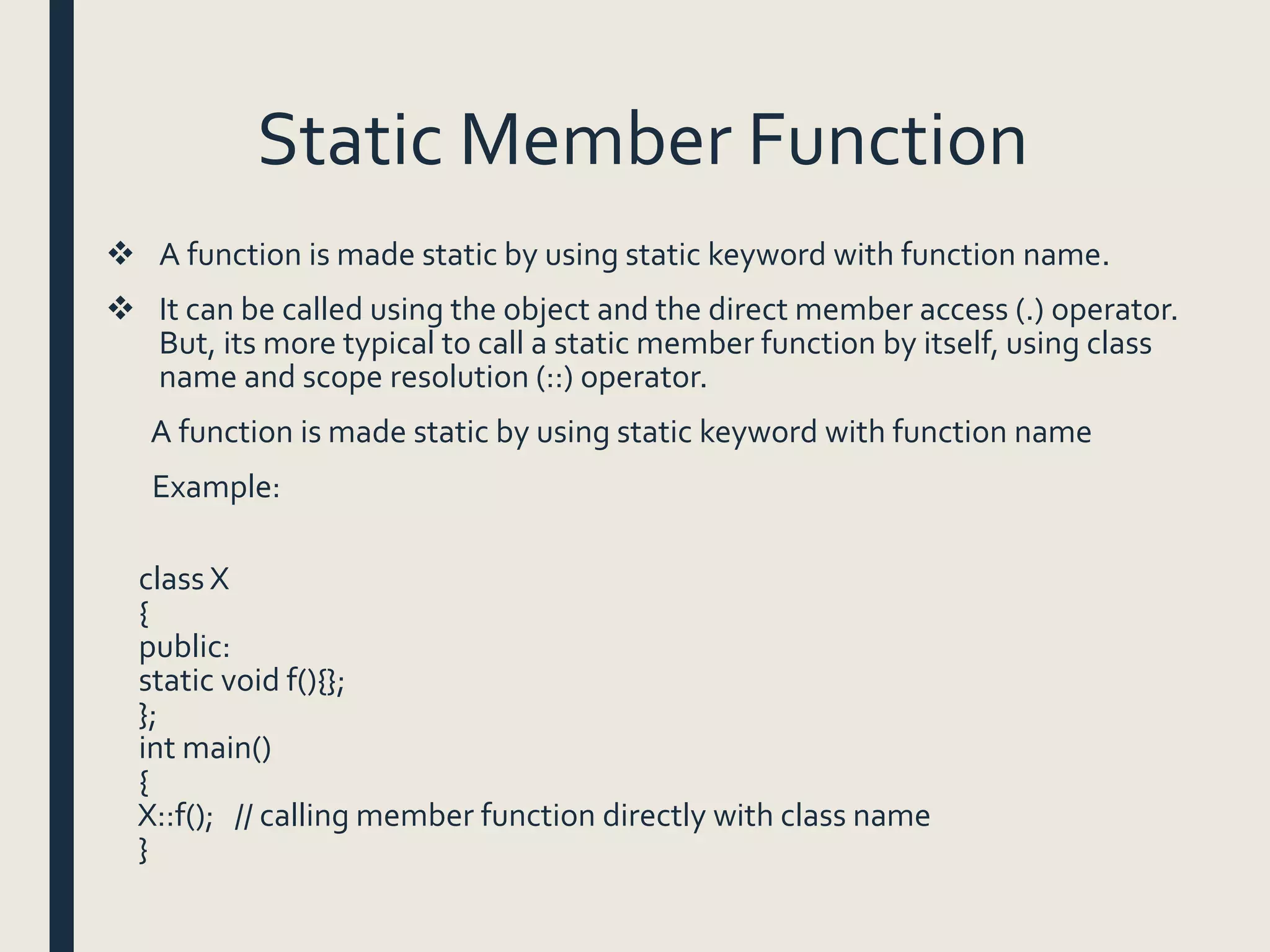
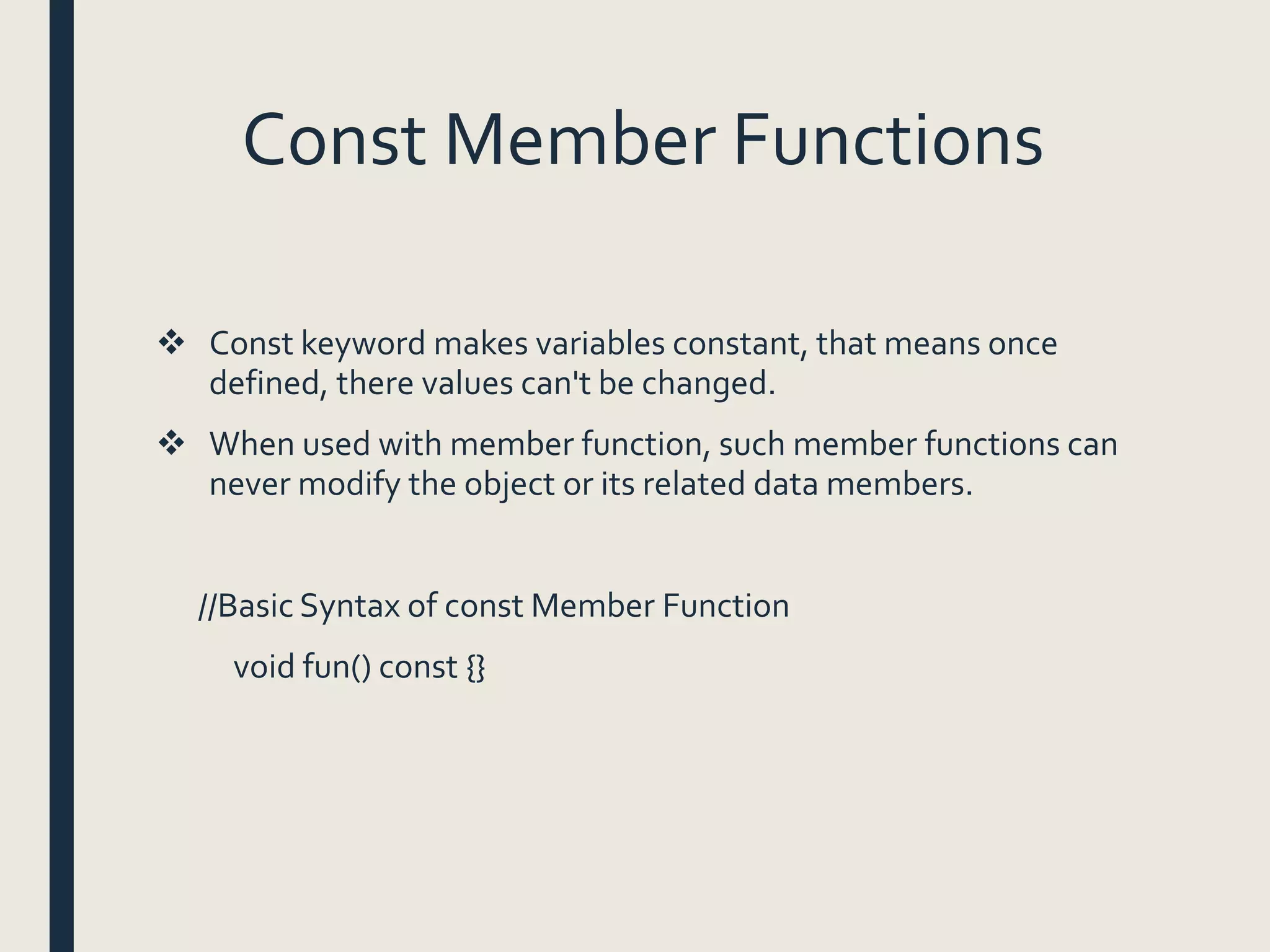
This document discusses data members and member functions in object-oriented programming. It defines data members as variables declared inside a class and member functions as functions declared inside a class. It covers accessing public, private, and protected data members, defining member functions inside and outside the class, and different types of member functions like static, const, inline, and friend functions. The document provides examples and explanations for each concept to help explain how data members and member functions work in object-oriented programming.







![InsideThe Class Definition
A member function of a class can be defined inside the class. However,
when a member function is defined inside the class, the class name and
the scope resolution operator are not specified in the function header.
