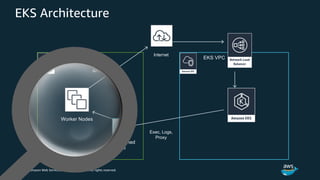
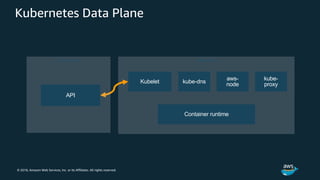
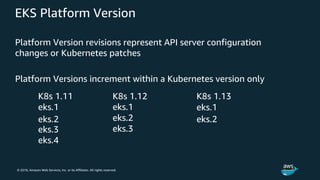
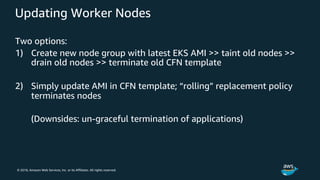
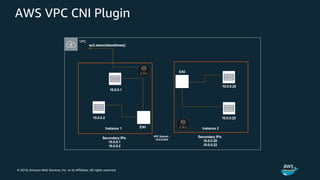
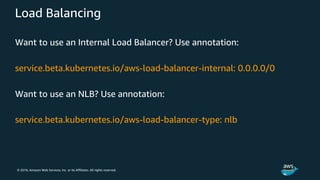
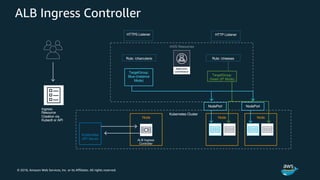
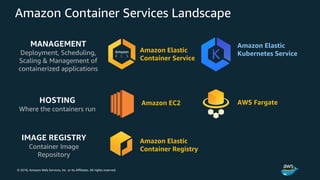
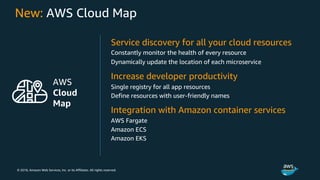
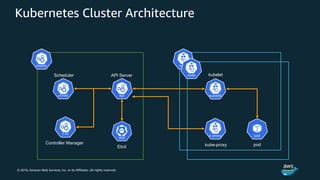
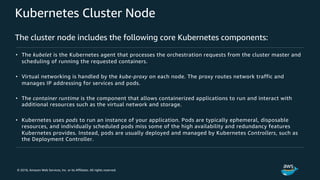
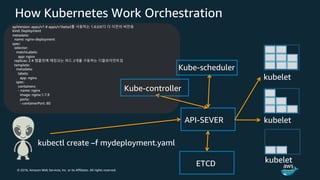
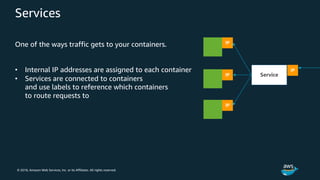
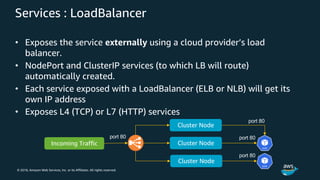
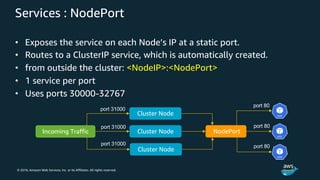
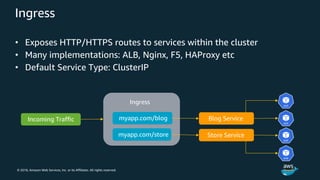
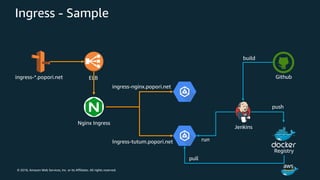
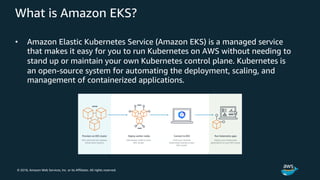
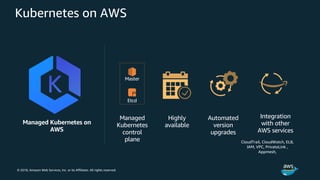
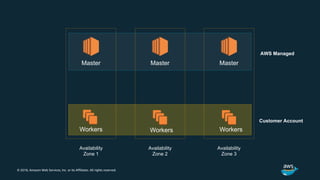
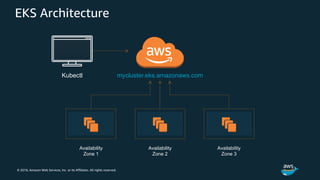
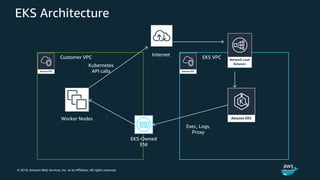
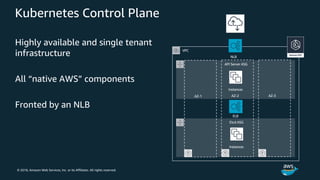
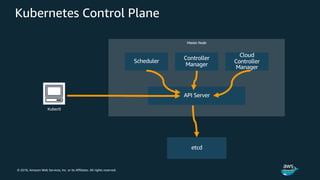
The document discusses Amazon Web Services container management services and Kubernetes. It provides an overview of AWS services like Amazon ECS, EKS, Fargate, ECR, Cloud Map and App Mesh. It also describes Kubernetes concepts like pods, deployments, services, namespaces and control plane/data plane architecture. Amazon EKS is highlighted as a managed Kubernetes service that makes it easy to run Kubernetes on AWS without operating the control plane.




















![© 2018, Amazon Web Services, Inc. or its Affiliates. All rights reserved.
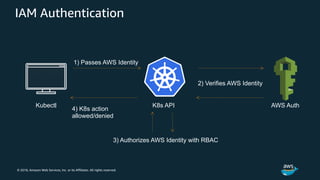
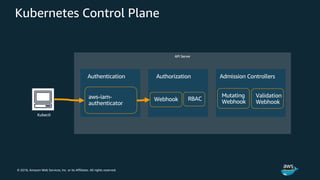
kubectl configuration
# [...]
users:
- name: aws
user:
exec:
apiVersion: client.authentication.k8s.io/v1alpha1
command: aws-iam-authenticator
args:
- "token"
- "-i"
- "CLUSTER_ID"
- "-r"
- "ROLE_ARN"
# no client certificate/key needed here!](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/container-workshop-0827-k8seks-190830071956/85/Kubernetes-EKS-AWS-45-320.jpg)