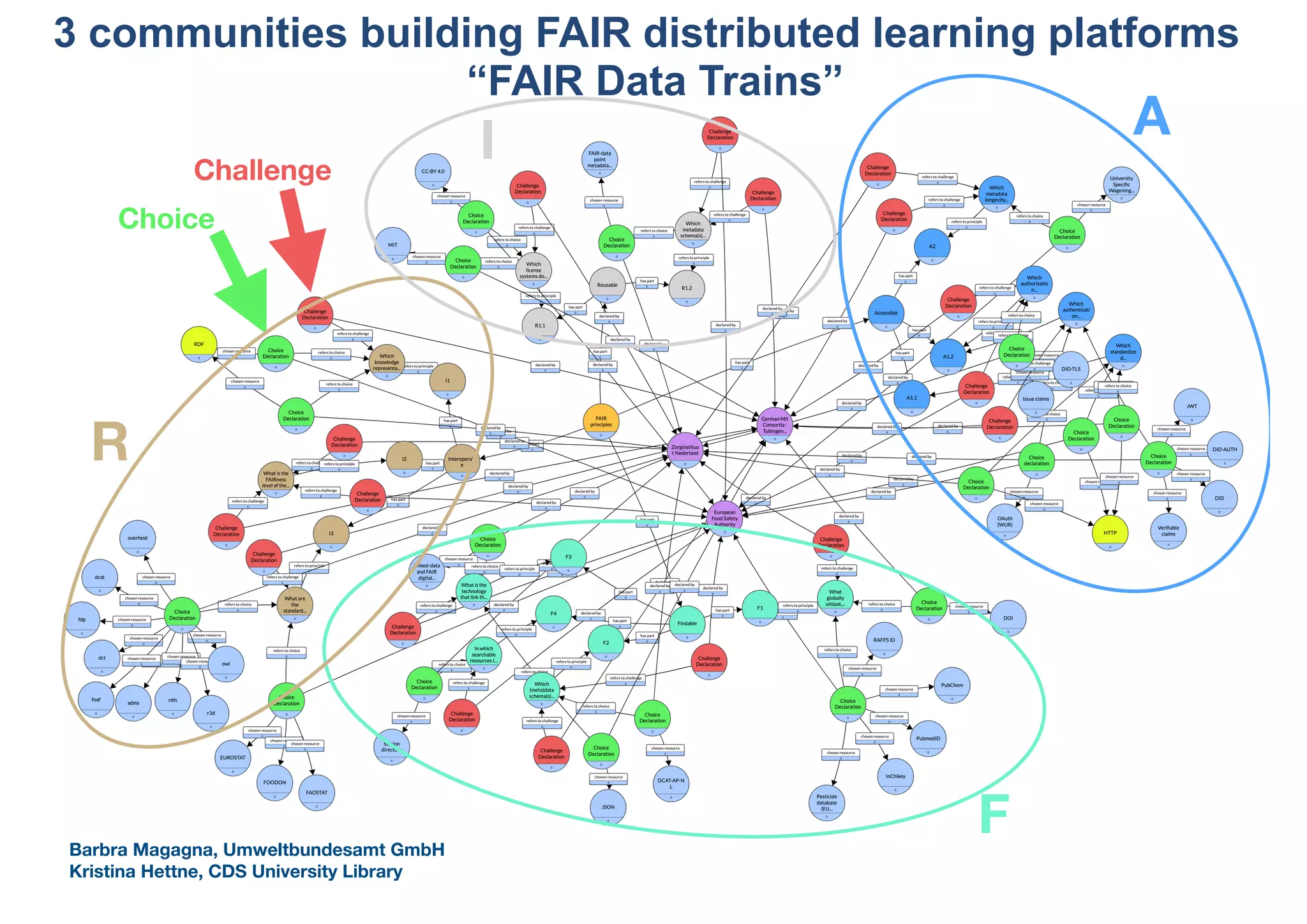
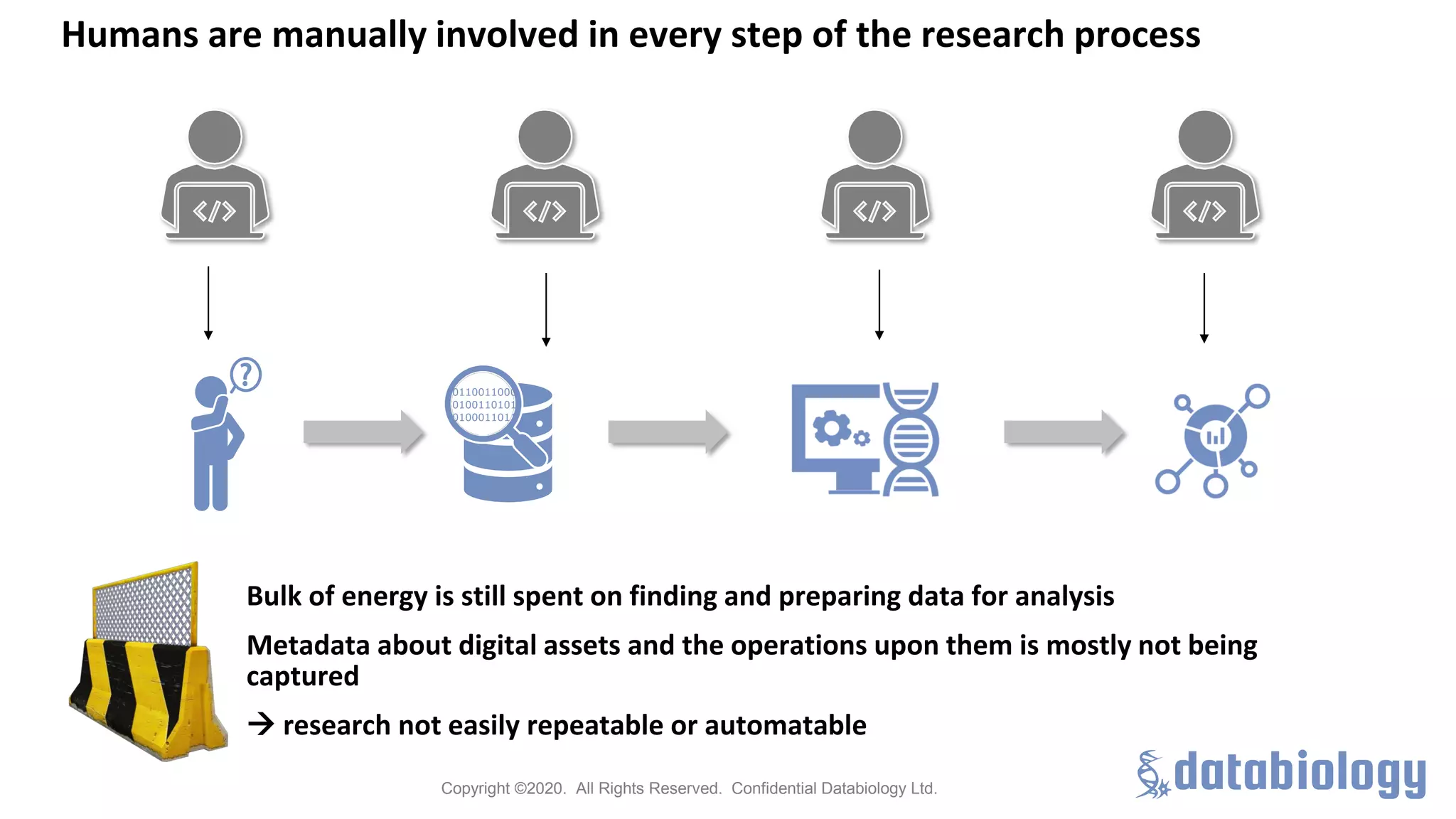
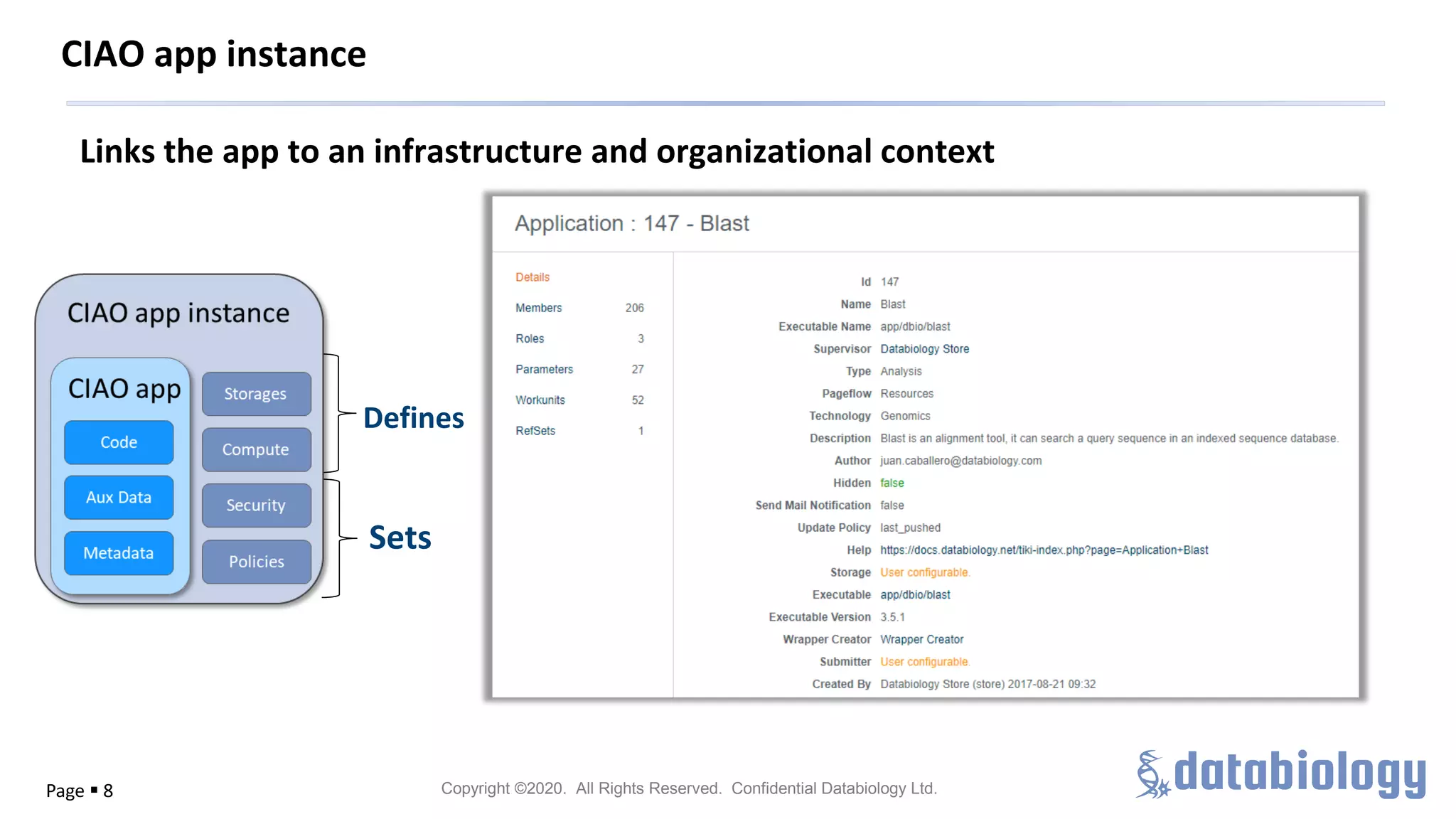
