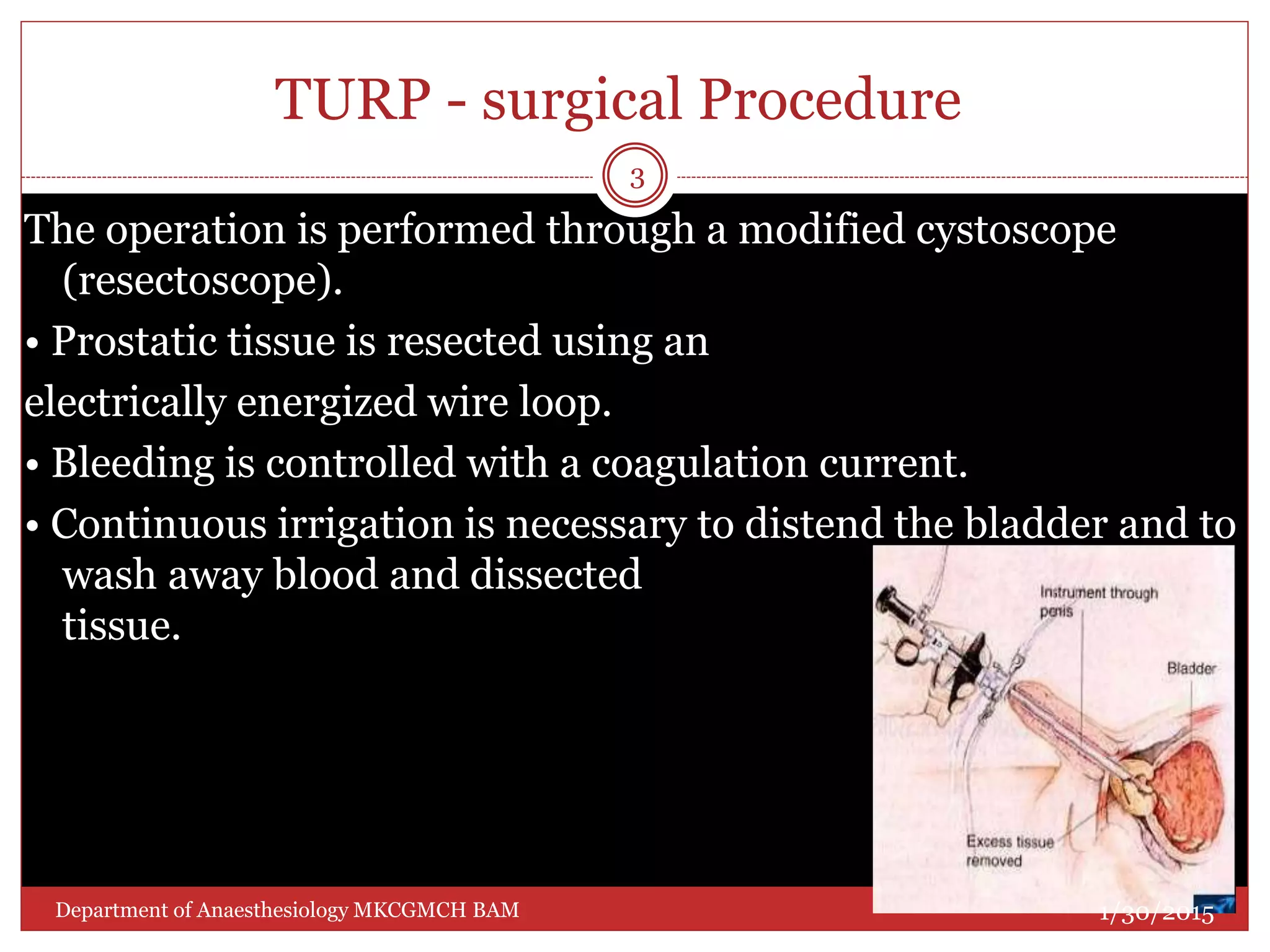
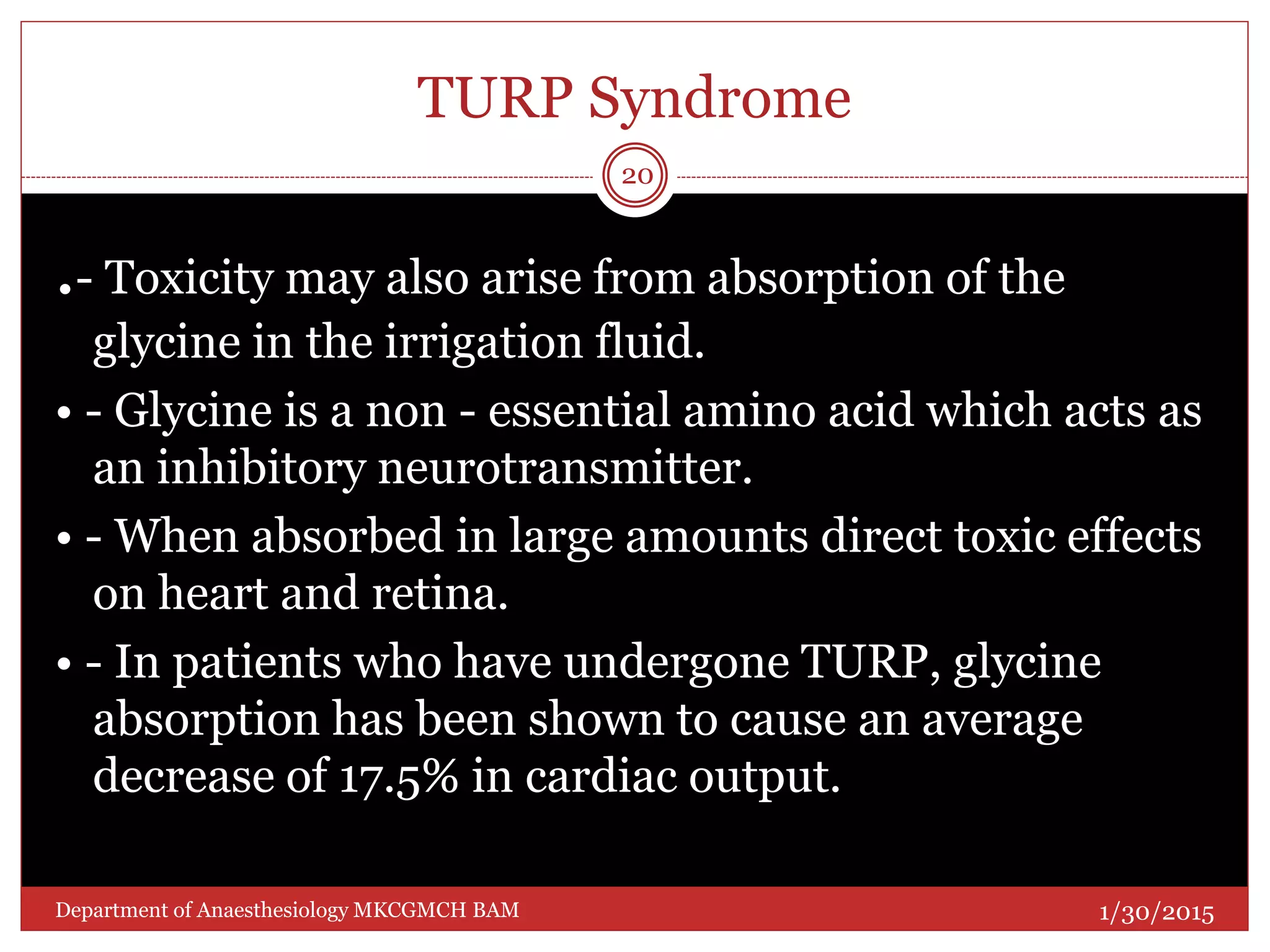
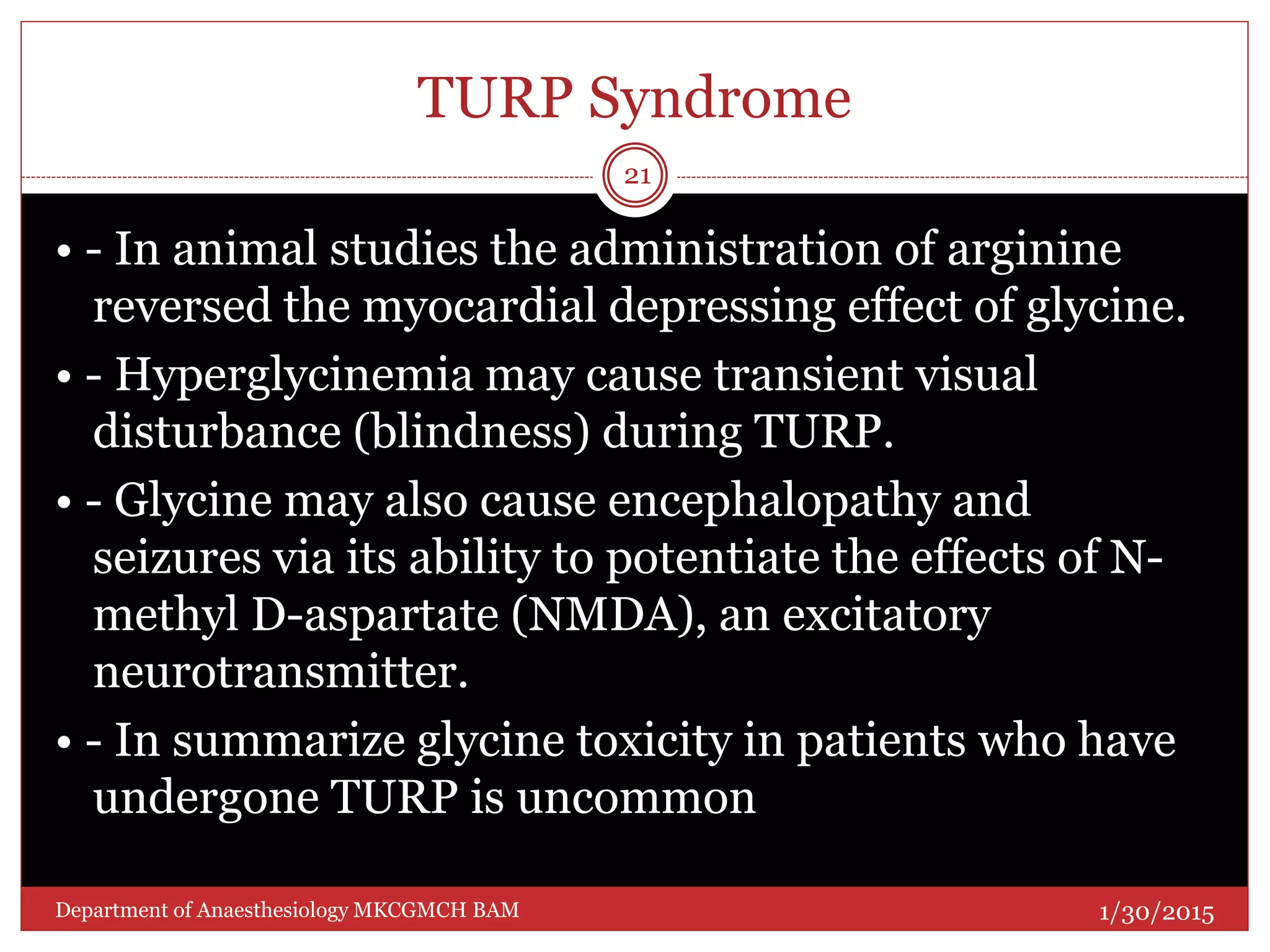
