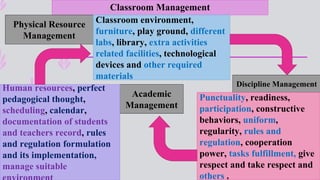
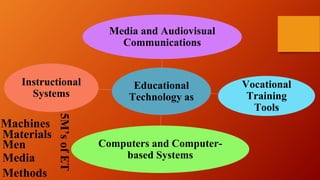
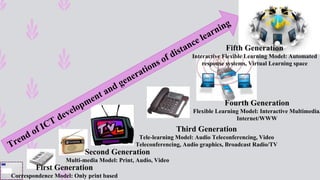
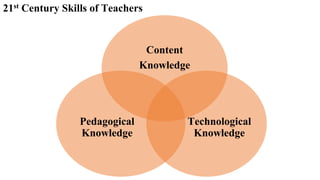
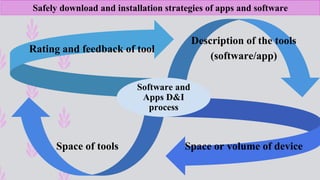
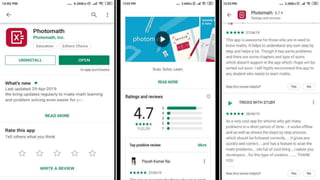
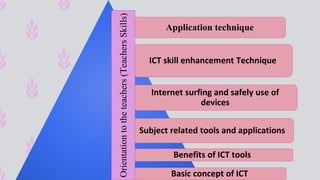
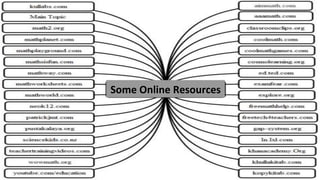
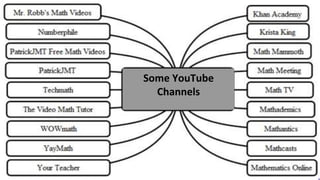
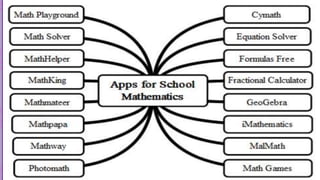
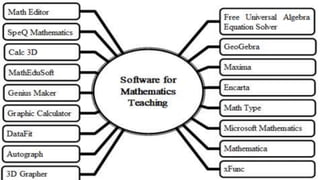
The document discusses the integration of ICT in education within the context of open and e-learning, emphasizing flexibility, learner-centeredness, and various models of distance learning. It highlights the current state of internet and computer access in Nepal, the benefits of ICT in enhancing learning outcomes, and the importance of digital literacy and safety. The document also outlines the roles of ICT in teaching, academic research, and administrative support, along with necessary skills and strategies for effective ICT utilization.