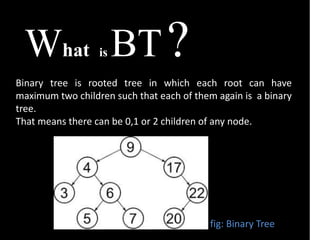
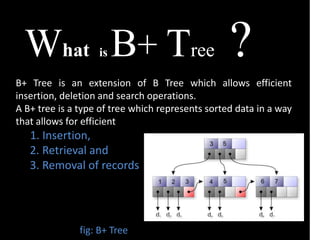
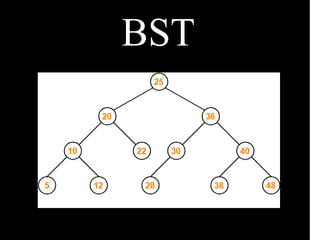
The document presents an overview of biometric systems, detailing their operations, stages, types, and performance measures. It also discusses the challenges faced by these systems, such as recognition performance, security, and privacy issues. Additionally, it covers clustering methods, indexing techniques, and data structures like binary trees and B+ trees used for efficient database management.







![Fuzzy C Means
Fuzzy C Means (FCM) is a feature clustering technique
wherein each feature point belongs to a cluster by some
degree that is specified by a membership grade [3]. These
kind of clustering algorithms are known as objective
function based clustering.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/indexingoflargebiometricdatabase-190517070813/85/Indexing-of-large-biometric-database-14-320.jpg)