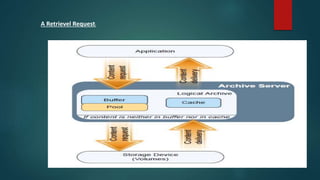
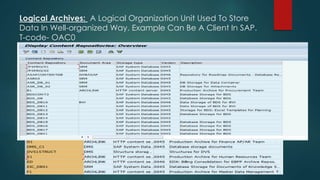
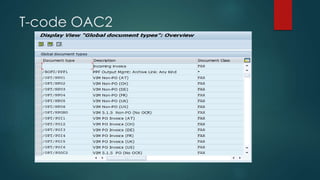
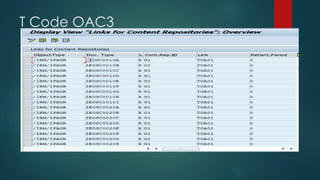
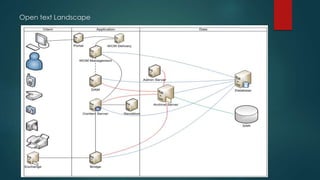
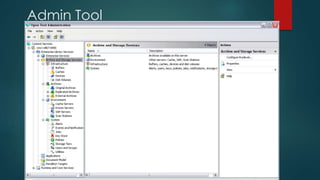
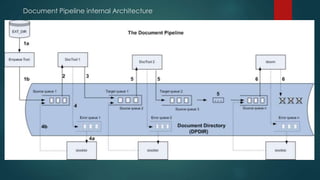
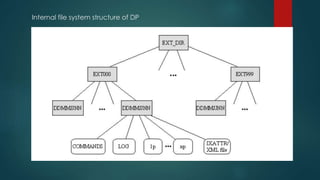
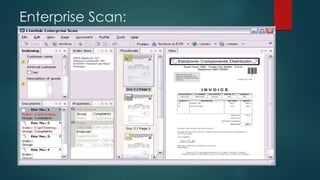
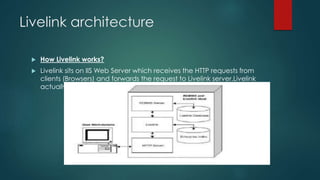
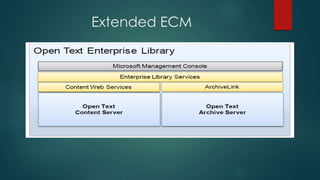
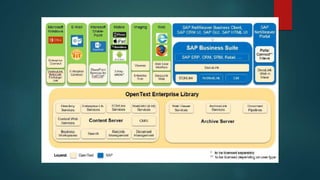
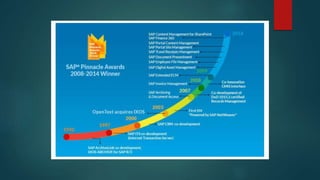
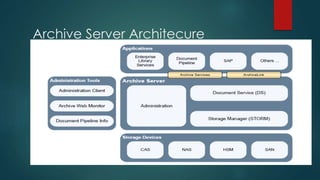
This document provides an overview of OpenText and its product landscape. It discusses the typical 3-tier architecture with database, application, and presentation layers. It describes the Livelink and Archive Server applications, their architecture, administration tools, and typical document workflows. Key components include the Archive Server, Livelink, Pipeline Server, and various administration tools for managing the OpenText landscape.





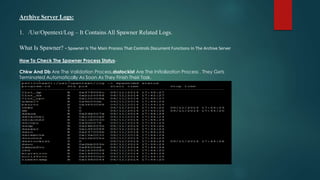
![/Usr/Opentext/Tomcat/Logs- It Will Give You All Tomcat, RCS Related Logs .
What Is Tomcat- /Software/Tomcat/Apache-tomcat-5.5.23 ?- Tomcat Makes The Web Services Available
Through Rcs And Needs To Be Running In Order To Successfully Archive And Retrieve Documents.
What Is RCS - Runtime And Core Services- It Work As An Gateway To Open Text Aplication,it Is Used To
Provide Connection Between Your Content Server(formally Known As Livelink ) With Your Archive Server
(Open Text Runtime And Core Services)
Common Problem In Archive Server:
User Cannot Retrieve Document From SAP If The Rcs.Log For The Archive Server Shows The Following
Message
WARN [Cs-workerthread #32] Otx.LES : Com.Opentext.Livelink.Service.Core.Exceptionutil - Could Not
Access Server
Login To Admin Server And Check The Livelink Server 9.7.1/Content Server10.1 Service And Make Sure It Is
Running, If It Is Running Check To Make Sure Llserver.Exe Is Not Running At 63%.
Start /Stop Procedure Of Archive Server:
Su – Otxadm Or Sudo Su – Otxadm
Stop Spawner – ./Run.Sp Stop
Stop Tomcat – ./Run.Tc Stop
Make Sure There Are No Processes Running As Otxadm – Ps-ef | Grep Otxadm
If There Are Still Process Running As Otxadm – Kill -9 <PID>
Start Spawner – ./Run.Sp Start
Start Tomcat – ./Run.Tc Start](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/5d805104-910e-45f1-ad89-a050d5e3a0bf-151008165104-lva1-app6892/85/OPEN-TEXT-ADMINISTRATION-8-320.jpg)