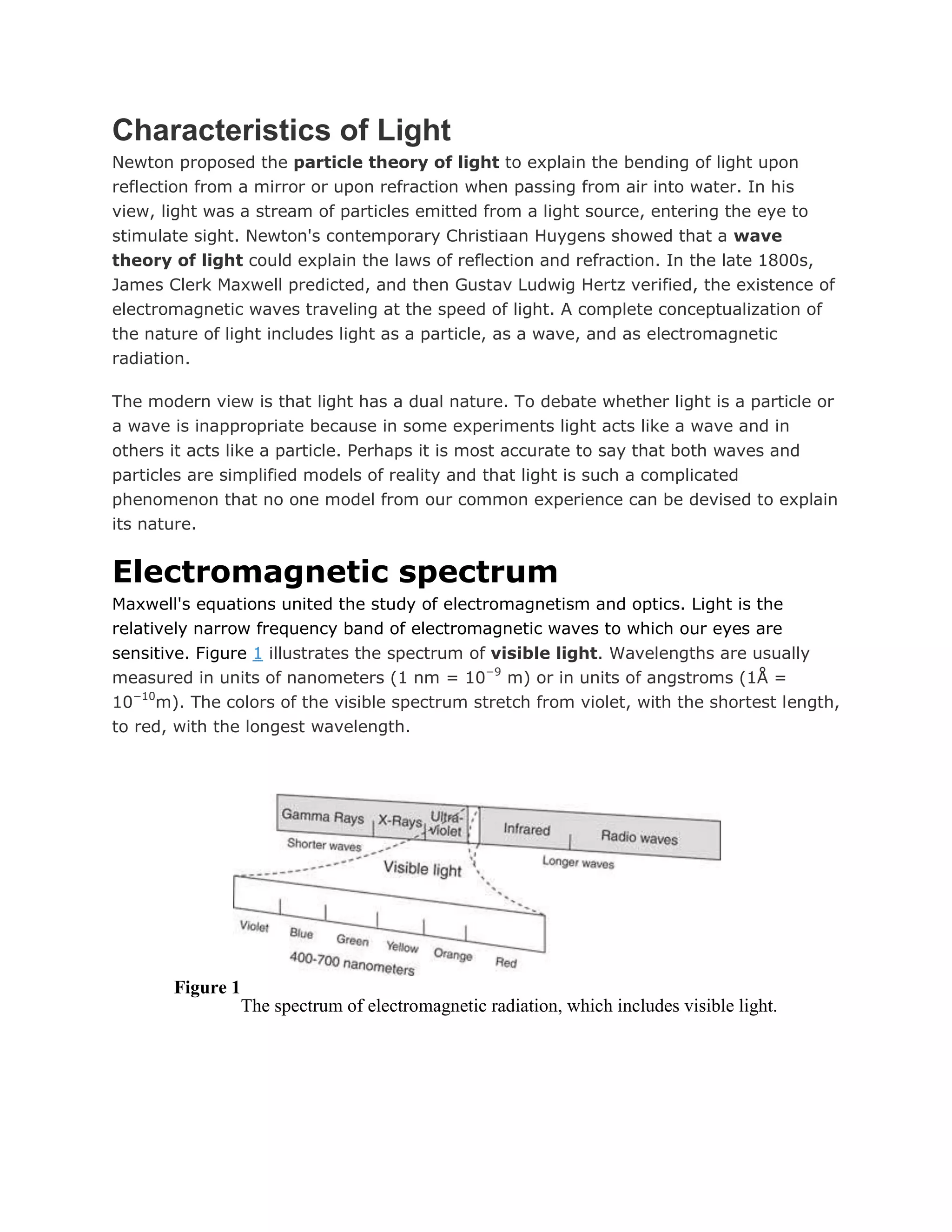
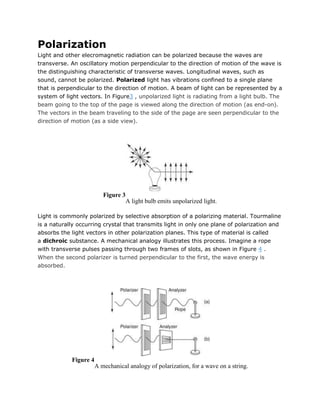
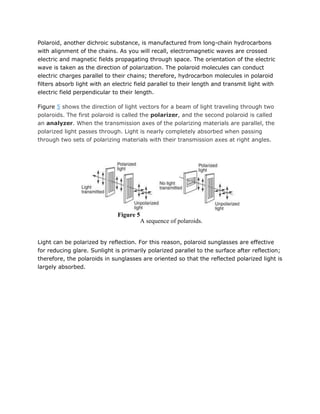
Light is electromagnetic radiation that exhibits properties of both waves and particles. It travels as transverse electromagnetic waves at a speed of approximately 300,000 km/s in a vacuum. When light interacts with matter, it can be reflected, refracted, dispersed, absorbed, or cause materials to become polarized. Key phenomena include reflection at interfaces, refraction due to changes in refractive index, dispersion causing separation of wavelengths, selective absorption of different colors, and polarization of light through restricting vibrations to one plane.