Embed presentation
Downloaded 106 times



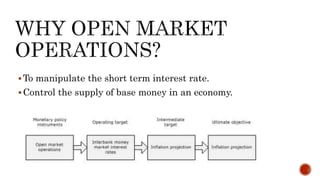

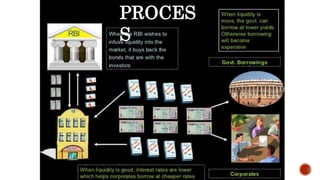





The document discusses the Reserve Bank of India's (RBI) Open Market Operations (OMO), which involve buying and selling government securities to manage rupee liquidity and influence short-term interest rates. It highlights the impact of these operations on inflation, corporate borrowing conditions, and the overall economy, particularly in the context of post-1991 economic reforms. The document notes that OMOs are employed by the RBI to control money supply, maintain inflation targets, and stabilize exchange rates.









