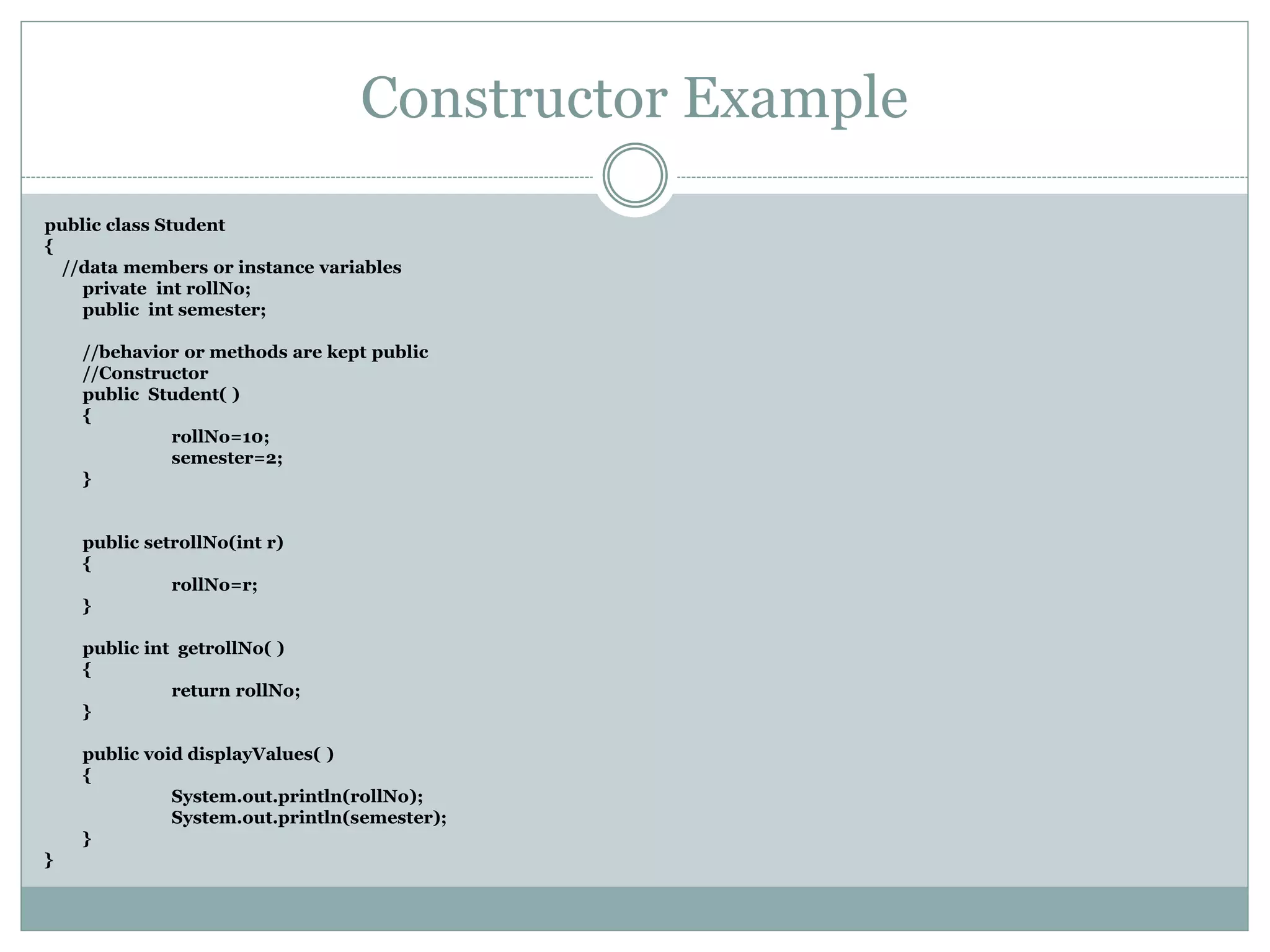
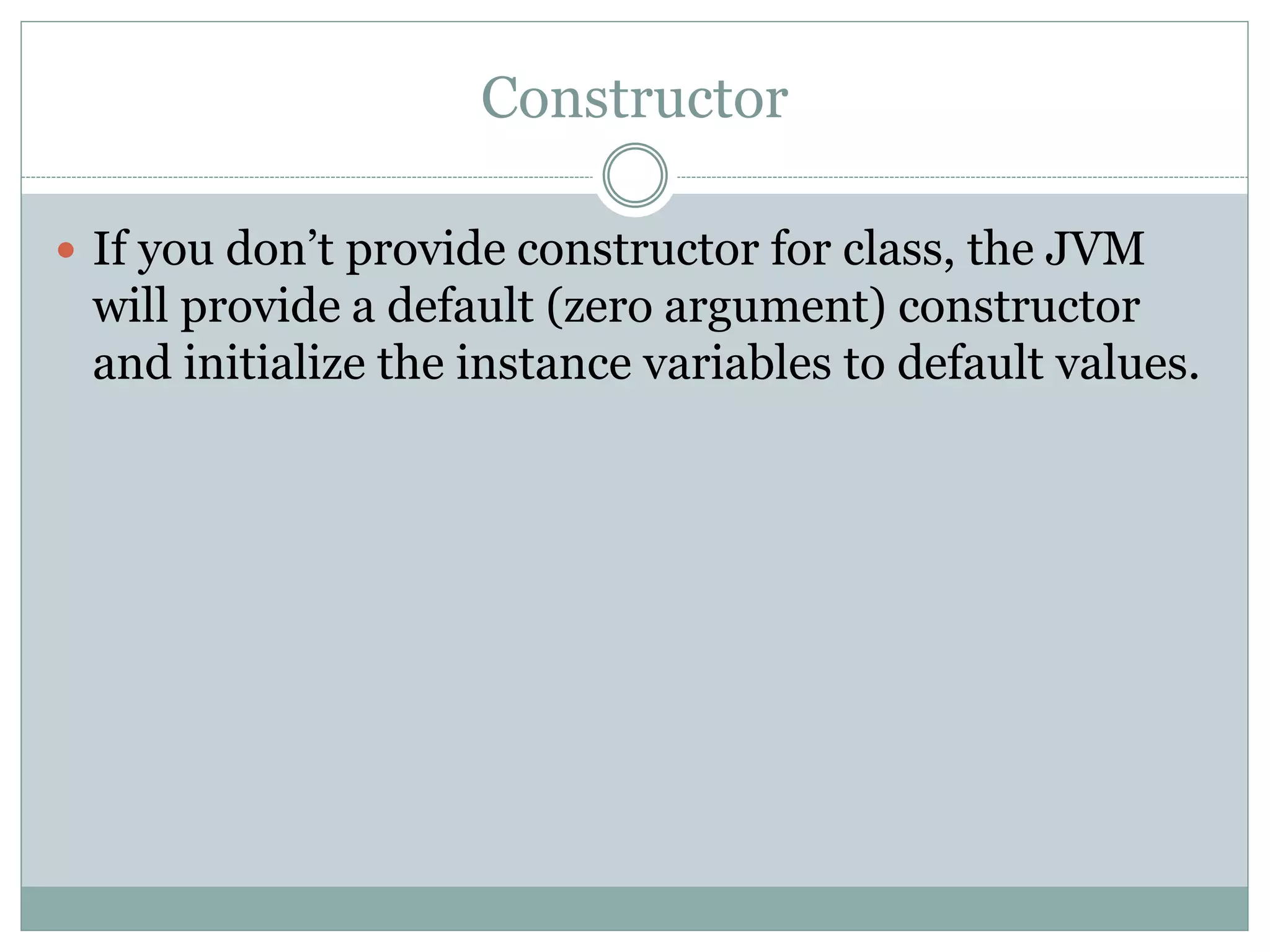
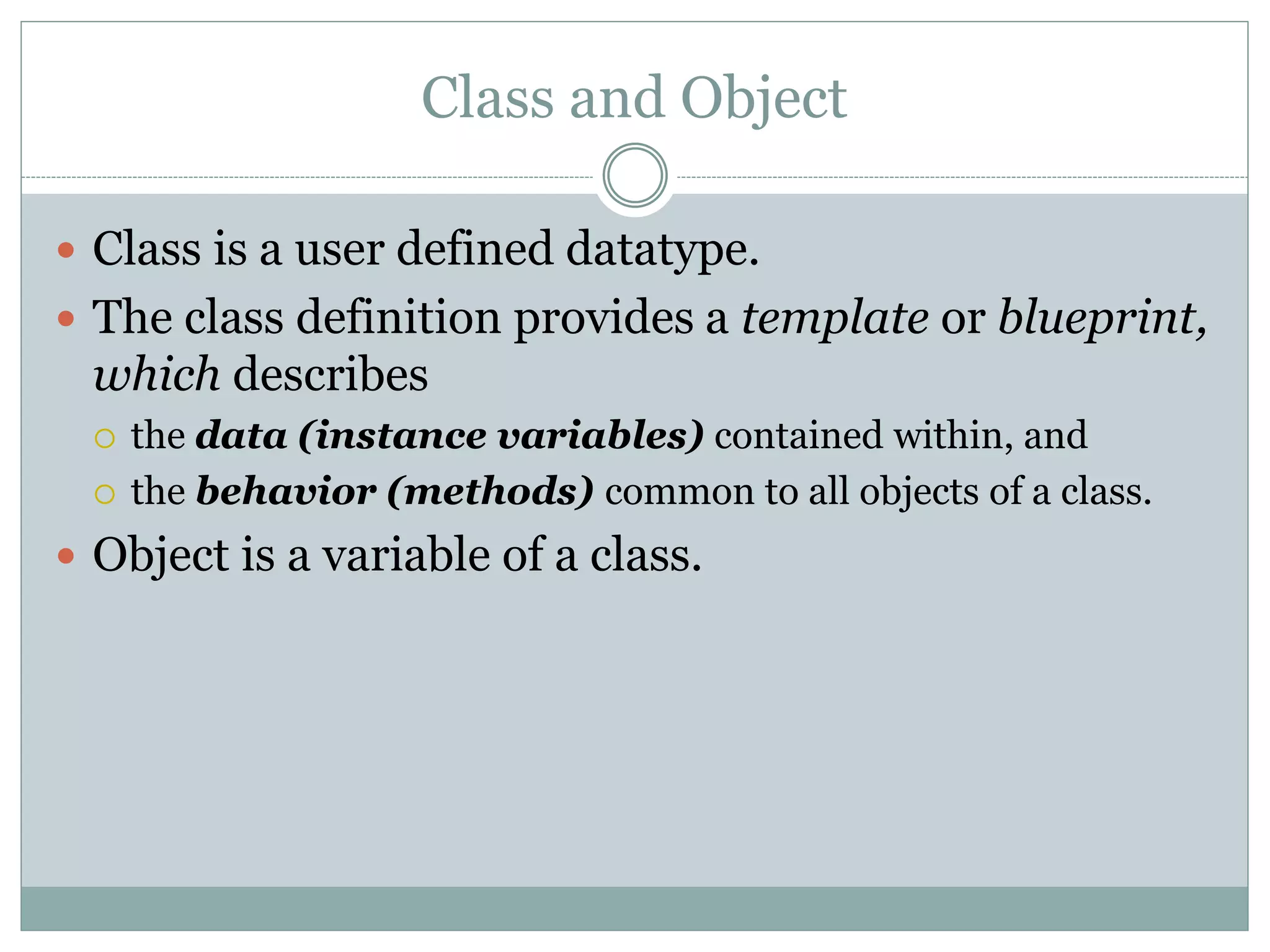
