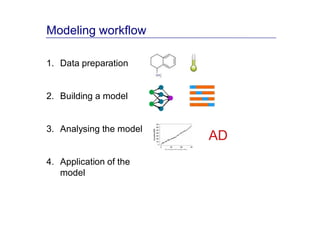
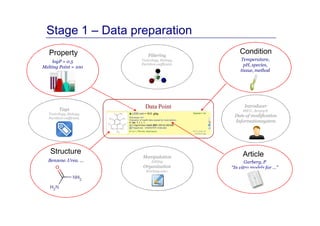
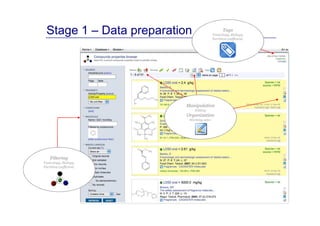
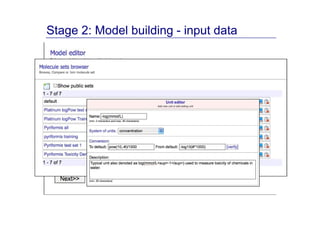
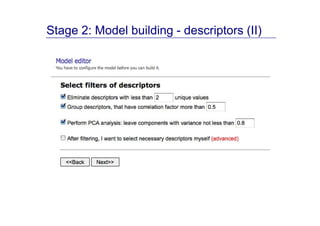
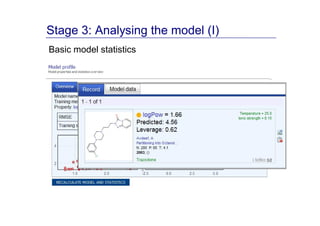
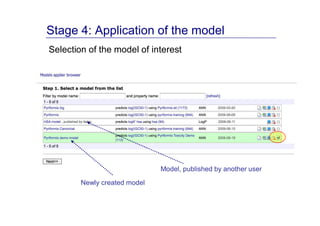
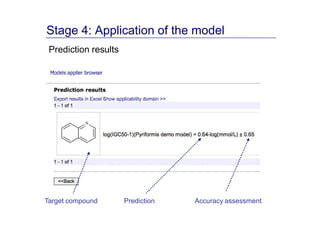
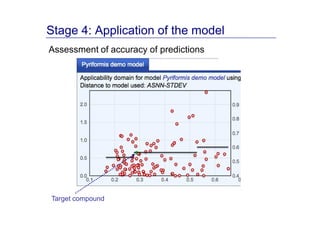
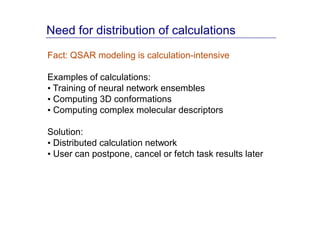
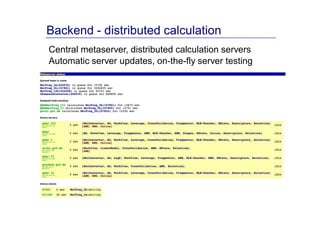
The document discusses an online chemical modeling environment developed by Iurii Sushko and Sergey Novotarskiy, which aims to enhance collaboration in quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) modeling. Unlike existing alternatives that are complex and not user-friendly for chemists, this platform emphasizes simplified modeling workflows and integrates collaboration-targeted features. It supports distributed calculations and automatic updates to enhance modeling accuracy and efficiency in analyzing physicochemical properties.