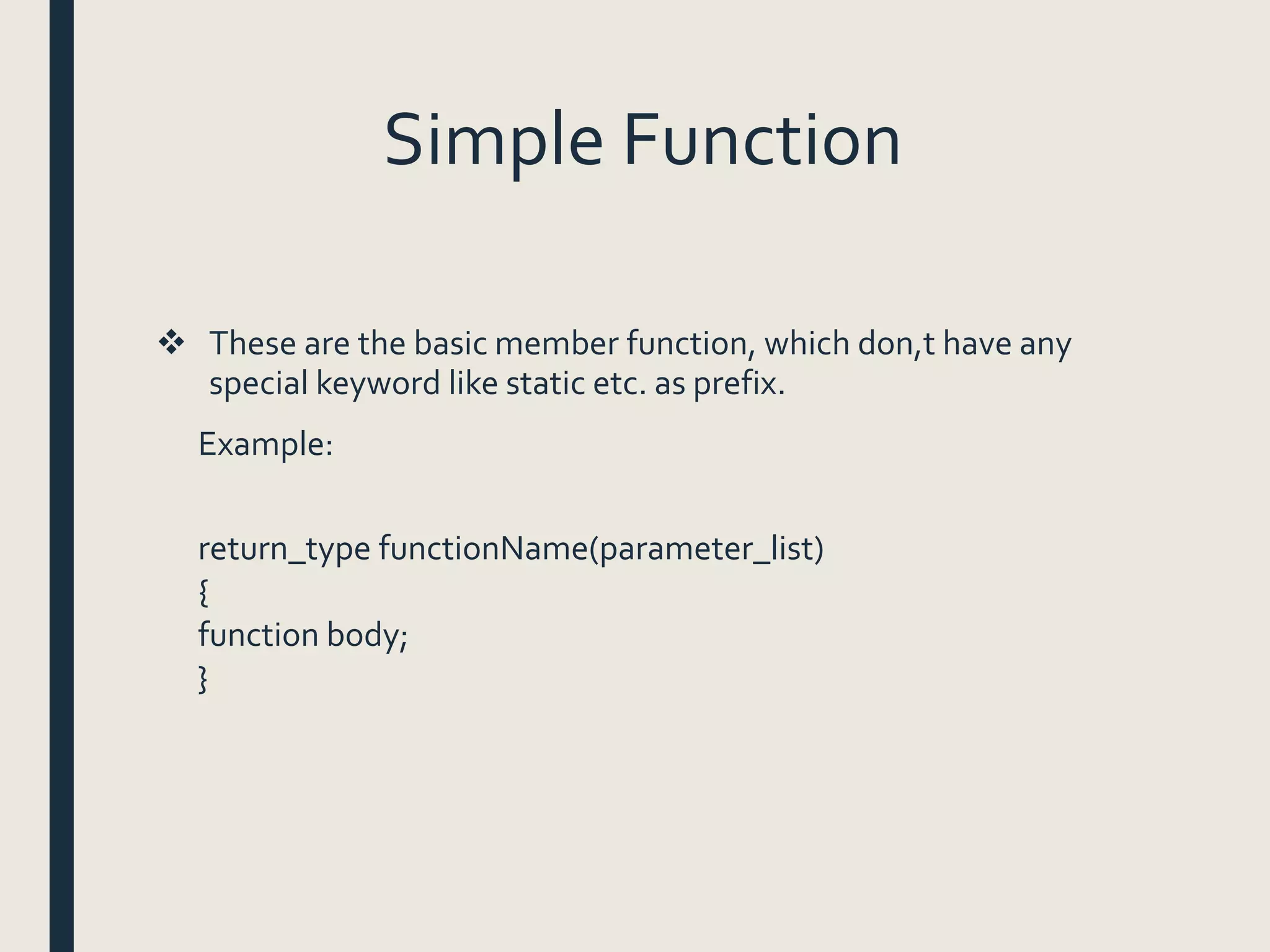
Example :
class book
{
char title[30];
float price;
public:
void getdata(char [],float); II declaration
void putdata()//definition inside the class
{
cout<<"nTitle of Book: "<<title;
cout<<"nPrice of Book: "<<price;
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datamembersandmemberfunctions-161109175340/75/Data-members-and-member-functions-10-2048.jpg)
![OutsideThe Class Definition
Defining a member function outside a class requires the function declaration to be
provided inside the class definition.
Example:
Class book
{
// body of the class
} :
void book :: getdata(char a[],float b)
{
// defining member function outside the class
Strcpy(title,a):
price = b:
}
void book :: putdata ()
{
cout<<"nTitle of Book: "<<title;
cout<<"nPrice of Book: "<<price;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datamembersandmemberfunctions-161109175340/75/Data-members-and-member-functions-11-2048.jpg)



![References
■ Books
[1]. By E Balagurusamy “Object Oriented ProgrammingWith C++” ,TATA McGraw-
Hill Publishing Company Limited, 2008
■ Web Links
[2]. https://www3.ntu.edu.sg/home/ehchua/programming/cpp/cp3_OOP.html
---OOP Basics
[3]. http://www.studytonight.com/cpp/accessing-data-
members.php
---Accessing Data Members
[4]. http://www.studytonight.com/cpp/member-functions-cpp.php
---Member Functions
[5]. http://www.studytonight.com/cpp/types-of-member-function.php
---Types of Member Function](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datamembersandmemberfunctions-161109175340/75/Data-members-and-member-functions-19-2048.jpg)