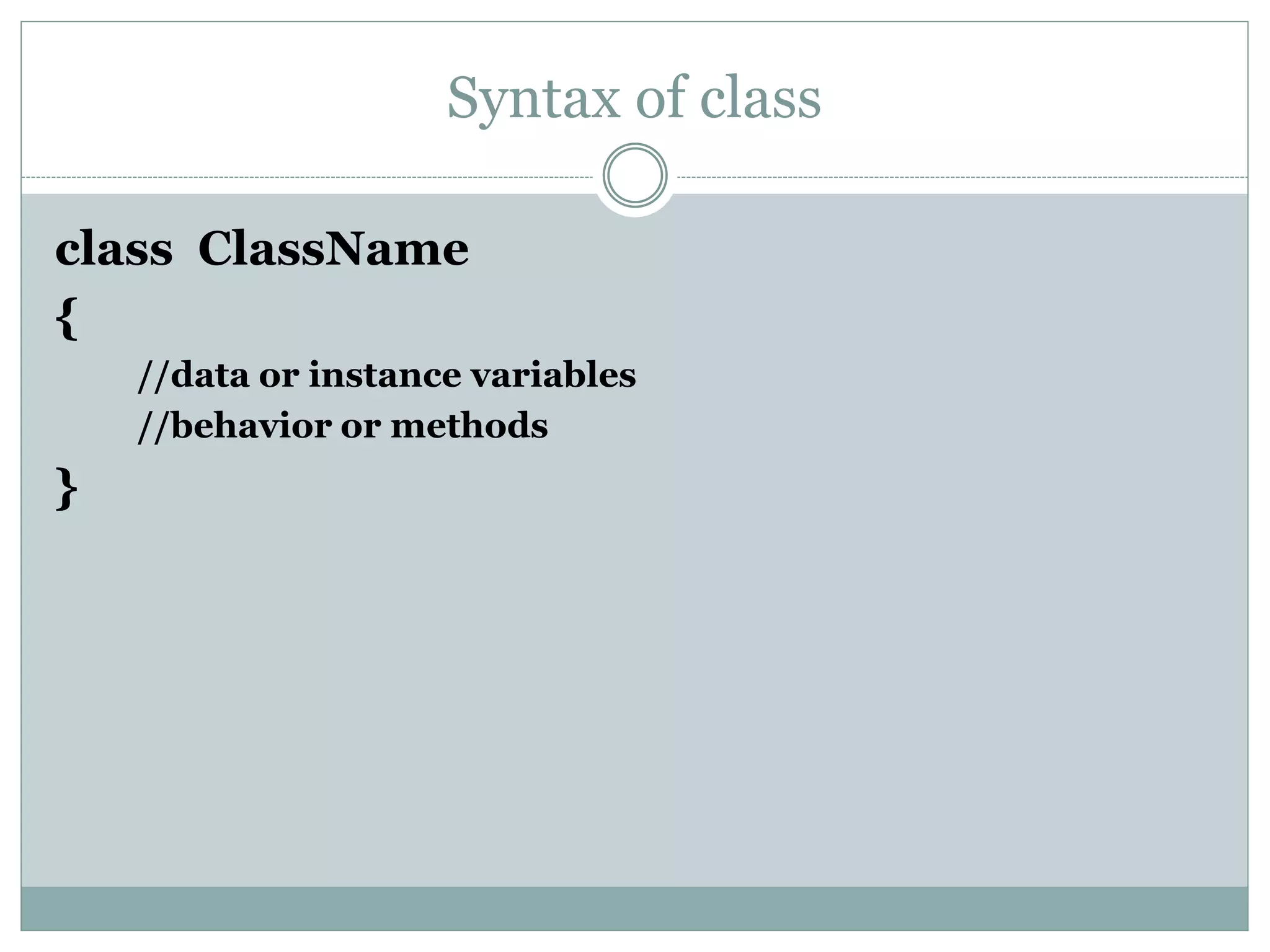
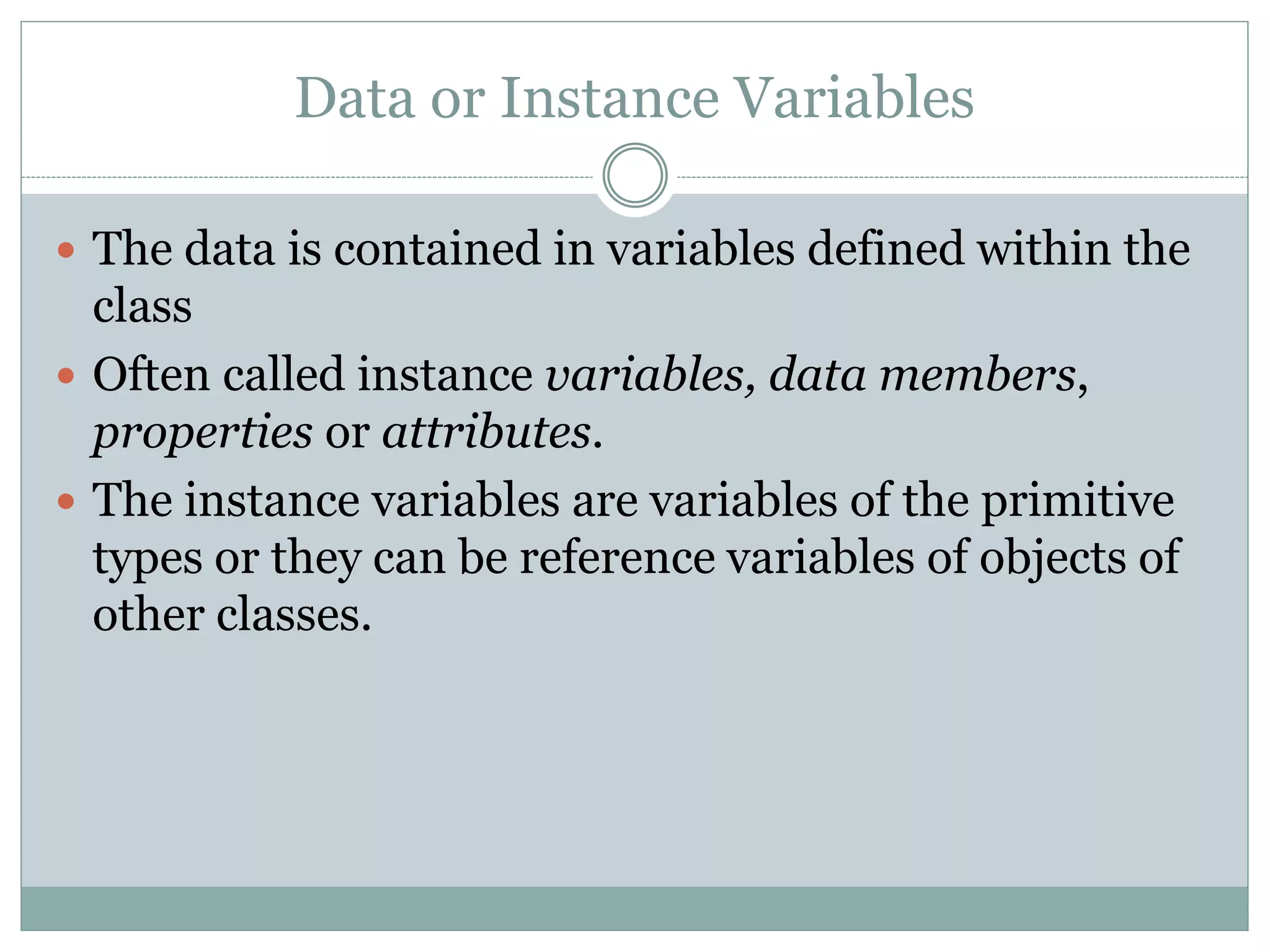
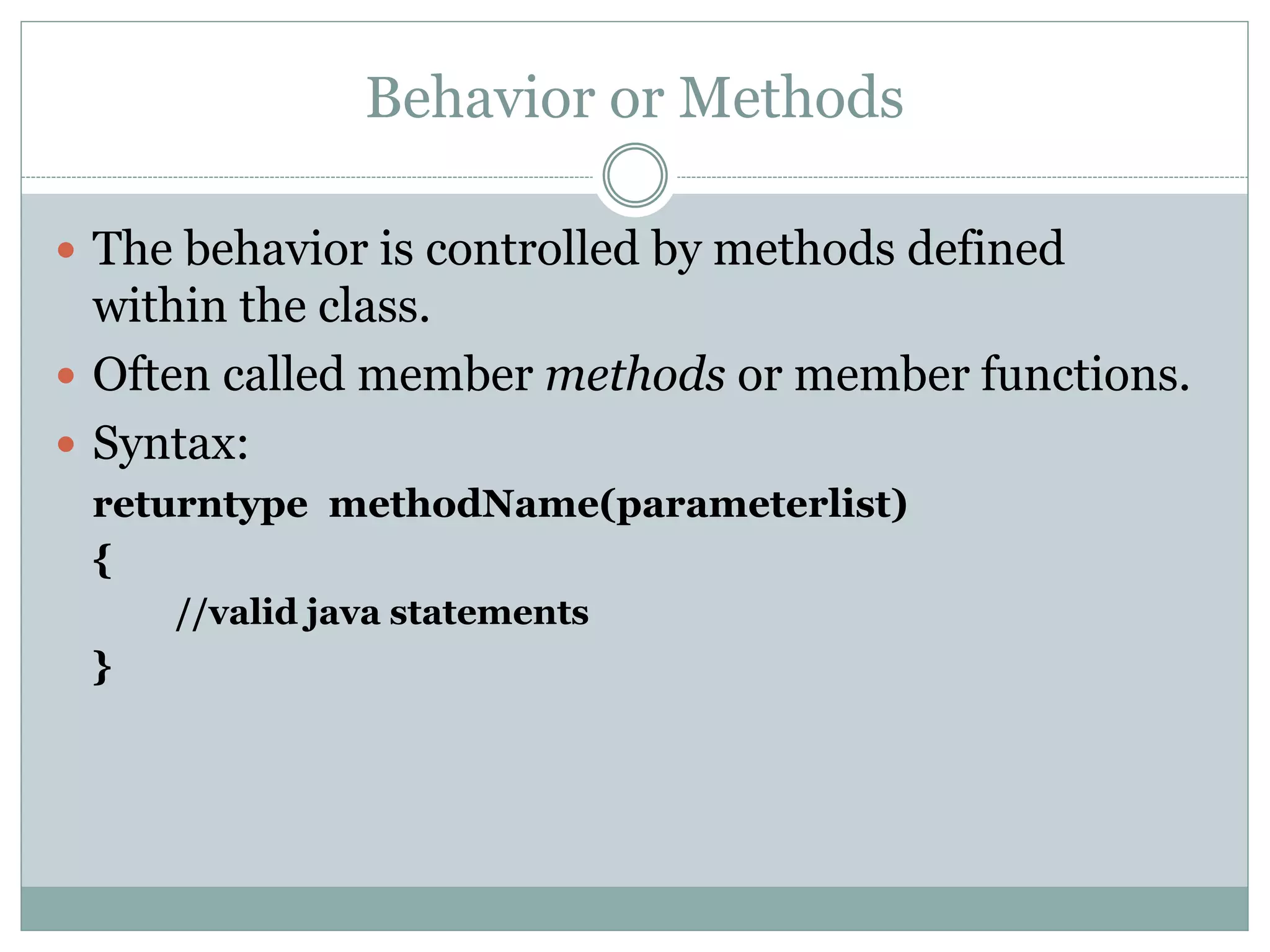
This document discusses key concepts of object-oriented programming including classes, objects, instance variables, methods, constructors, access specifiers, and more. A class defines the data and behavior of objects through instance variables and methods. An object is an instance of a class that allocates memory and can access class members. Constructors initialize objects. Access specifiers determine object member accessibility. Examples demonstrate how to declare classes, objects, and access members to understand OOP concepts.

