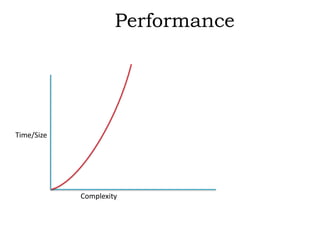
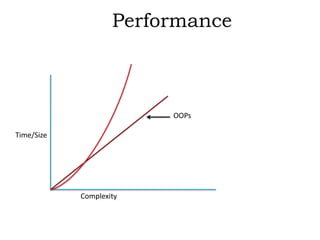
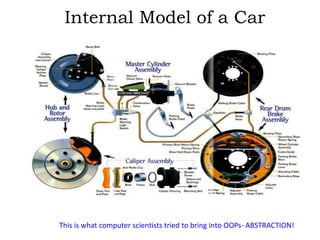
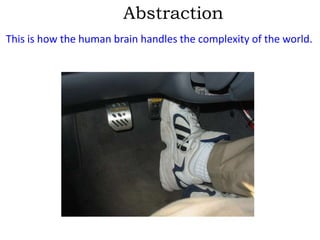
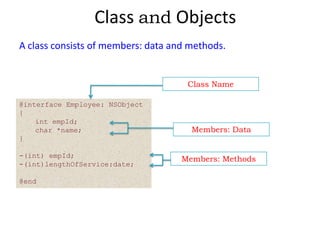
This document discusses object-oriented programming (OOPs) principles and how they are implemented in Objective-C. It explains that OOPs aims to emulate the human brain through abstraction, encapsulation, and other principles. It provides examples of key OOPs concepts in Objective-C like classes and objects, inheritance where subclasses inherit from superclasses, encapsulation which hides complexity, and polymorphism which allows one interface to work for multiple classes through dynamic binding and message passing. The document demonstrates how these OOPs features are exhibited in Objective-C code.











![Objects
id date=[ [ Date alloc ] init ]; New Date object allocated
[ date release];
Releasing the variable](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tiyasioops-120216064549-phpapp01/85/OOPS-features-using-Objective-C-20-320.jpg)
![Inheritance
Superclass Rectangle.m
#import “Rectangle.h”
Superclass Rectangle.h
@implementation Rectangle
@interface Rectangle: NSObject
{ -(id) init
int length; {
int width; if(self=[super init])
} {
length = 8;
-(int) area; width = 5;
}
@end return self;
}
-(int) area
{
int area1=length * width;
}
@end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tiyasioops-120216064549-phpapp01/85/OOPS-features-using-Objective-C-21-320.jpg)
![Inheritance
Subclass printAreaOfRectangle.h
#import “Rectangle.h”
@interface printAreaOfRectangle: Rectangle
-(void) printVal;
@end
Subclass printAreaOfRectangle.m
#import “printAreaOfRectangle.h”
@implementation printAreaOfRectangle
(void) printVal
{
NSLog(@”Area = %d”,[self area]);
}
@end](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tiyasioops-120216064549-phpapp01/85/OOPS-features-using-Objective-C-22-320.jpg)

![Polymorphism
main
{
Window *W = [[Window alloc] init];
View *V = [[view alloc] init];
[W flush];
[V flush];
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tiyasioops-120216064549-phpapp01/85/OOPS-features-using-Objective-C-24-320.jpg)
![Dynamic binding + Message Passing
main
{
Window *W = [[Window alloc] init];
View *V = [[view alloc] init];
[W flush];
[V flush];
id anotherObj = W; Dynamic Binding
[anotherObj flush]; Message Passing
}
The flush message is passed to the variable anotherObj that is dynamically bound during runtime.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tiyasioops-120216064549-phpapp01/85/OOPS-features-using-Objective-C-25-320.jpg)

