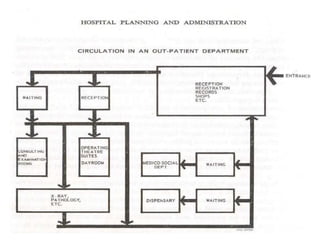
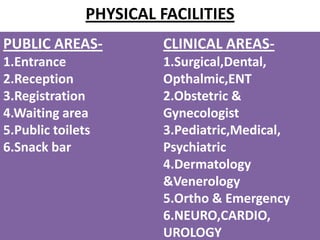
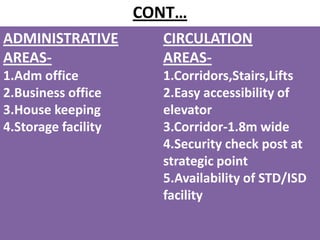
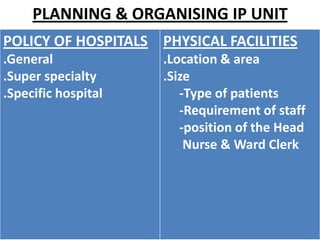
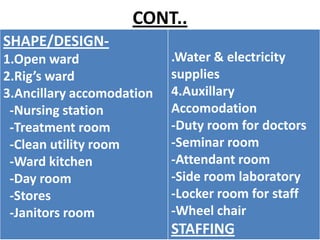
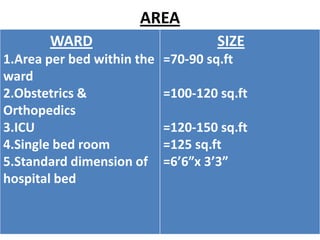
This document discusses outpatient (OPD) and inpatient (IPD) departments in hospitals. It provides background on the origins of OPDs, noting they emerged from dispensaries in the 17th century. It describes key aspects of OPDs like providing ambulatory care to non-admitted patients, acting as the first point of contact, and including functions like screening and follow-up. IPDs require patients to be admitted for close monitoring during and after procedures. The document outlines factors to consider in planning OPD and IPD departments, like physical facilities, staffing, and clinical/service facilities. It emphasizes the importance of integrating OPD and IPD physically, functionally and clinically.