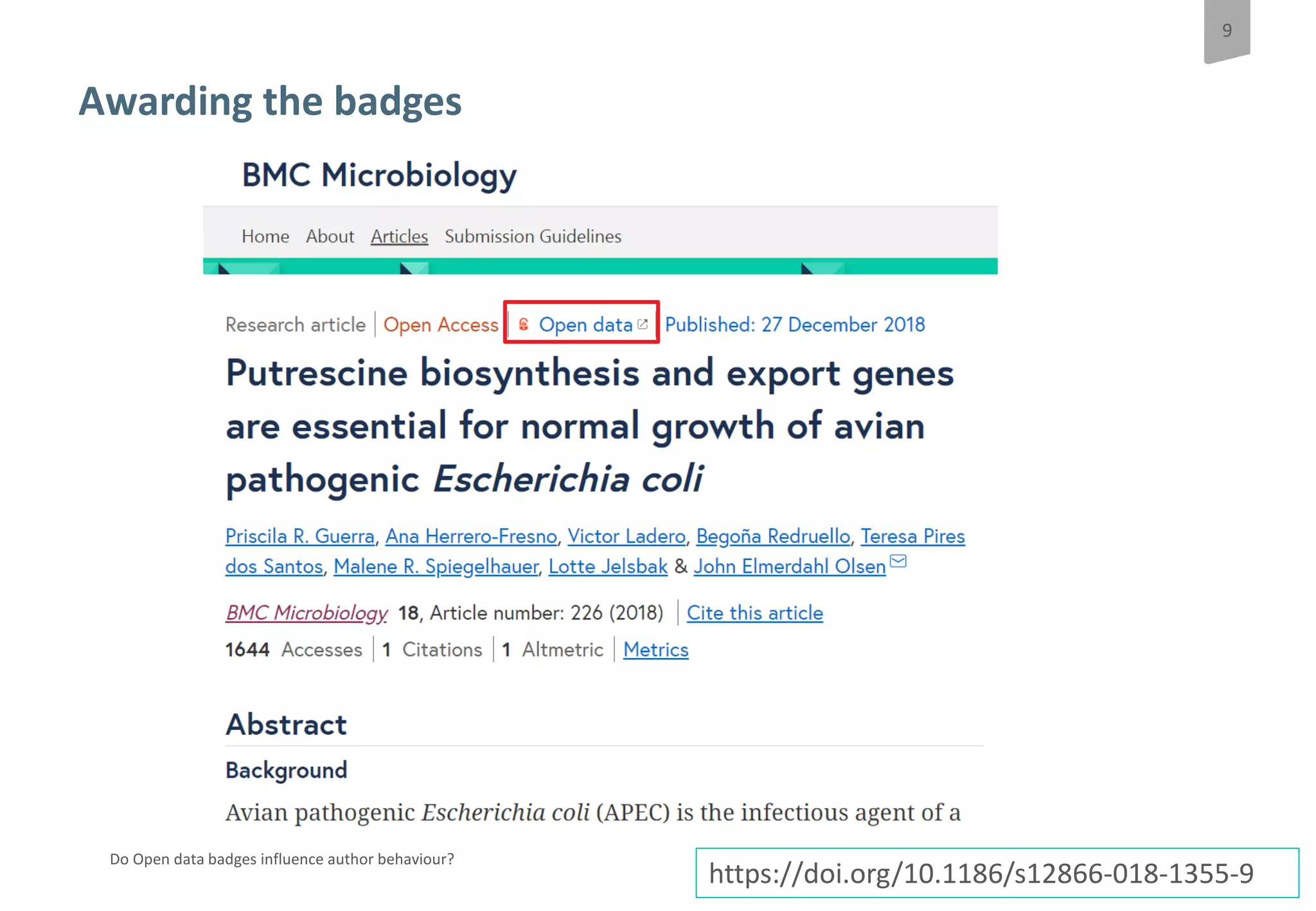
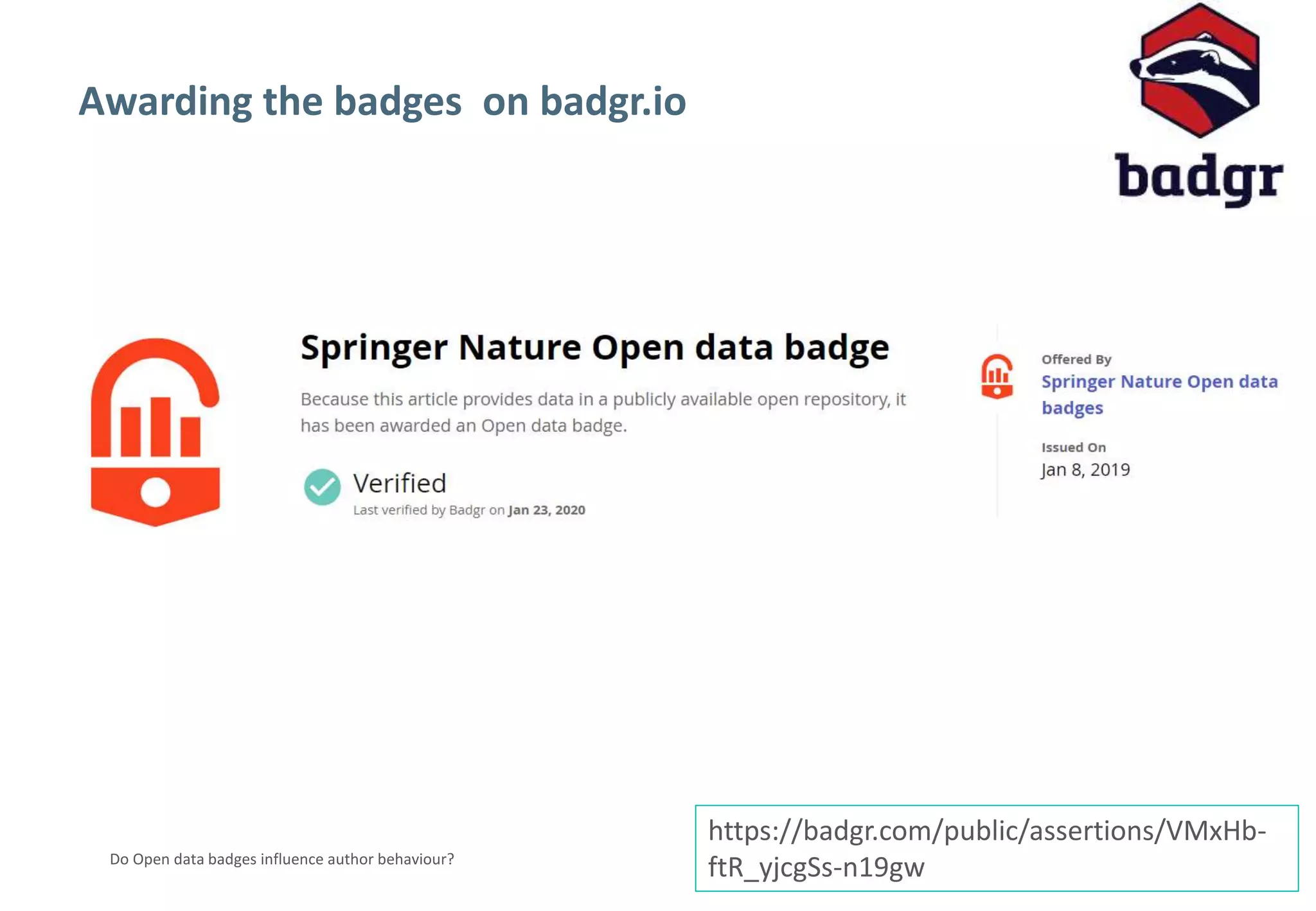
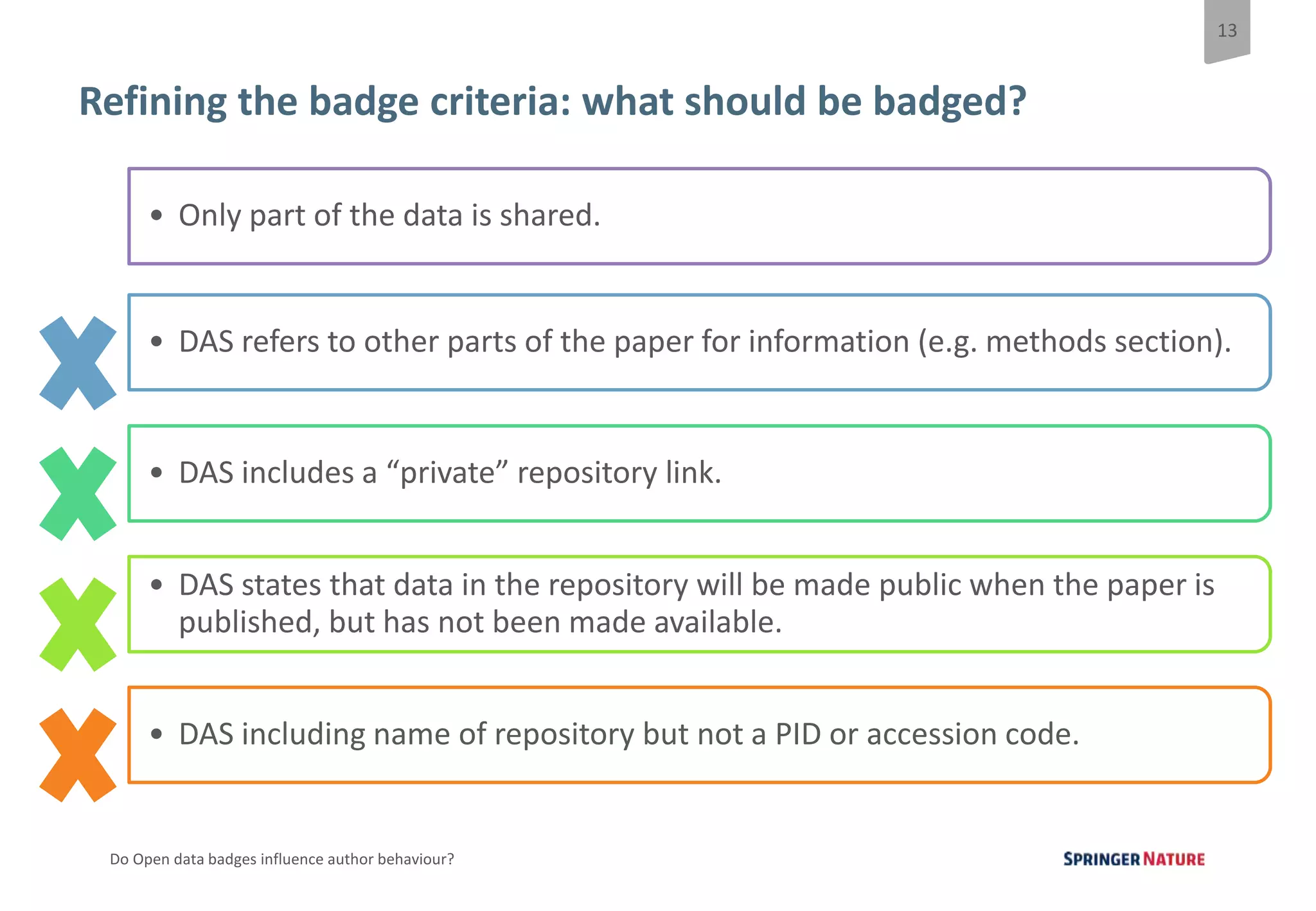