![Example
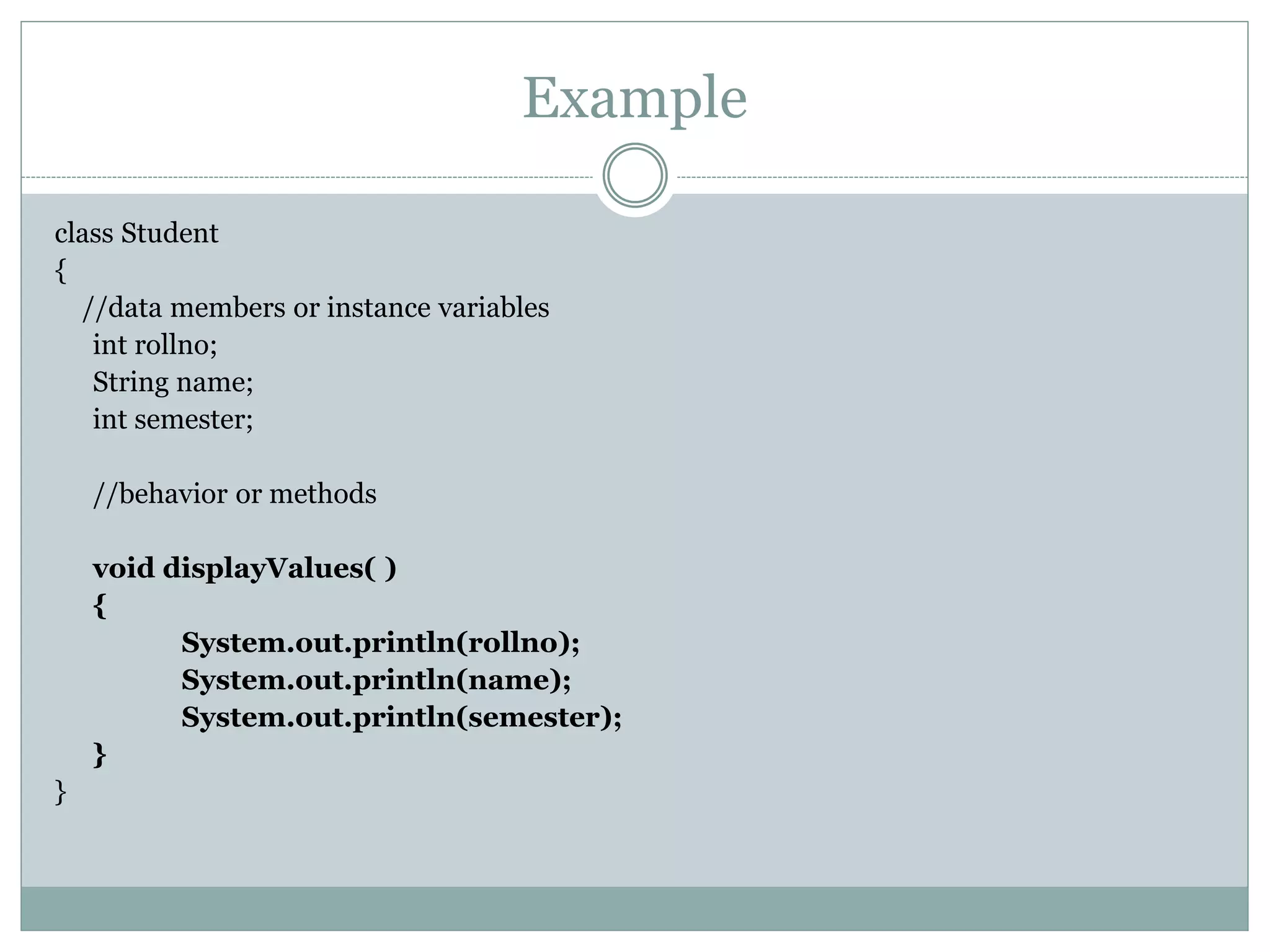
class Student
{
//data members or instance variables
int rollno;
String name;
int semester;
int[] marks;
//behavior or methods
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oop-140610124409-phpapp01/75/OOP-concepts-5-2048.jpg)

![Example
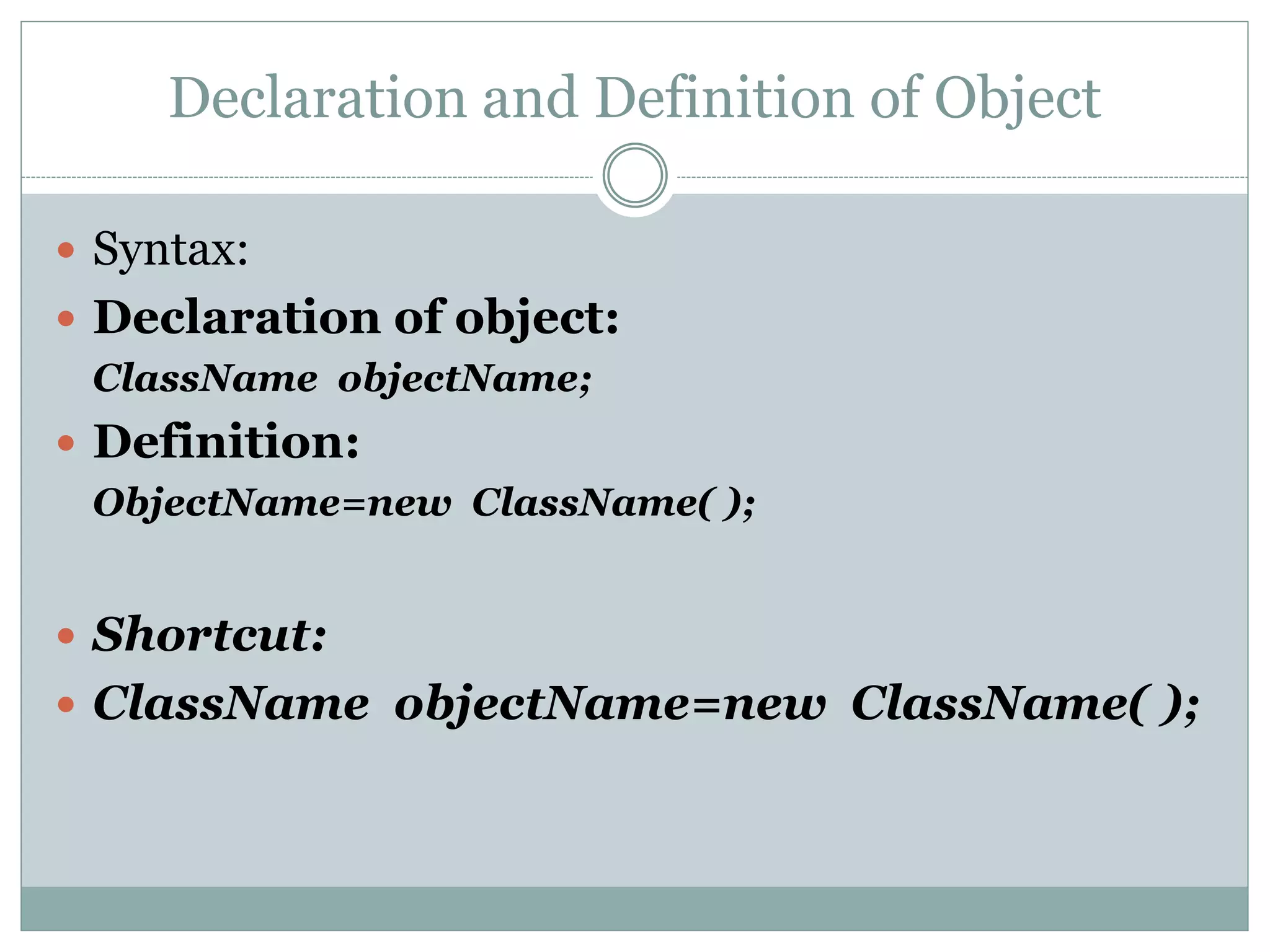
Objects are created in the main method or any other
class.
public class StudentDriver
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Student s;
s=new Student( );
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oop-140610124409-phpapp01/75/OOP-concepts-10-2048.jpg)
![Example Continued..
public class StudentDriver
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Student s;
s=new Student( );
s.semester=2;
s.rollNo=123; //Not Allowed as its private
s.displayValues( );
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oop-140610124409-phpapp01/75/OOP-concepts-14-2048.jpg)


![Example cont..
public class StudentDriver
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Student s;
s=new Student( );
s.semester=2;
System.out.println(s.semester);
s.setrollNo(123);
System.out.println(s.getrollNo( ));
int r;
r=s.getrollNo();
System.out.println(r);
s.displayValues( );
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/oop-140610124409-phpapp01/75/OOP-concepts-17-2048.jpg)