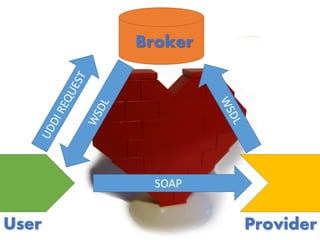
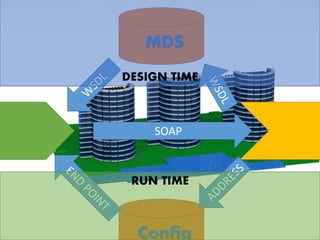
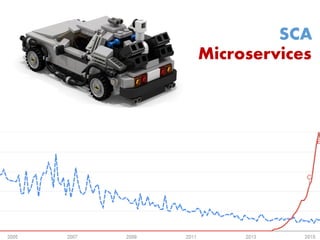
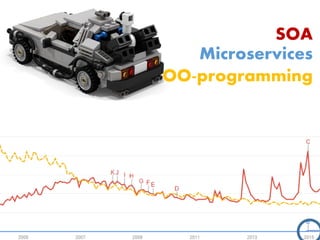
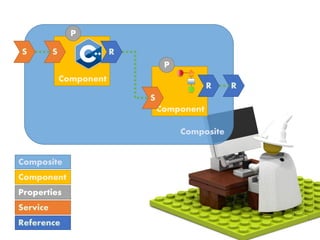
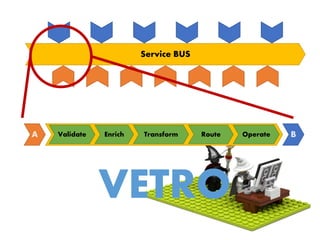
The document provides an extensive overview of Oracle SOA Suite 12c including the certification tracks, key components, and architecture related to service-oriented architecture (SOA). It covers various topics such as BPEL modeling, service mediation, deployment, troubleshooting, business rules, and event processing. Additionally, it discusses the role of Oracle's governance capabilities and adapters in integrating cloud and mobile applications.




























![foo
/foo
/foo/bar
//bar
/foo/*
//*
/foo/bar[@name=‘a’]
/foo/bar[1]/@name
/foo/bar[@price > 300]
/foo/bar[1]
<foo>
<bar name=“a” price=“150”>
This is a bar
</bar>
<bar name=“b” price=“300”>
This is a bar
</bar>
<bar name=“c” price=“350”>
This is a bar
</bar>
<bar name=“d” price=“400”>
This is a bar
</bar>
</foo>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oraclesoa12ccertday1-150520142857-lva1-app6891/85/Oracle-SOA-Suite-12c-1z0-434-Day-1-3-45-320.jpg)
