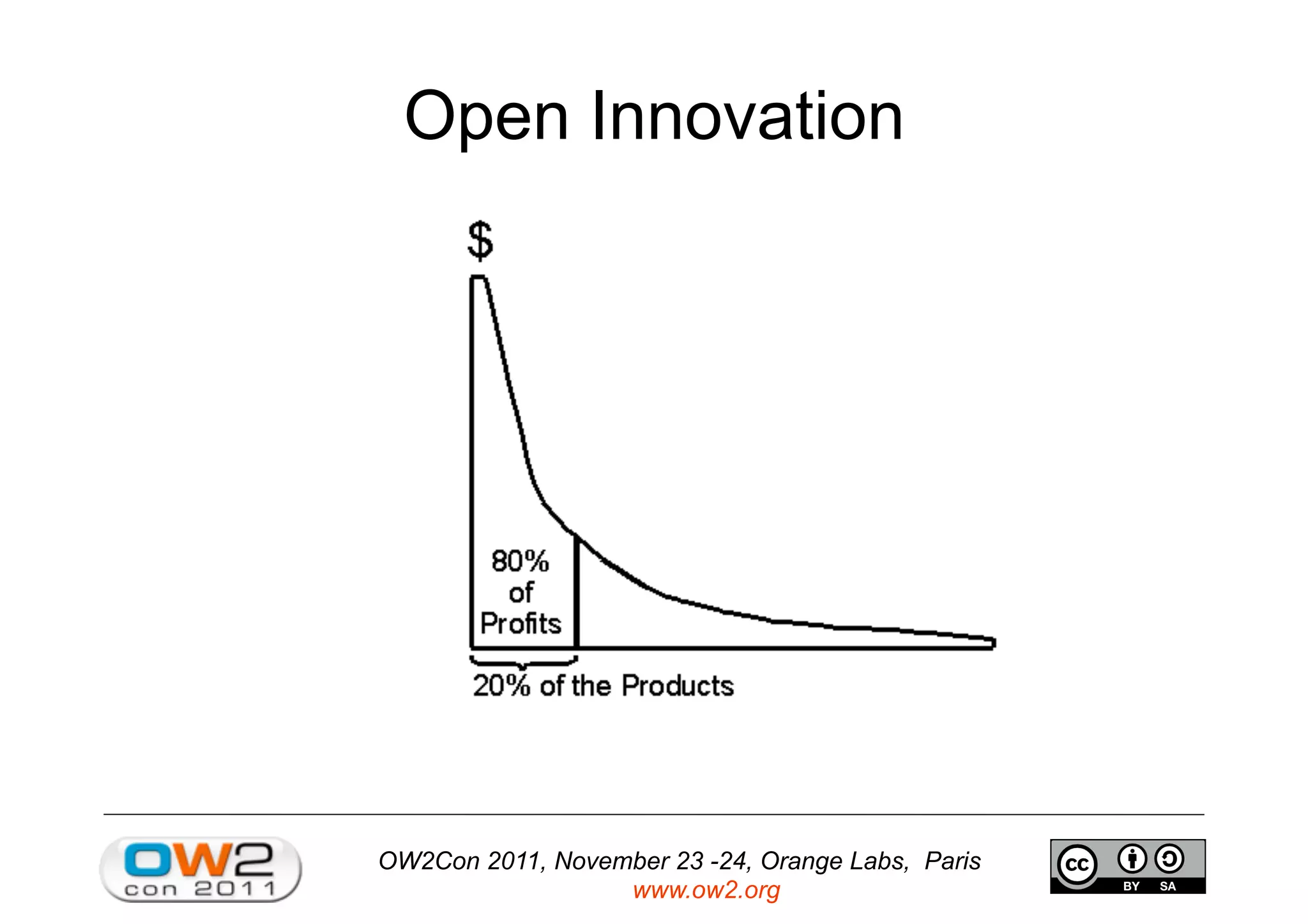
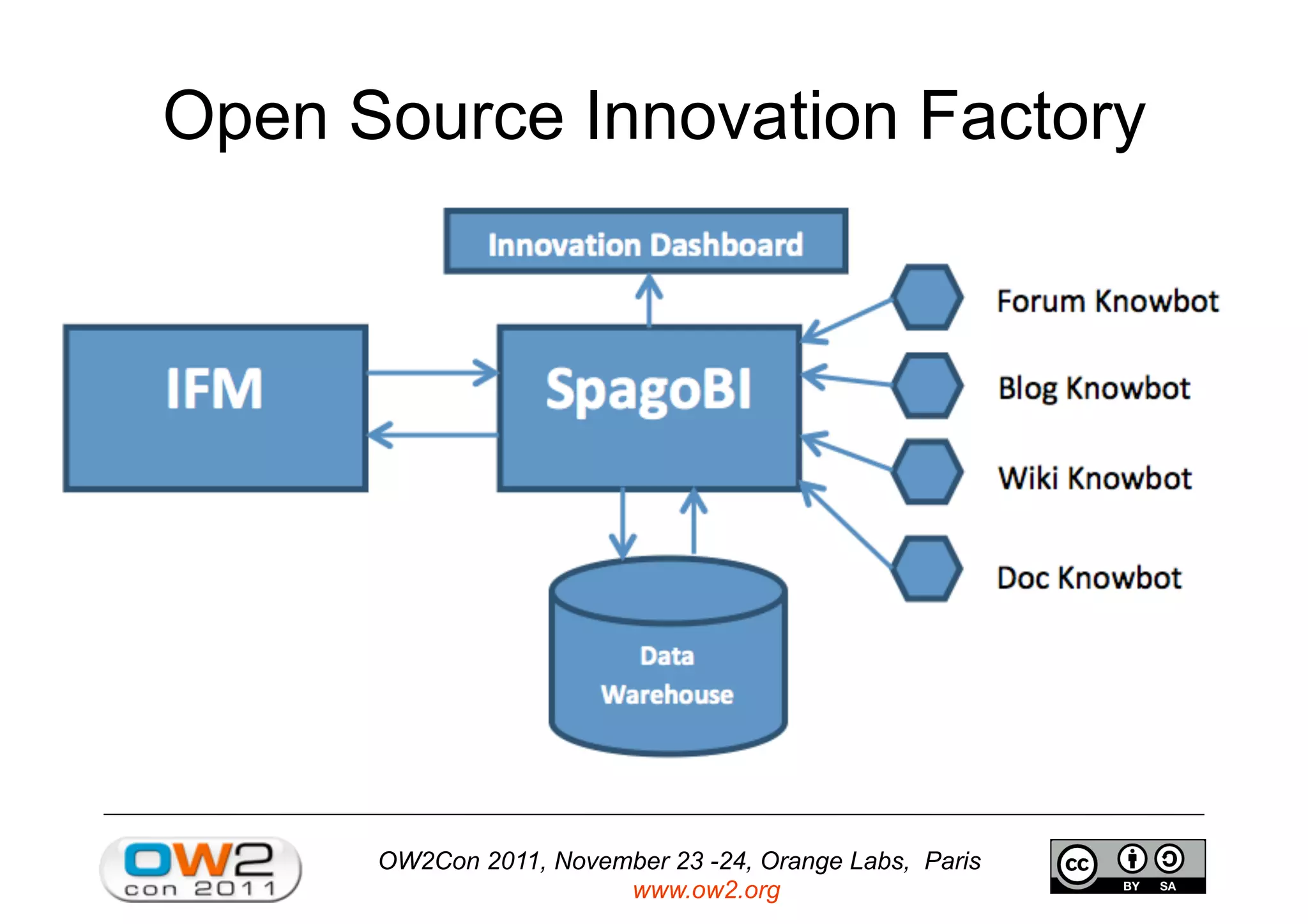
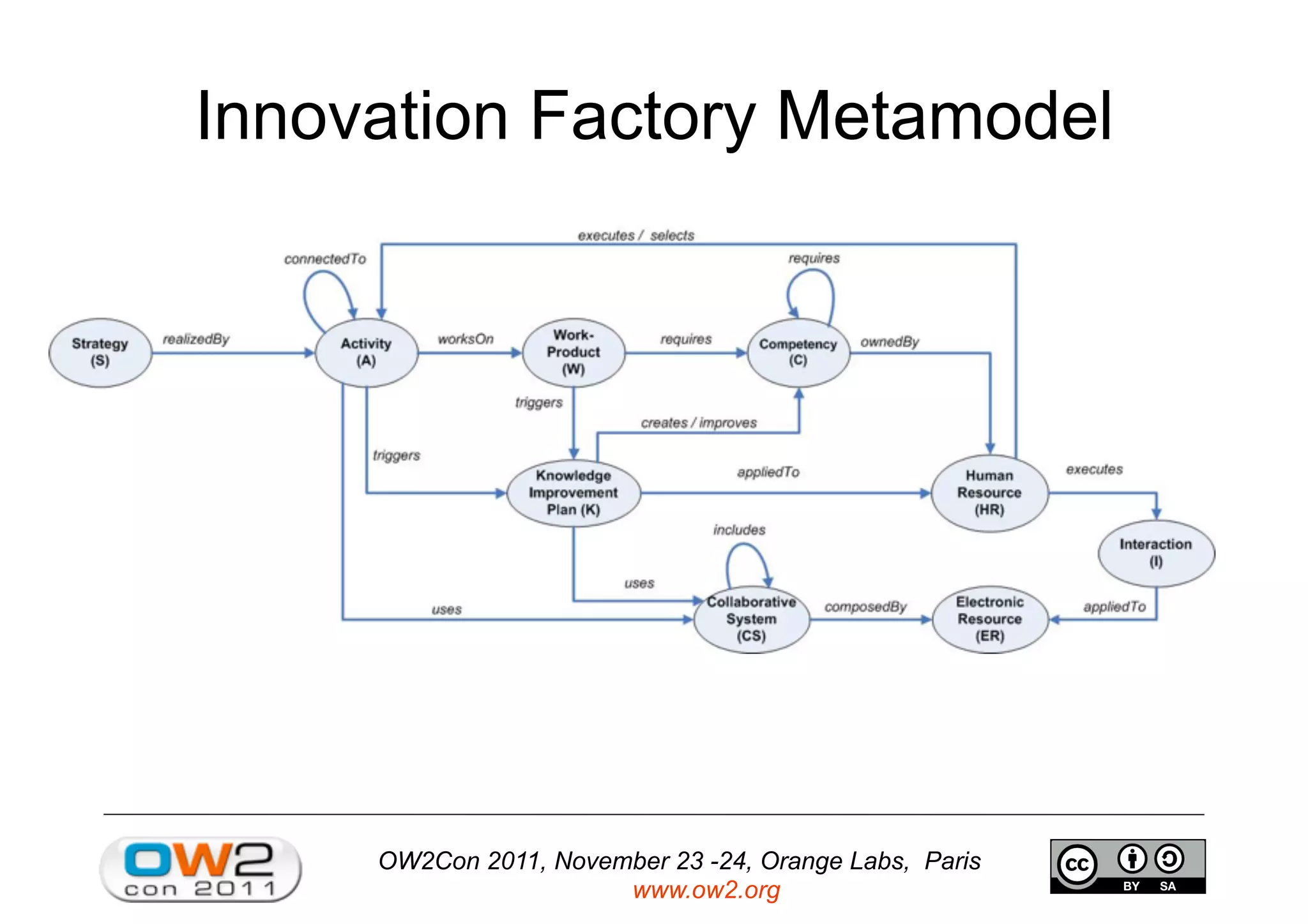
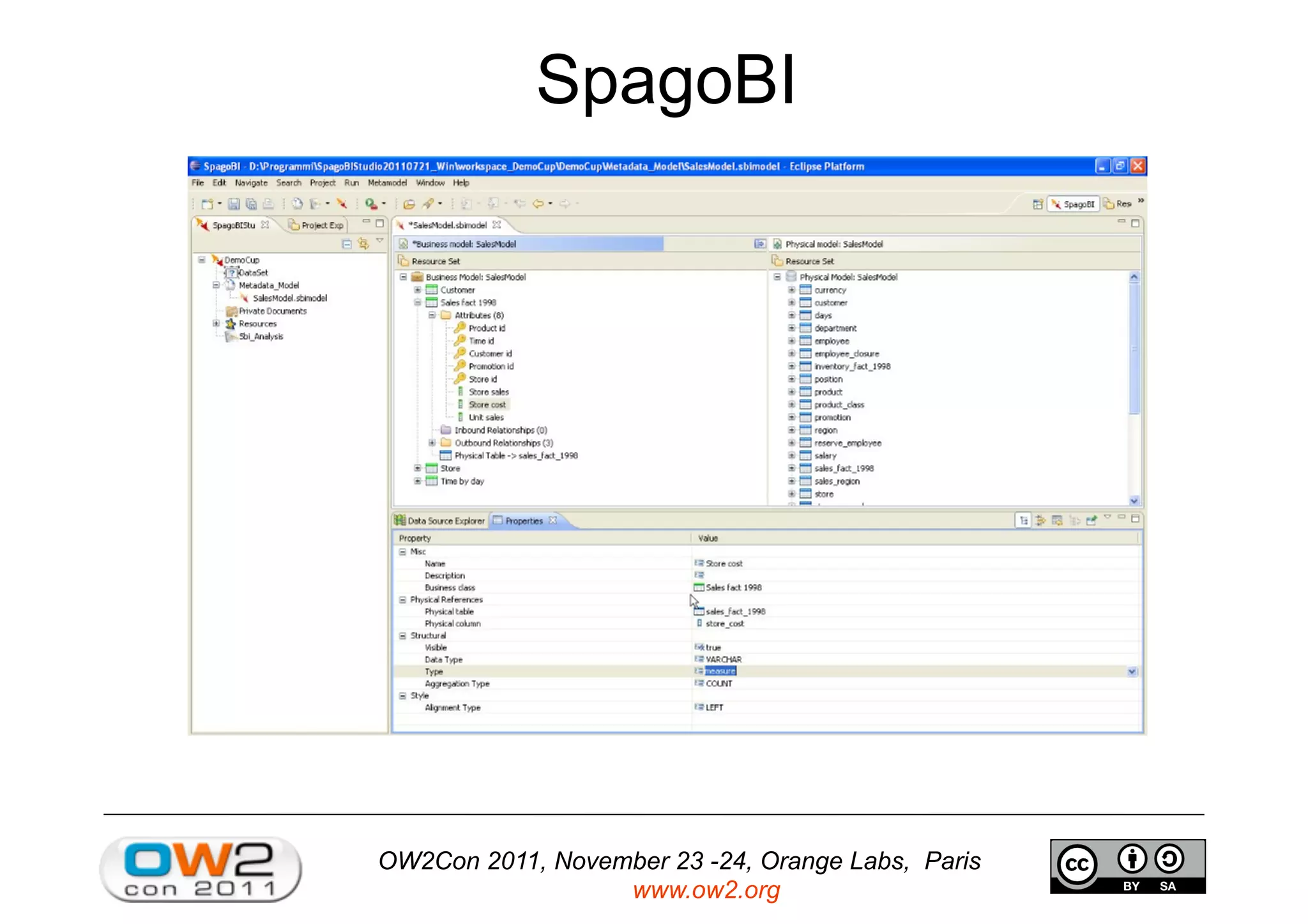
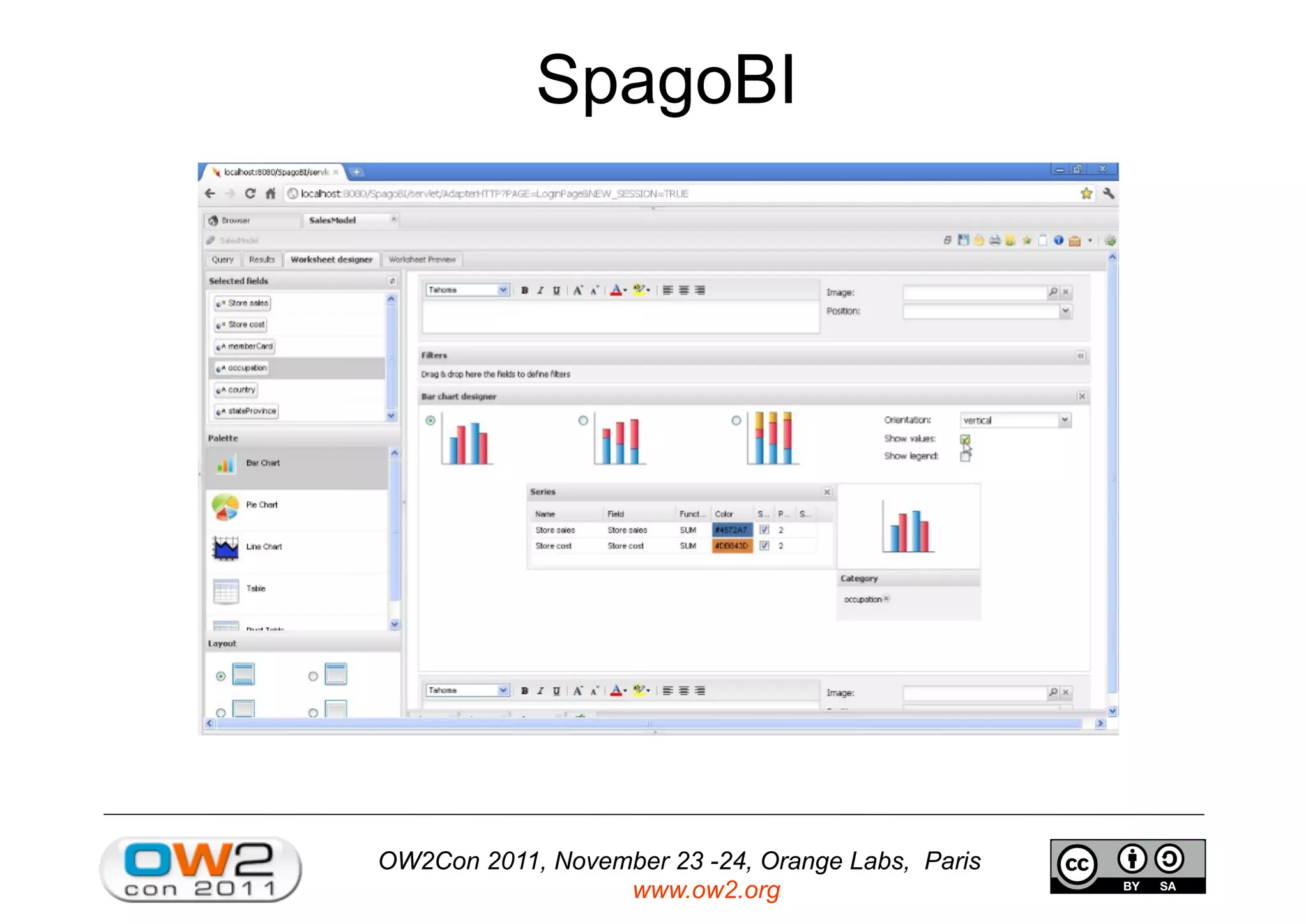