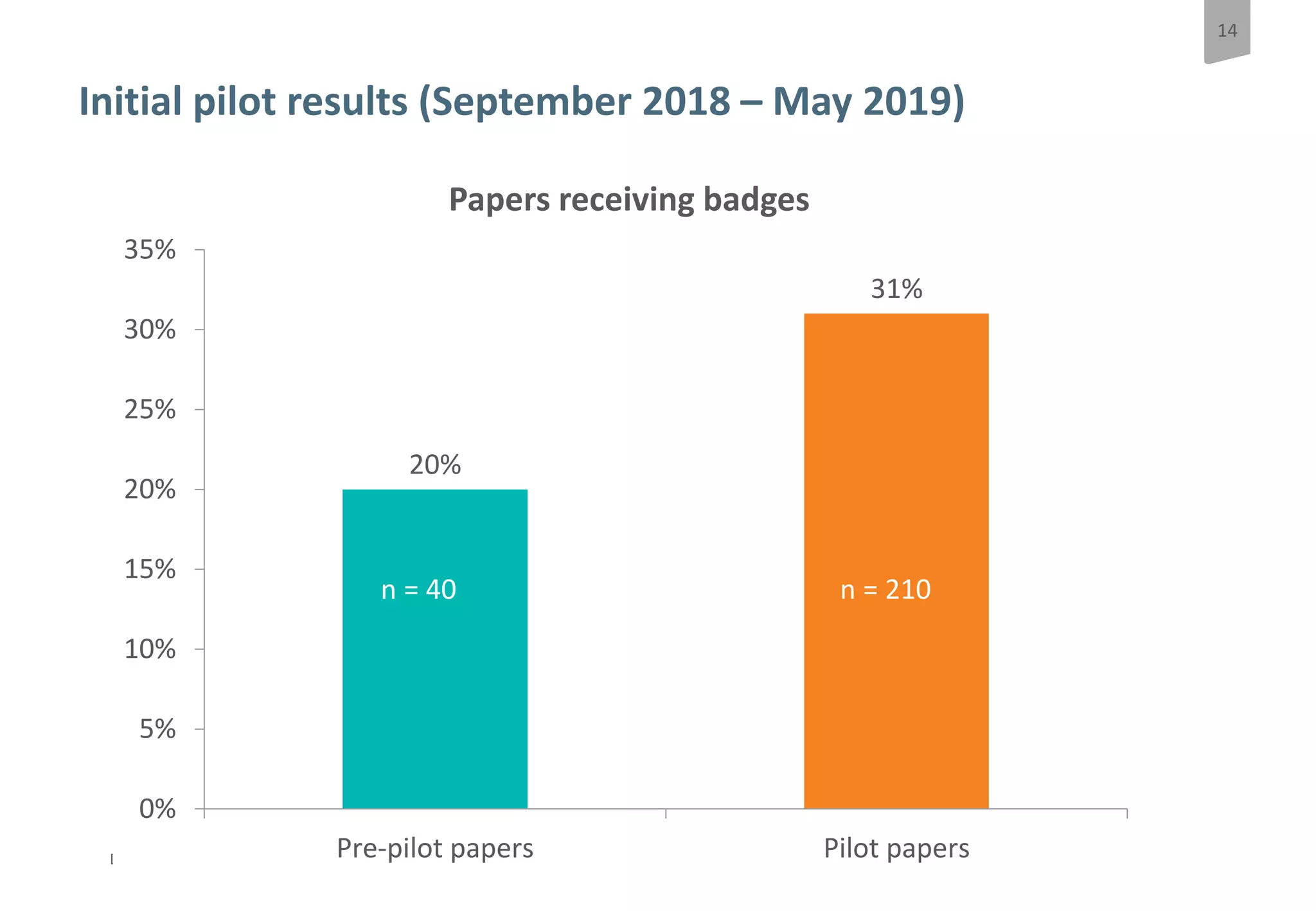
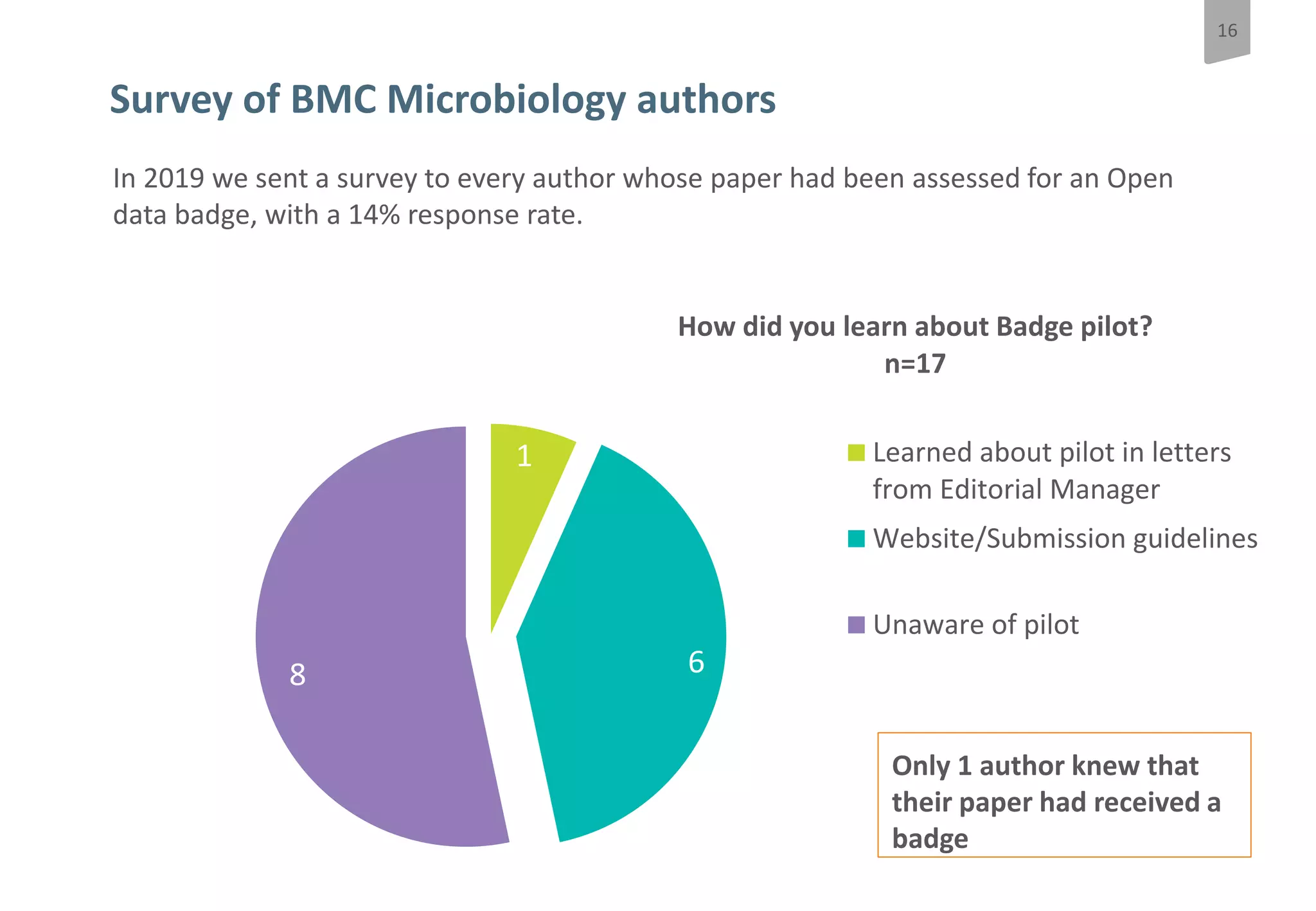
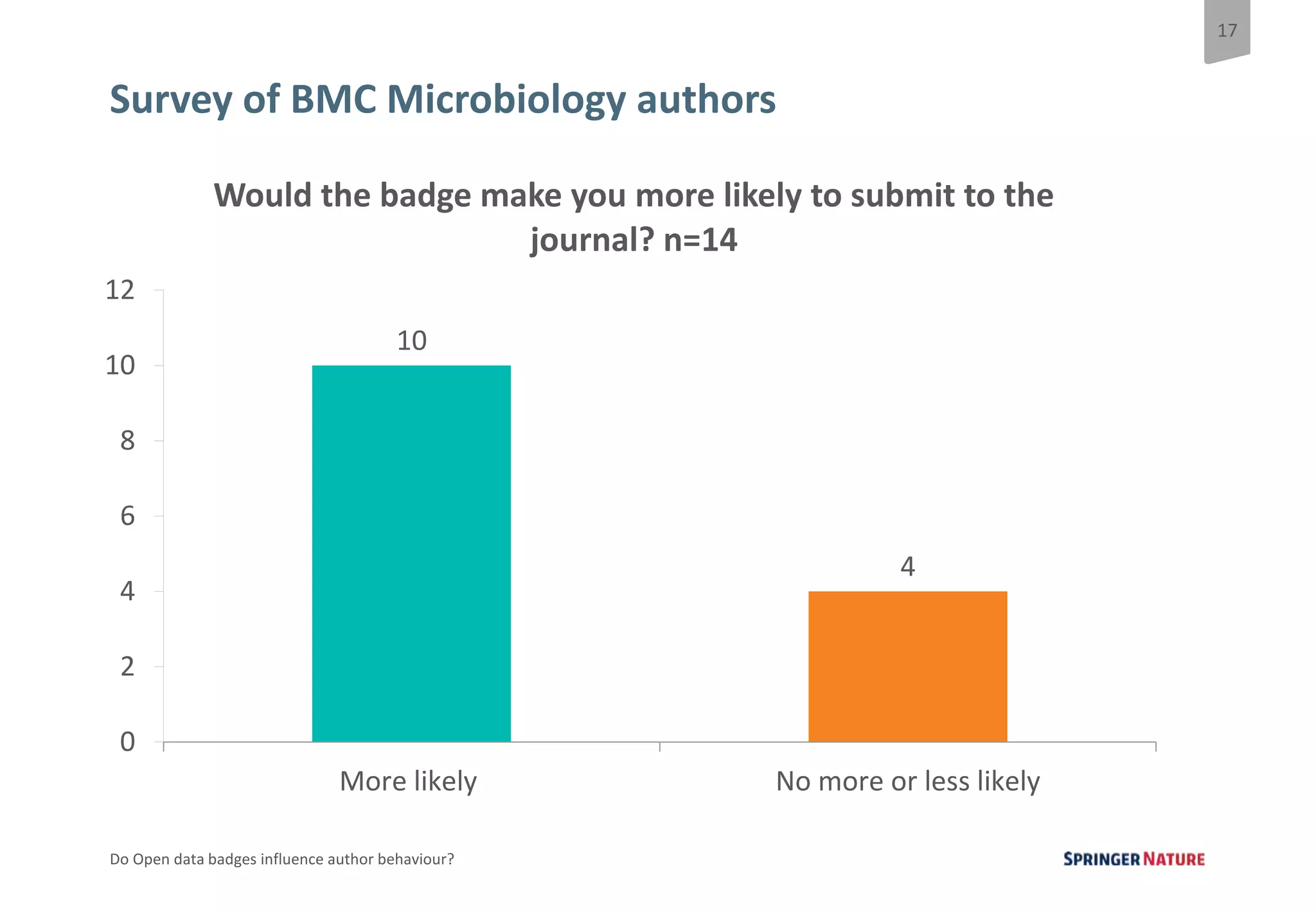