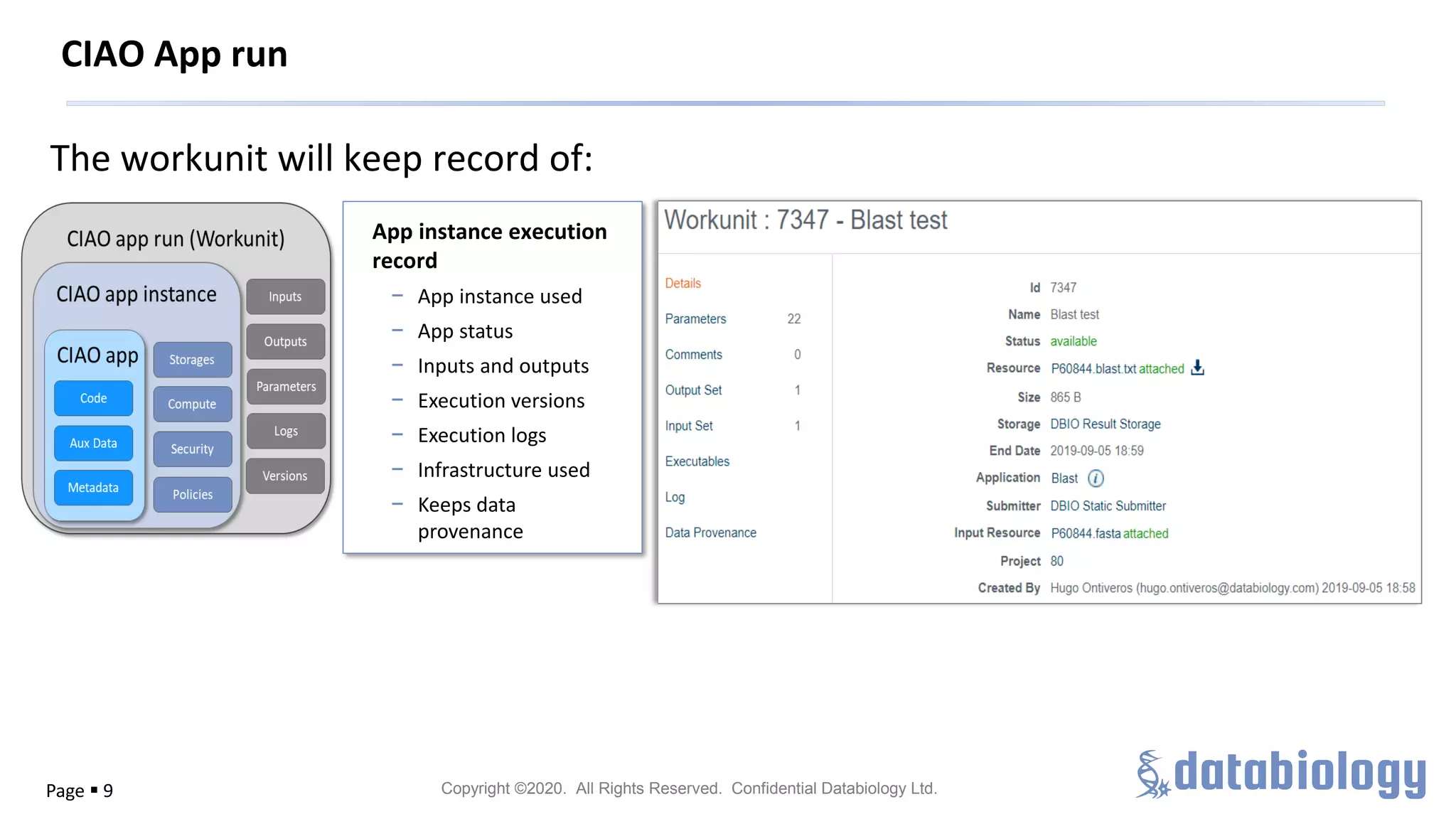
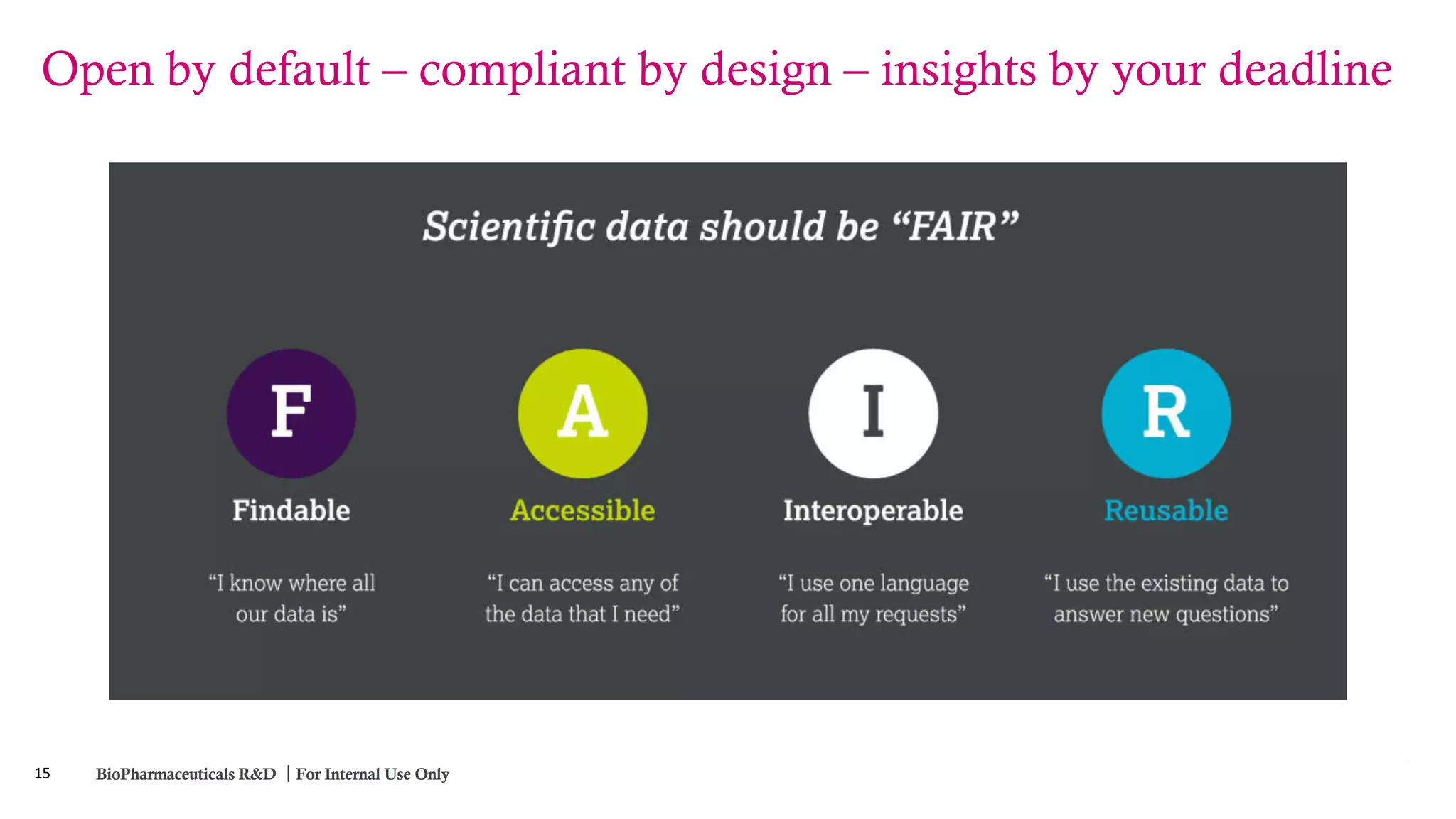
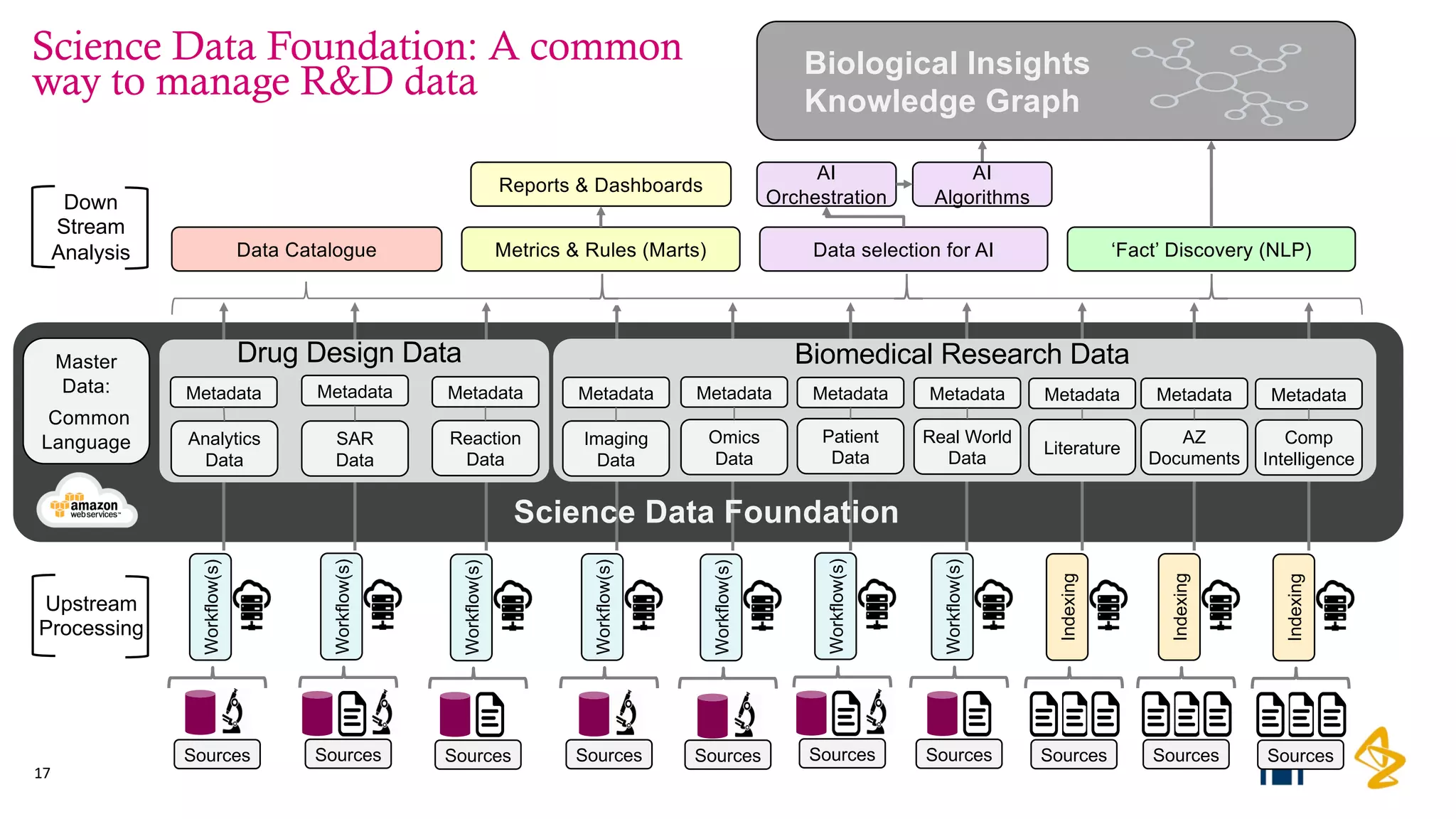