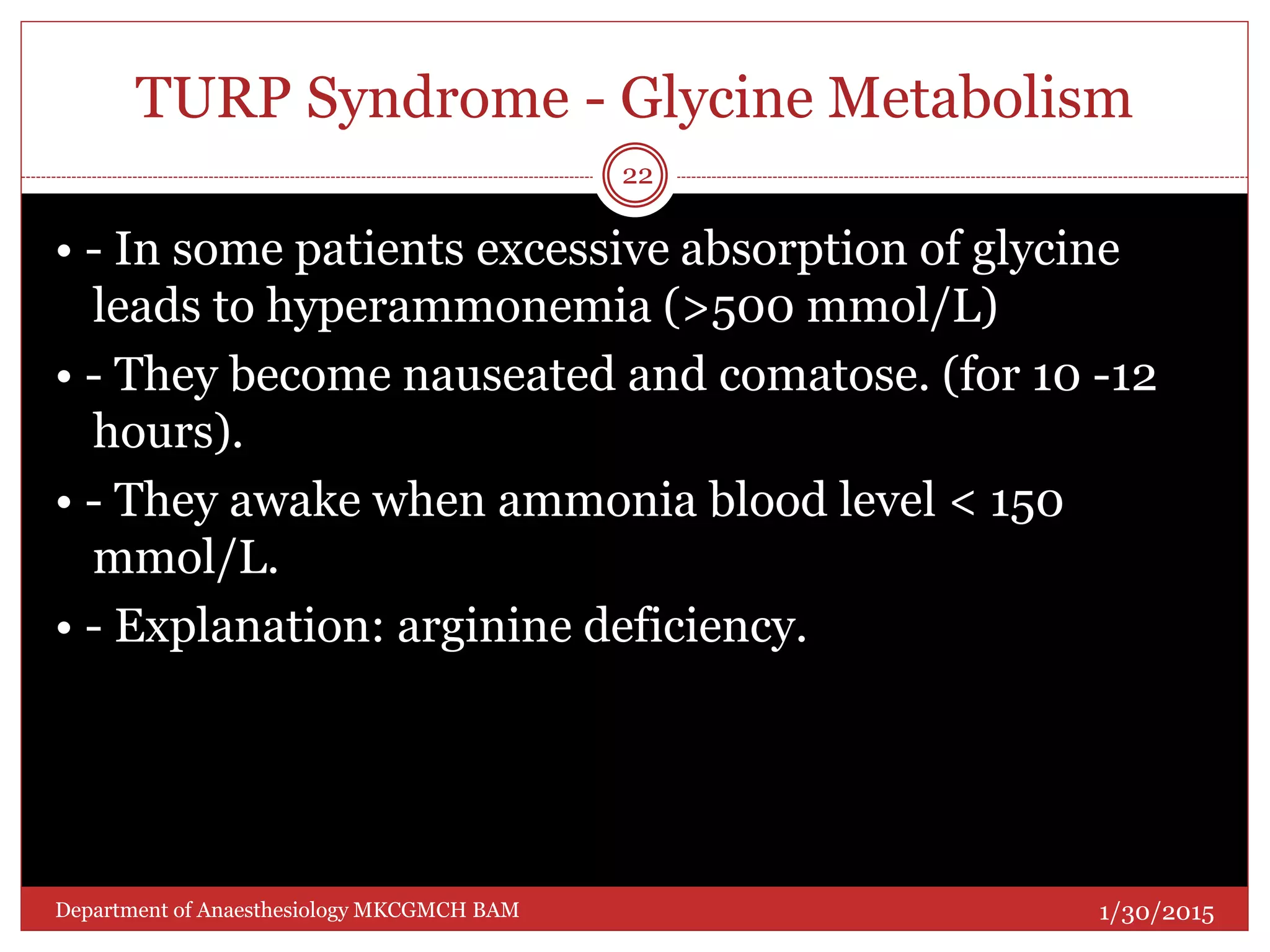
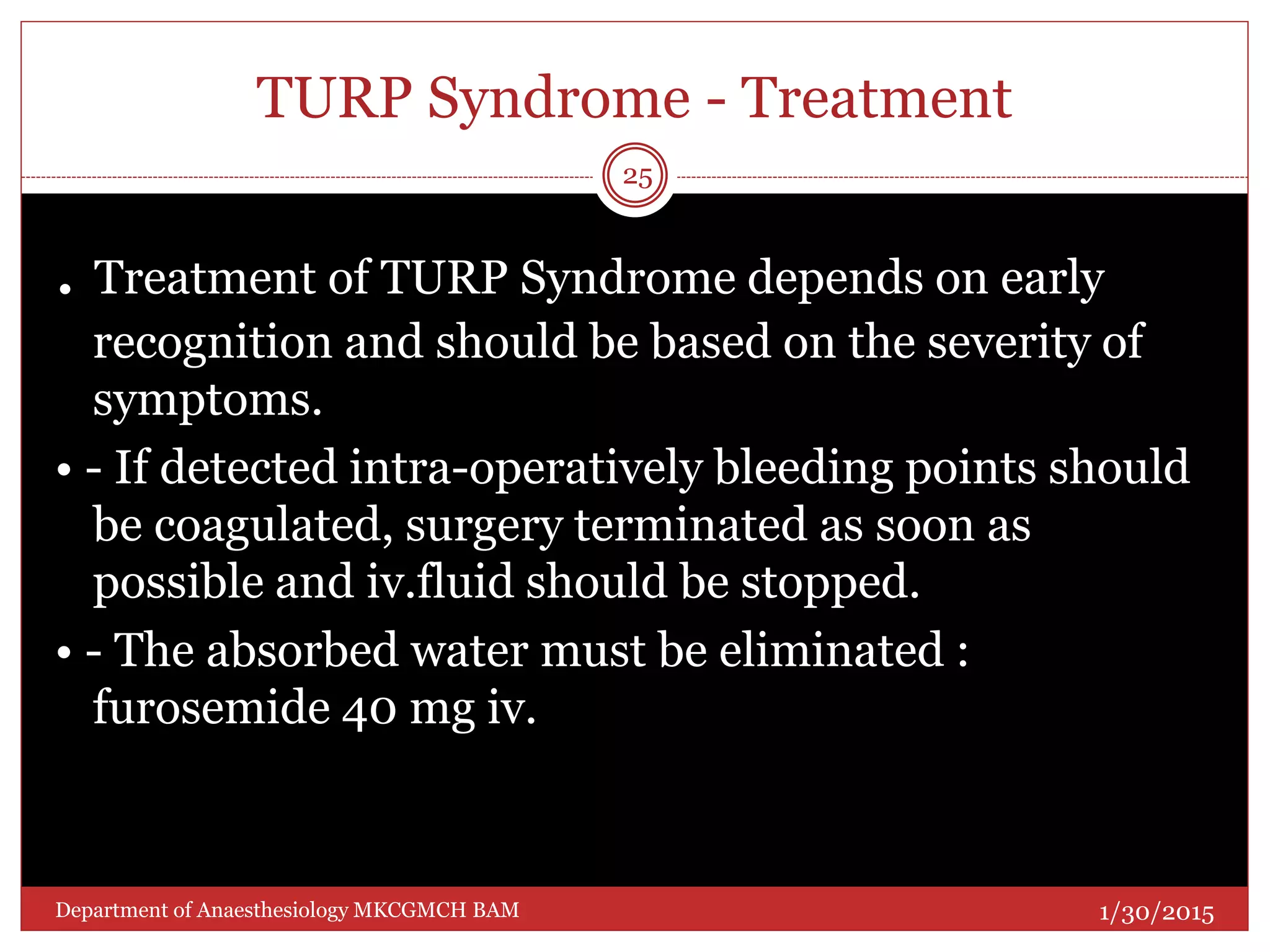
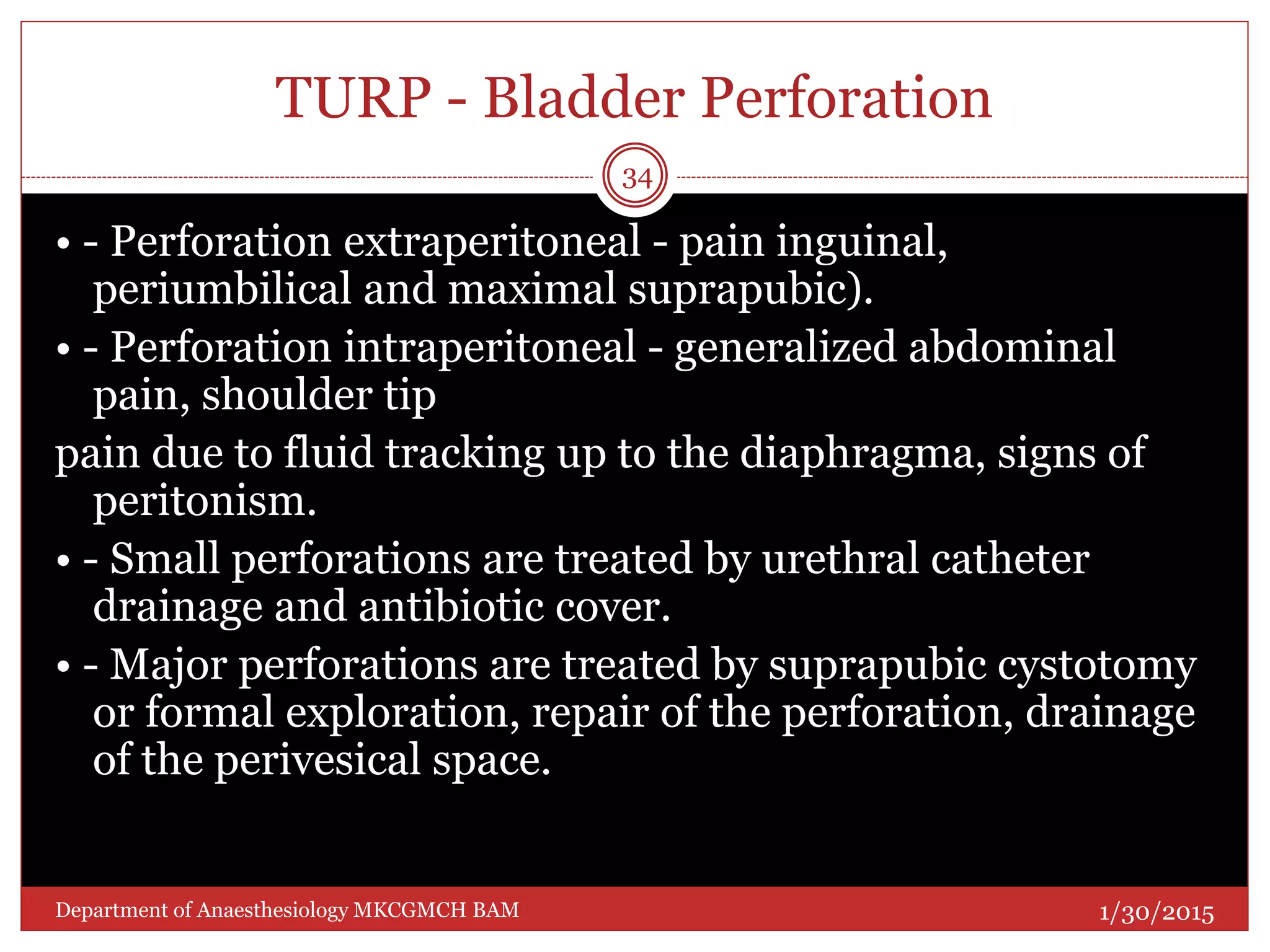
