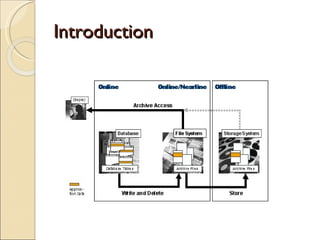
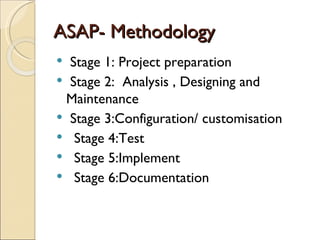
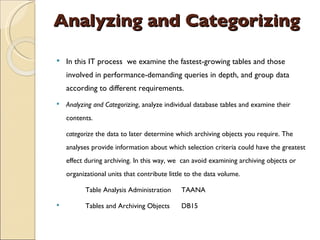
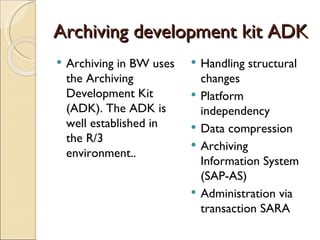
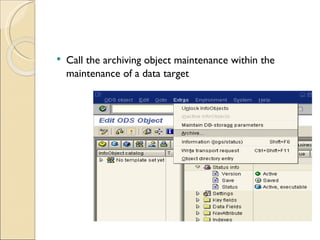
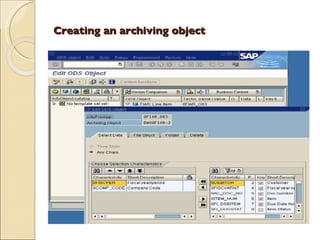
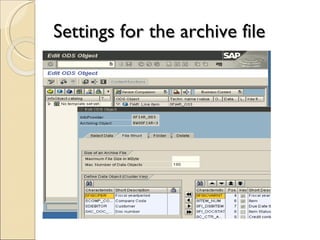
The document discusses the stages of SAP data archiving methodology including project preparation, analysis and design, configuration, testing, implementation, and documentation. It then covers reasons for data archiving such as resolving memory and performance issues, ensuring data growth remains moderate, and meeting legal storage requirements. Key data archiving requirements are also summarized such as hardware independence, release dependence, data dependencies, and maintaining enterprise/business structure.