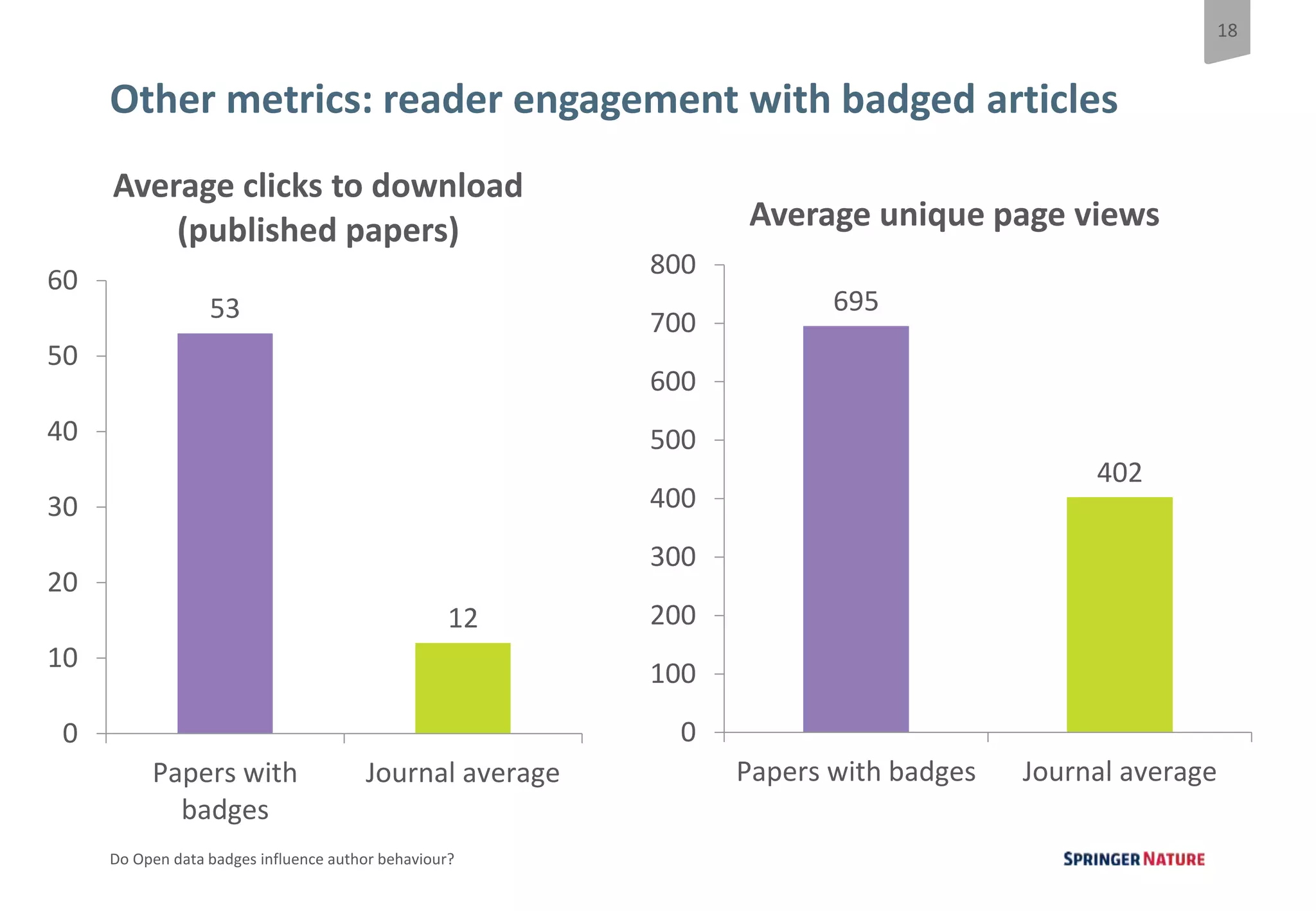
The document discusses a pilot study at Springer Nature to evaluate the impact of open data badges on author behavior, aimed at encouraging data sharing and increasing reader engagement. The initial findings indicate that data sharing increased significantly after the introduction of badges, although authors were often unaware of the pilot's existence and the potential effects on their behavior. Future steps include exploring automation of the badging process, expanding to more journals, and assessing different badging methodologies.