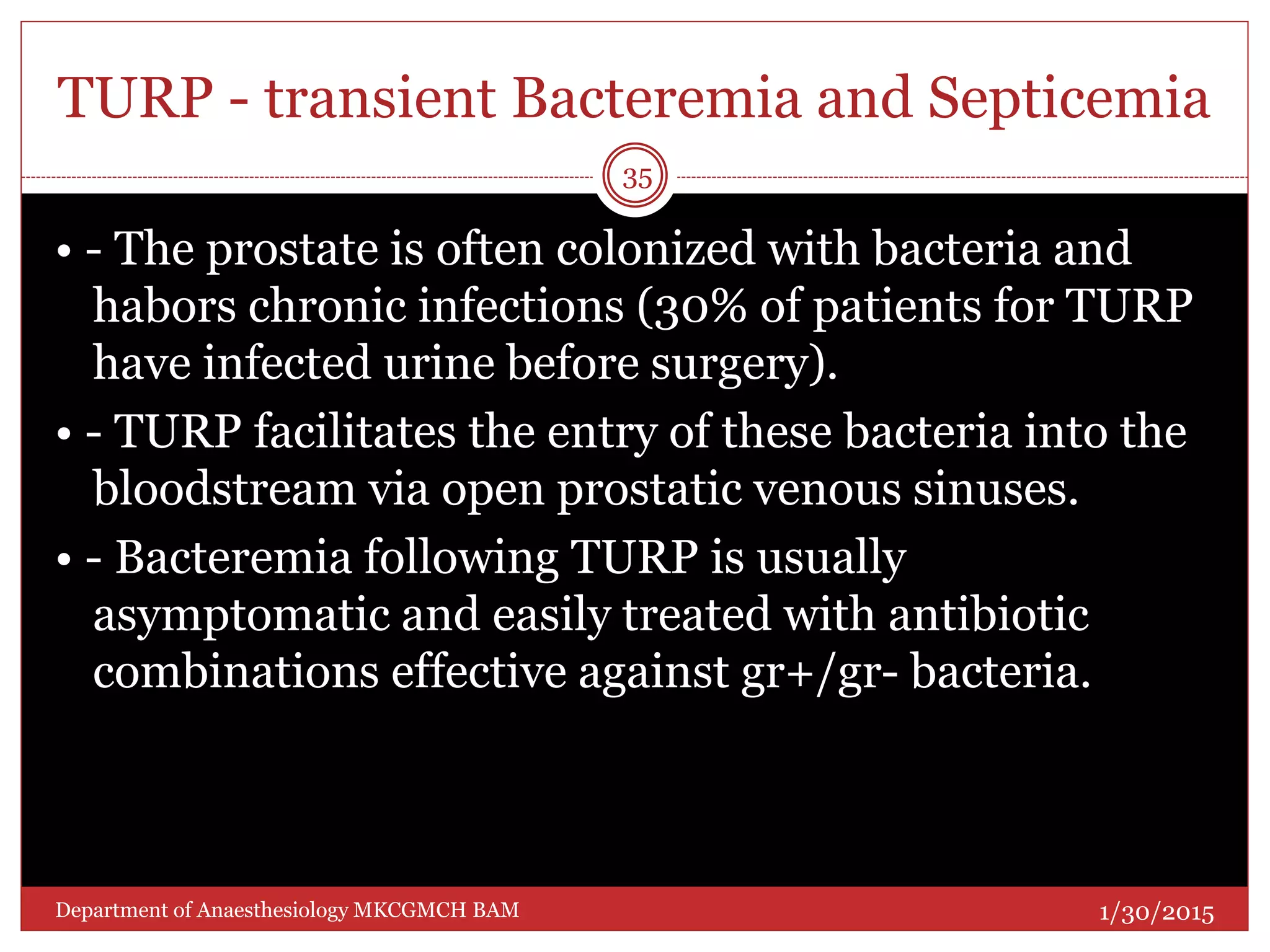
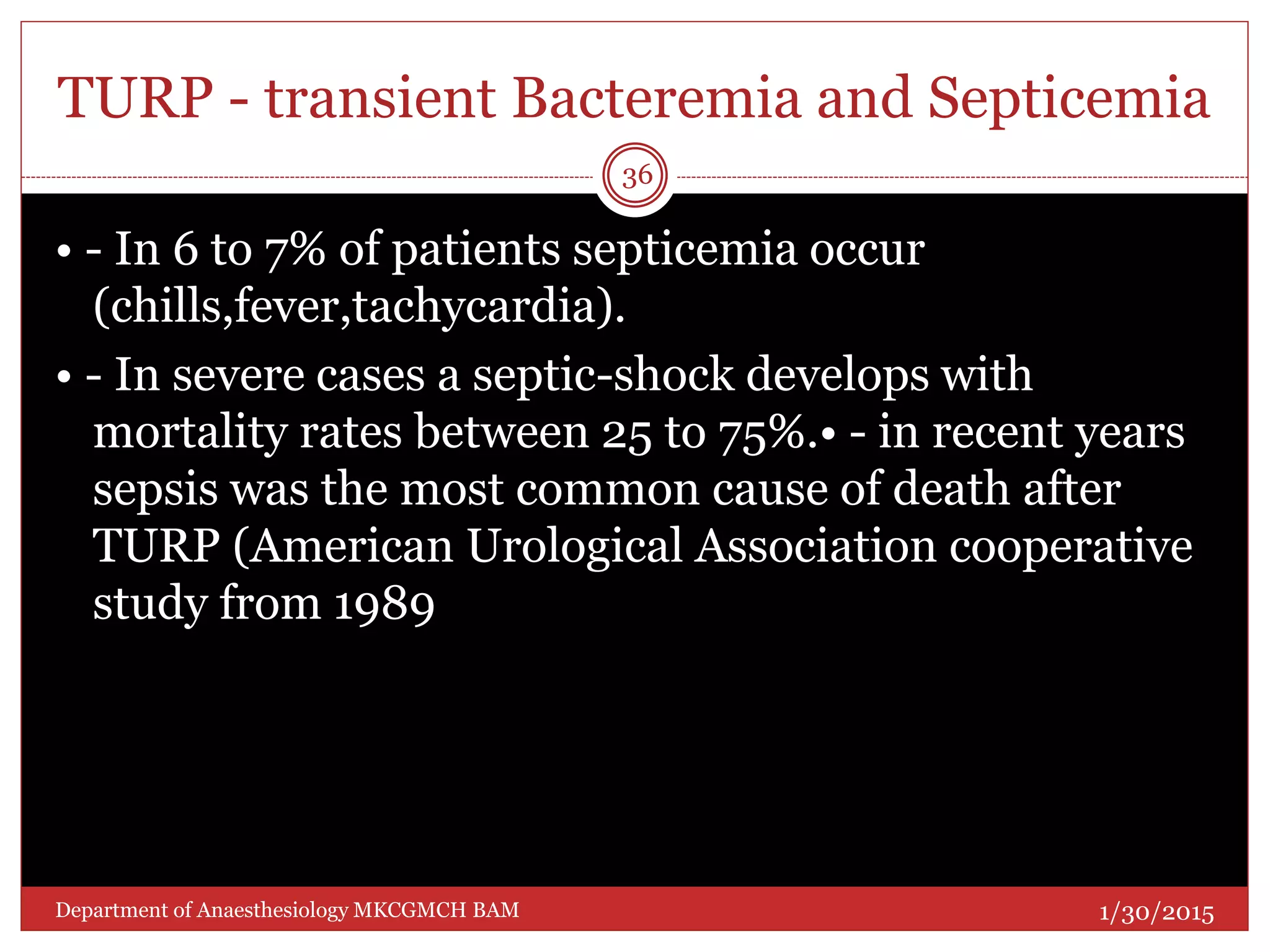
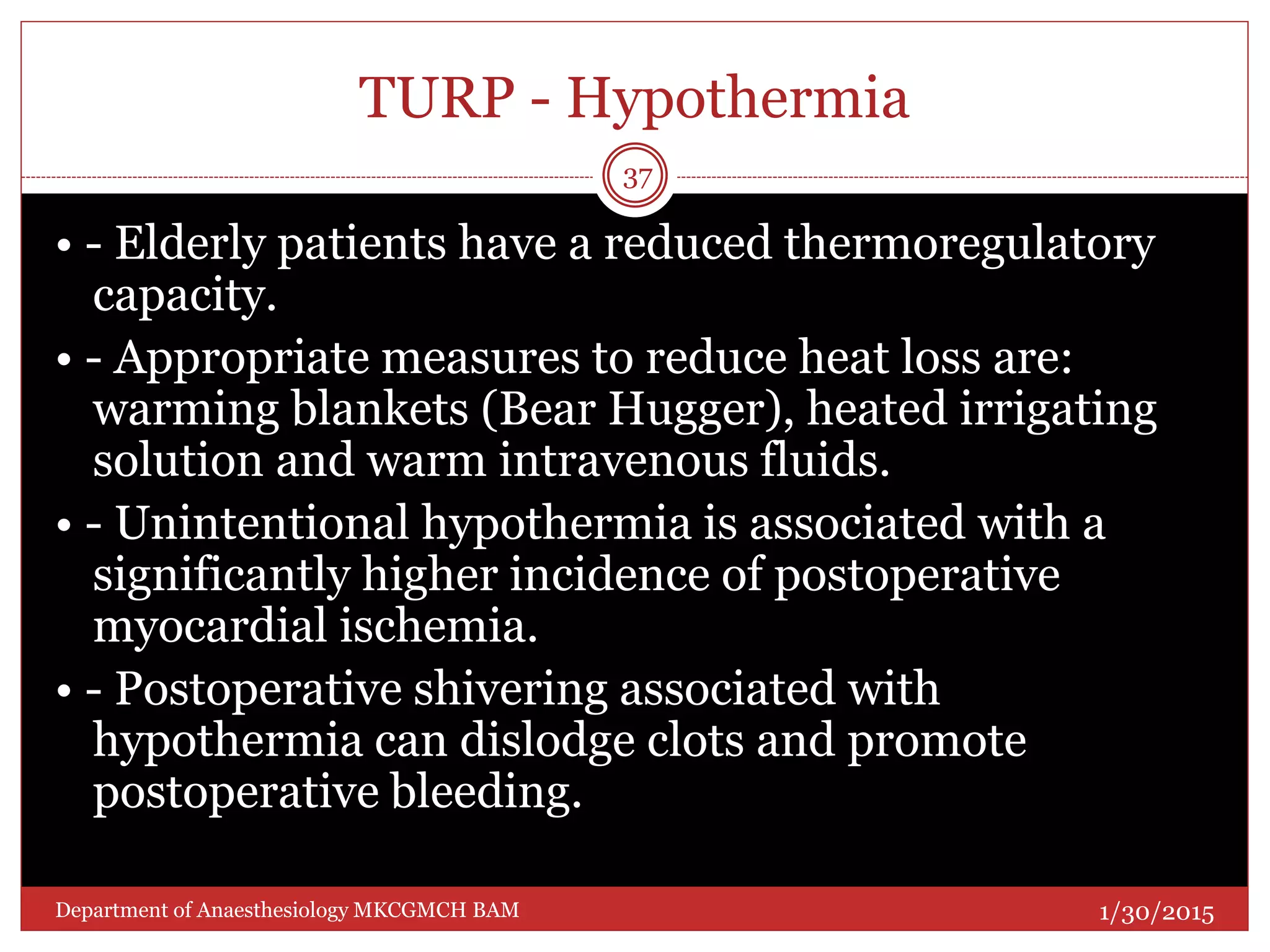
This document discusses Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) and associated anaesthetic considerations. TURP is the second most common surgery for men over 65 and involves using an electrically energized wire loop to resect prostatic tissue through continuous irrigation. Large volumes of irrigating fluid are commonly absorbed, which can cause TURP Syndrome characterized by fluid overload, hyponatremia, and potential solute toxicity. Patients undergoing TURP are often elderly with cardiovascular or pulmonary comorbidities and optimal anaesthetic management requires addressing these conditions as well as risks of fluid absorption, blood loss, and postoperative care.