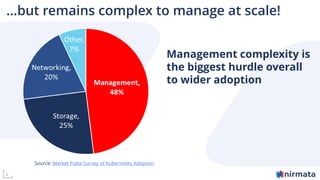
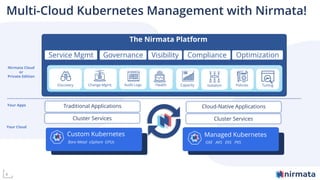
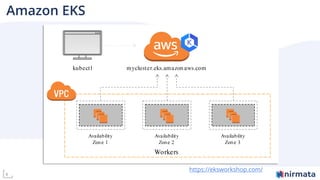
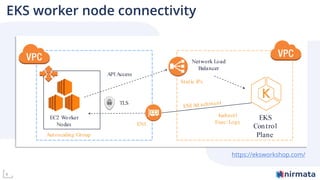
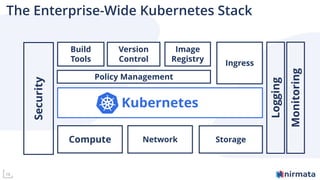
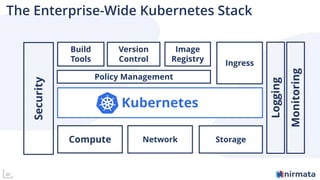
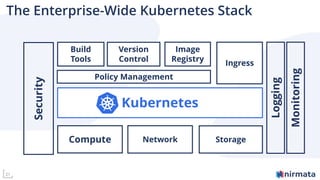
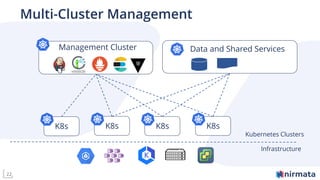
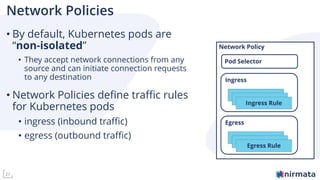
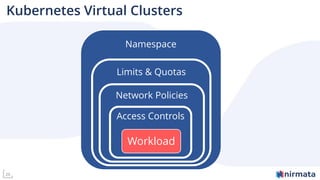
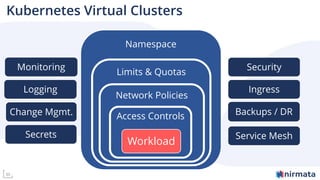
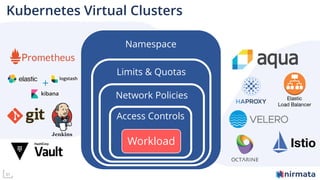
The document discusses operationalizing Amazon EKS for managing Kubernetes, detailing its complexities and providing an overview of necessary features and management strategies. It emphasizes the importance of cluster management, governance, and the need for efficient tools such as Nirmata for creating secure virtual clusters. The conclusion highlights Amazon EKS as a reliable solution for Kubernetes control plane provisioning, with Nirmata facilitating easier management for enterprises.