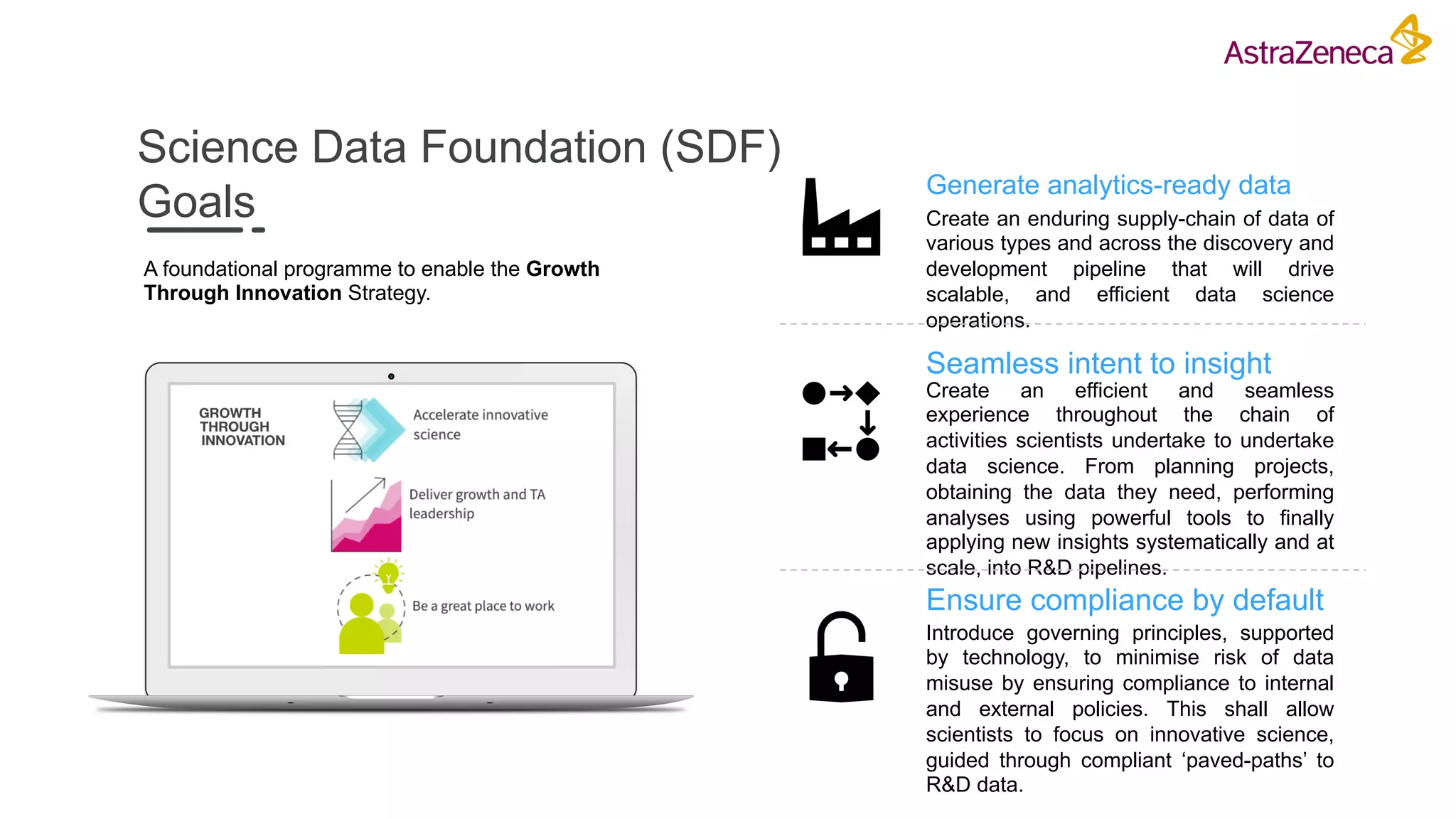
The Pistoia Alliance webinar held on May 14, 2020, focused on the FAIR principles (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reusable) as a means to enhance R&D processes in life sciences. Key speakers discussed the importance of implementing FAIR data practices to automate workflows, improve data collaboration, and leverage AI and data science for accelerated drug development. The overarching vision is to create a 'Science Data Foundation' to facilitate compliant and efficient access to diverse data types across research and development.































