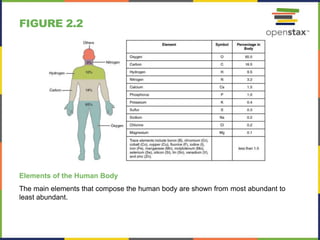
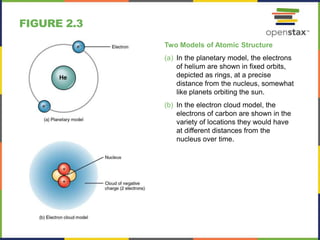
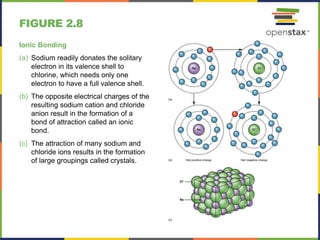
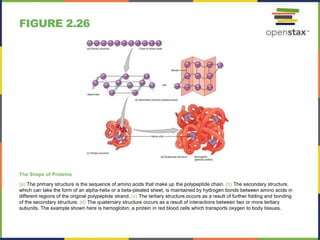
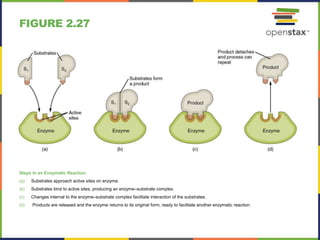
This document discusses the chemical level of organization of the human body. It includes 30 figures that illustrate key topics like DNA structure, the elements that compose the human body, atomic structure, the periodic table, isotopes of hydrogen, PET scans, electron shells, ionic and covalent bonding, hydrogen bonds, chemical reactions, enzymes, carbohydrates, lipids, amino acids, proteins, nucleotides, DNA, and ATP structure. The figures provide visual representations of these important anatomical and physiological concepts.