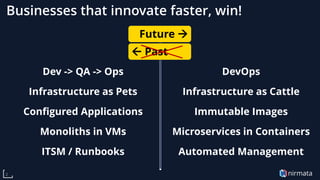
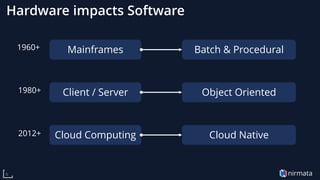
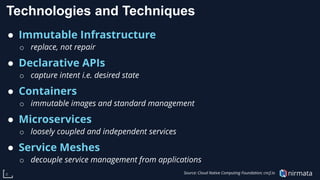
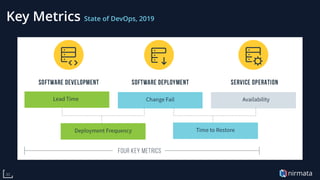
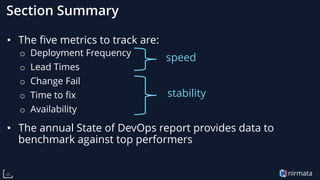
The document discusses the transformative role of Kubernetes in cloud-native DevOps, emphasizing its capabilities for automated deployment, scaling, and management of applications. It highlights the importance of organizational structure, best practices, and metrics for successful Kubernetes adoption, particularly through the use of virtual Kubernetes clusters for enabling secure self-service for development teams. Key benefits include increased agility, cost savings, and improved resource utilization, ultimately positioning cloud-native technologies as essential for modern enterprises.