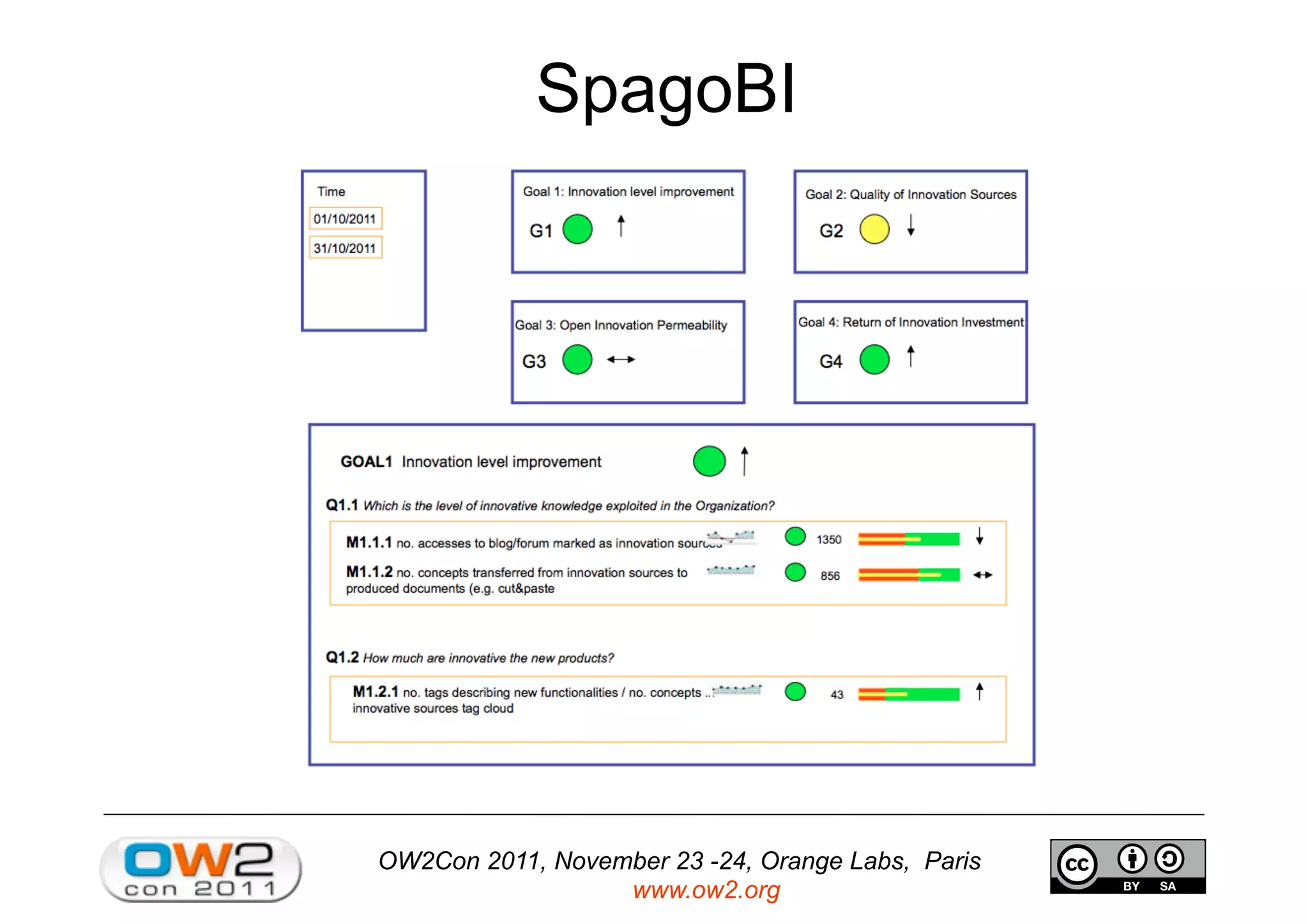
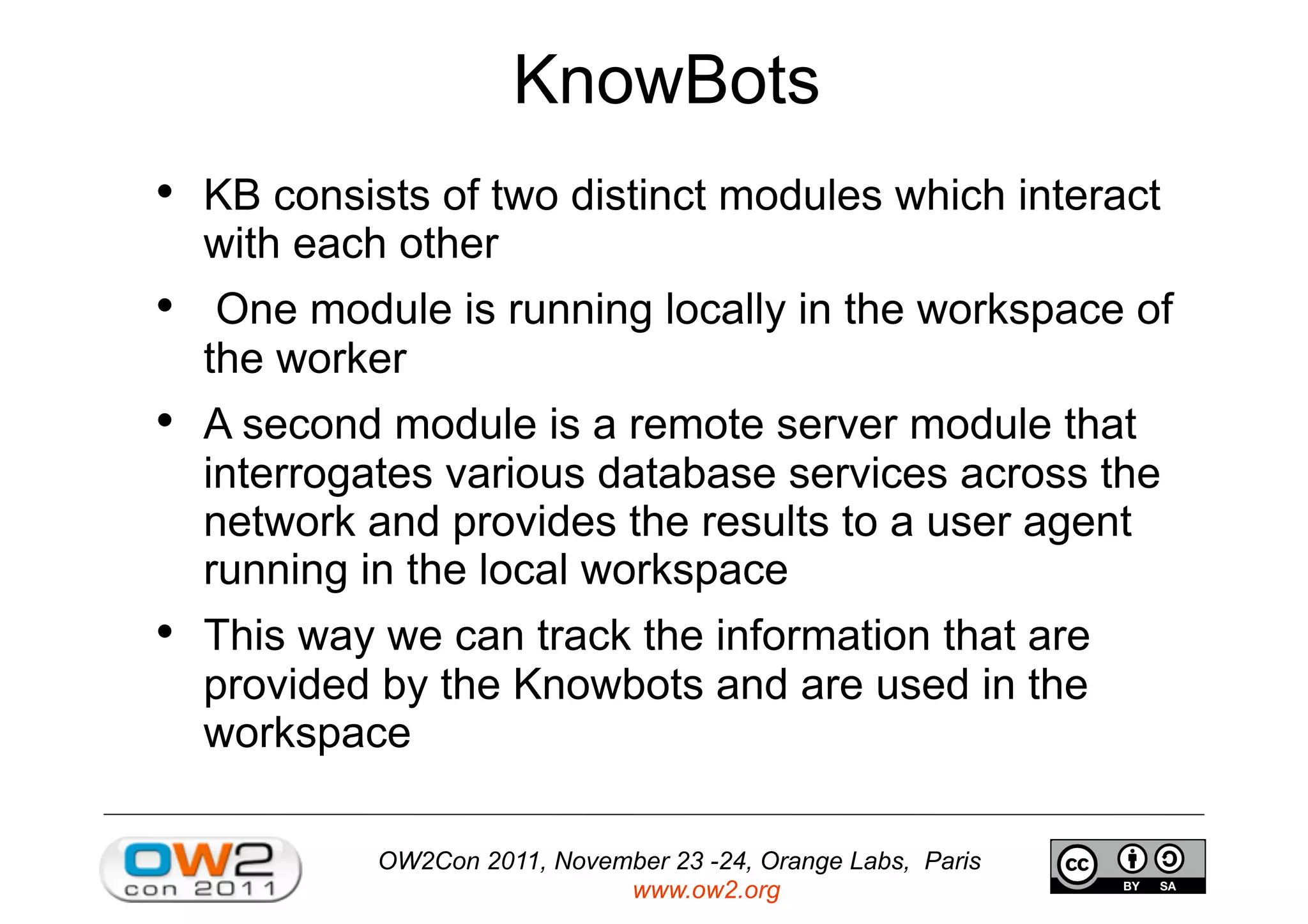
The document discusses an open source innovation factory framework that uses innovation metrics and knowbots to help companies reduce the time required to transfer innovative projects to real environments. Specifically, it presents a model that measures innovation activities and goals, uses the open source SpagoBI platform to analyze innovation data, and employs knowbots to acquire external knowledge to inform innovation processes. An example scenario for an aerospace company is provided to illustrate how the framework could optimize engine repair planning.
![OW2Con 2011, November 23 -24, Orange Labs, Paris
www.ow2.org
Open Source Innovation Factory
Paolo Ceravolo, Università degli Studi di Milano
in cooperation with Engineering Group
[Our Framework equipped with Innovation Metrics can
dramatically reduce the time required to transfer an
innovative project to a real environment]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ow2con11-paoloceravolov1-111223091417-phpapp02/75/Open-Source-Innovation-Factory-OW2con11-Nov-24-25-2011-Paris-1-2048.jpg)