1. Patient safety aims to prevent harm caused by errors and system failures in healthcare by applying safety science methods. Adverse events are common but preventable issues that cause unnecessary harm.
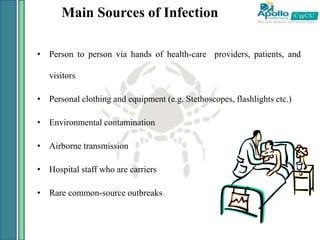
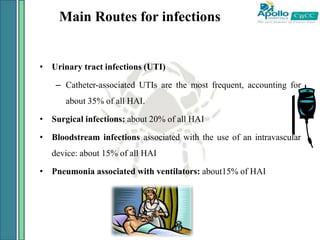
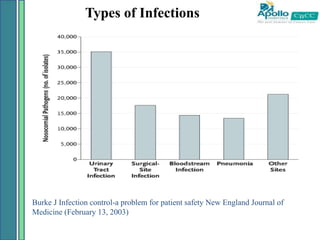
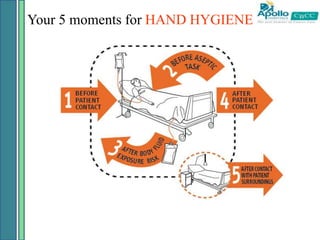
2. Healthcare-associated infections are a major global problem, affecting millions of patients annually. Following proper infection control procedures like hand hygiene and using personal protective equipment can help prevent transmission and reduce infection rates.
3. Nurses play a key role in infection prevention by maintaining clean clinical environments, properly washing hands, using protective barriers, and safely handling and disposing of medical sharps and wastes. Following recommended guidelines can help provide safe care and minimize infection risks for all patients.