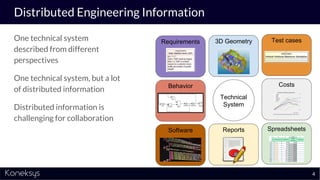
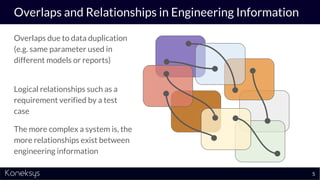
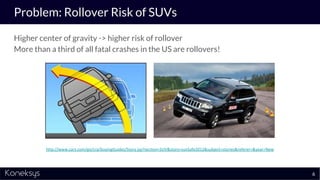
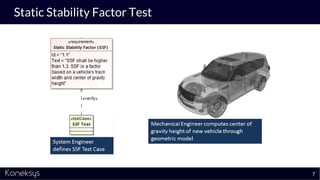
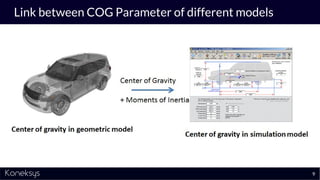
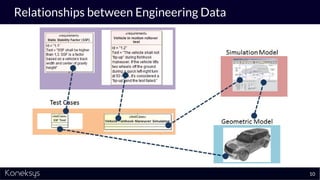
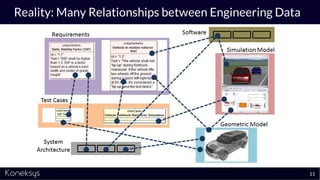
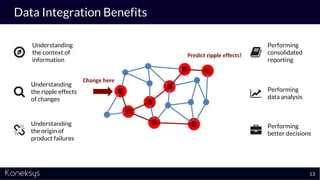
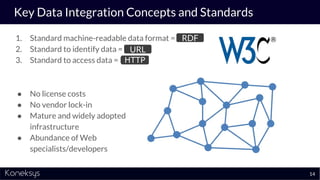
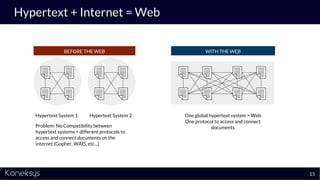
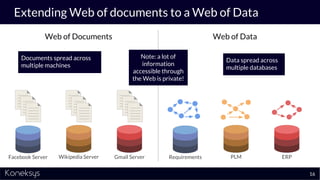
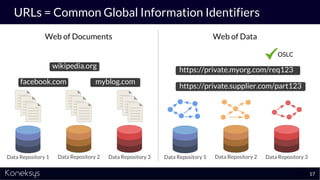
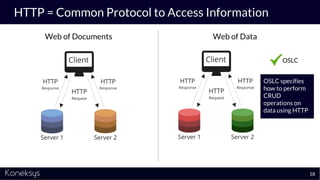
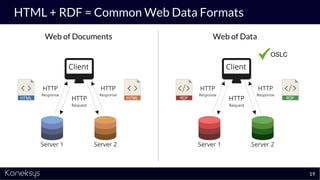
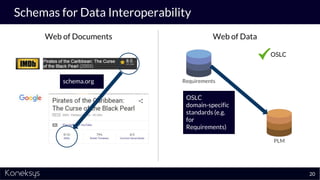
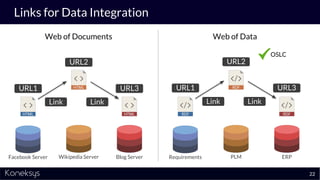
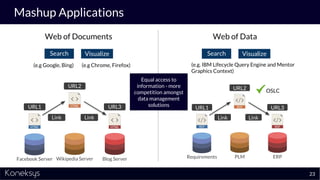
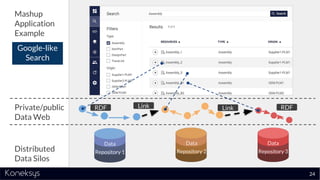
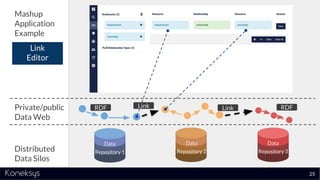
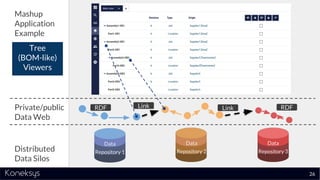
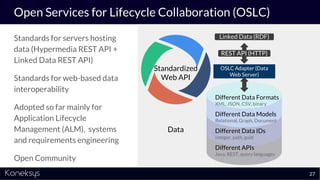
This document summarizes a webinar about Open Services for Lifecycle Collaboration (OSLC) and data integration. It introduces the presenter Axel Reichwein and his company Koneksys, which helps organizations create data integration solutions. It discusses challenges of distributed engineering data from different sources and the benefits of data integration. Key concepts discussed include using URLs, HTTP, and RDF to create a web of linked data. OSLC standards provide APIs to access and link data from different sources. This allows building mashup applications to search, visualize, and link engineering information across distributed systems.