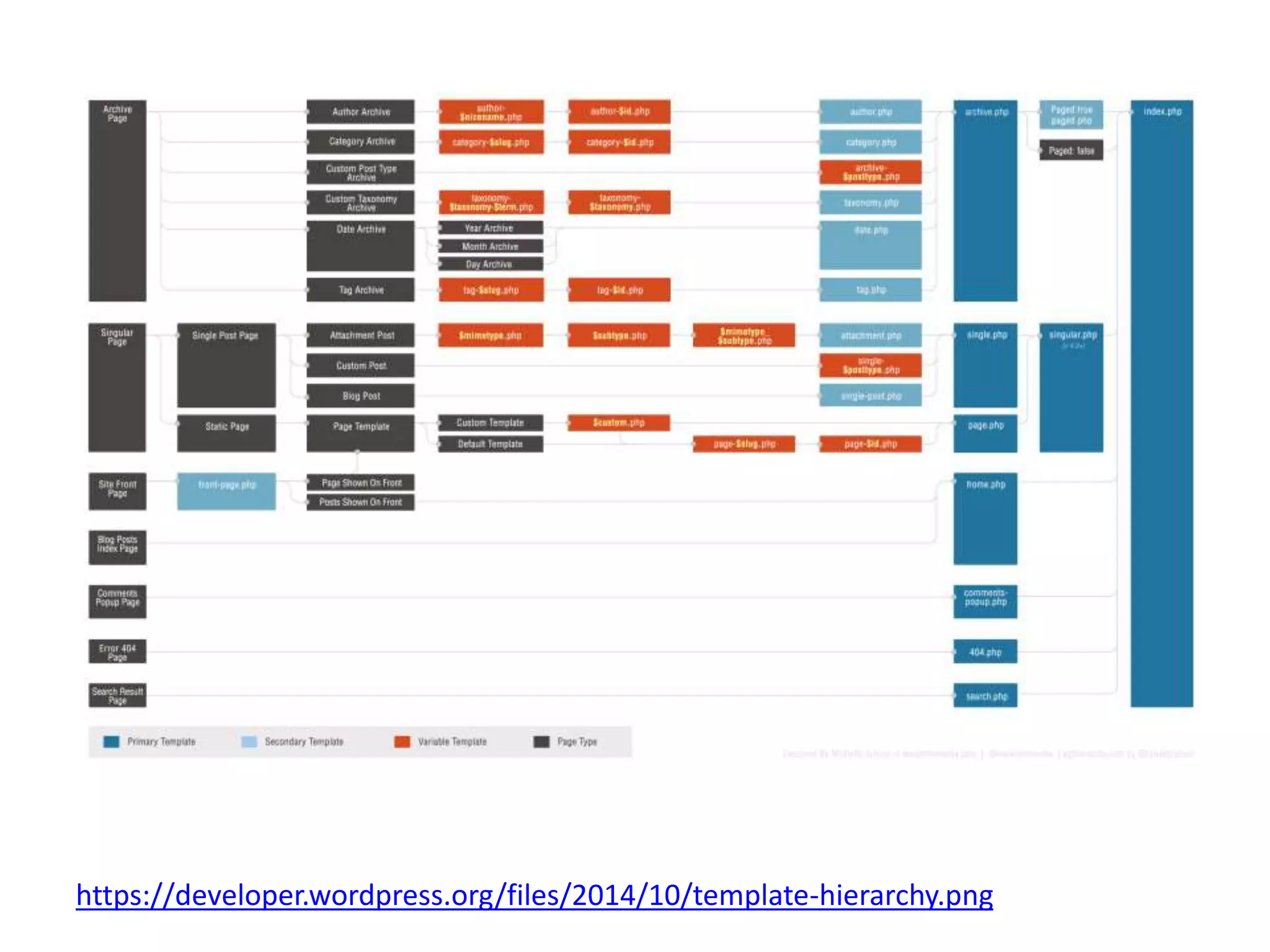
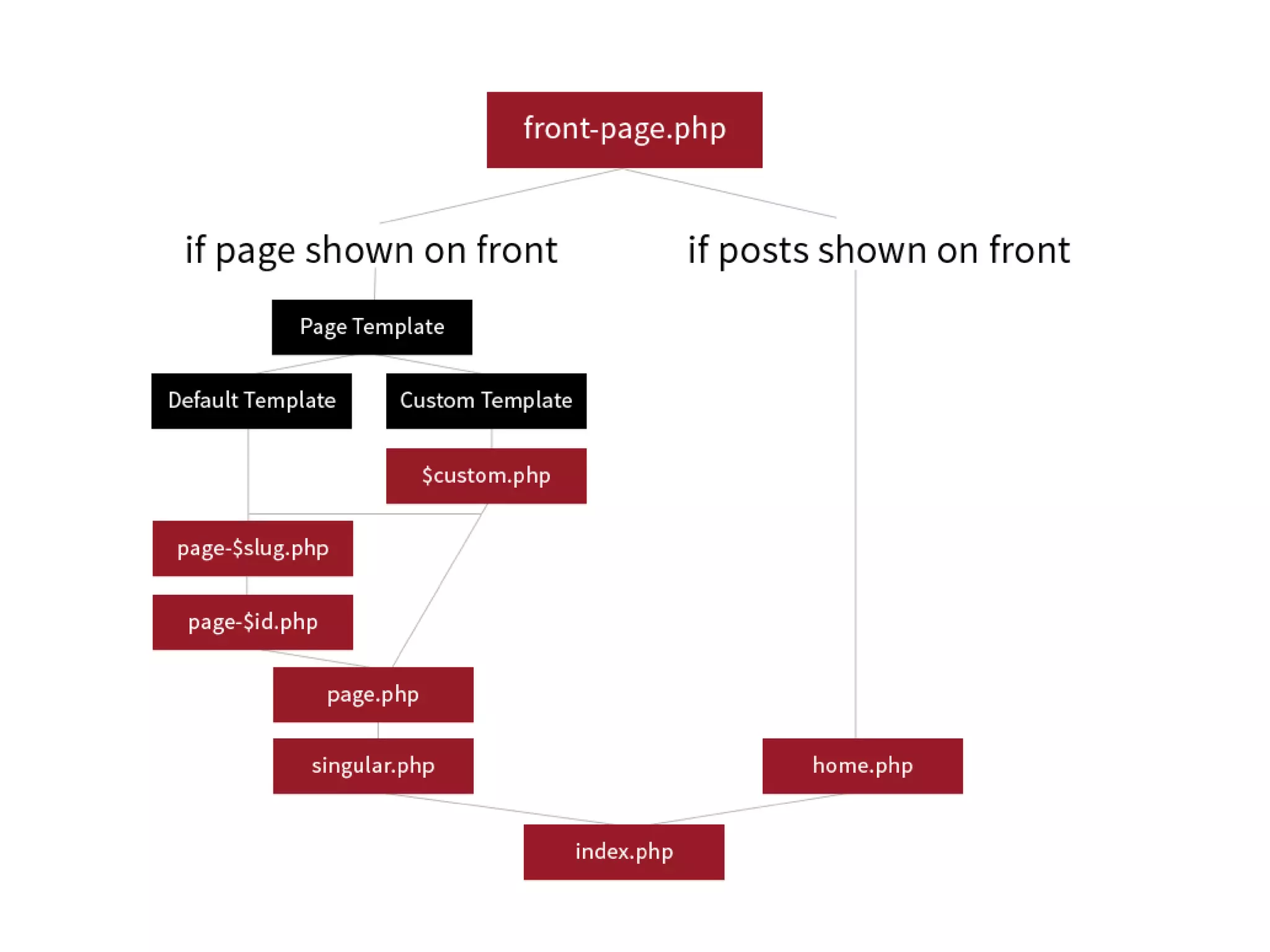
The document outlines the WordPress template hierarchy, distinguishing between webpages, posts, and pages, detailing how they are stored and managed within the wp_posts database. It discusses key template files like style.css and functions.php, explaining their roles in theme presentation and functionality, and how templates are selected based on specific logic. Besides, it addresses common template files and fallback mechanisms that WordPress employs when certain templates are missing, providing resources for further exploration of template hierarchy.