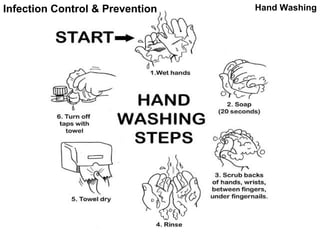
This document discusses infection transmission and control practices in healthcare settings. It describes the five main ways infections can be transmitted: contact, droplet, vehicle, airborne, and vectorborne. The four major infection control practices are then outlined as hand washing, protective barriers, care of equipment, and healthcare worker practices. Hand washing is emphasized as the most important practice, and the steps for proper hand washing technique are detailed. Other topics covered include protective barriers, sterilization and disinfection of equipment, and important terms in infection control.