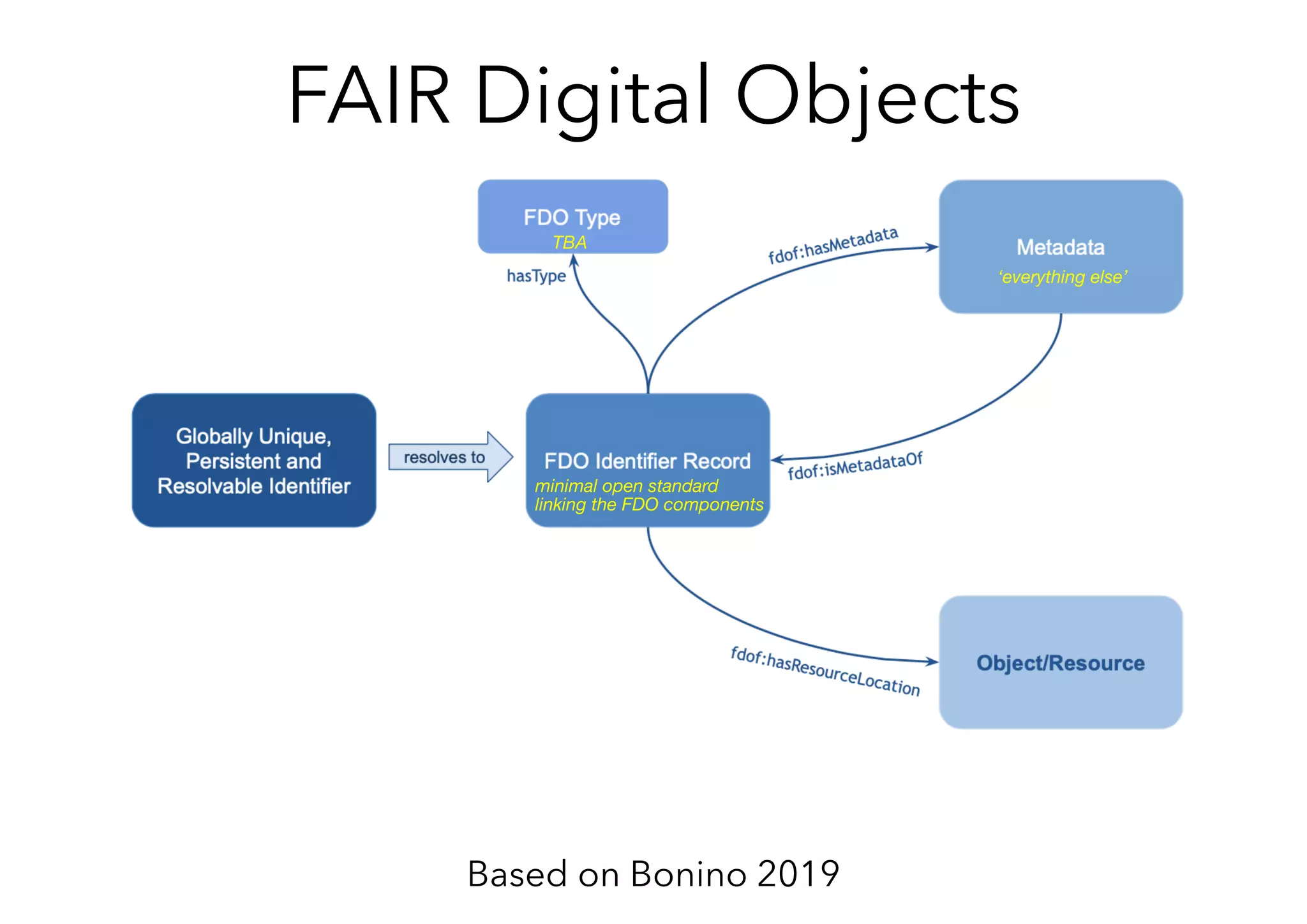











![Resolves to
GUPRI
ePIC
FAIR Digital Object Record
fdo:digitalObjectOfType fdo:MGFile ;
fdo:locationOfDO <https://hackathon.fair-dtls.surf-hosted.nl/EL/> ;
datacite:hasIdentifier :identifier ;
dct:conformsTo <https://hackathon.fair-dtls.surf-hosted.nl/shacl-record.ttl> .
fdof:hasResourceLocation
Resource
fdo:digitalObjectOfType
Type
MG File
fdof:hasMetadata fdof:isMetadataOf
Extensible Metadata
# metadata section
#<http://rdf.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubchem/compound/CID702> ; # Ethanol
#<http://rdf.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubchem/compound/CID5280450> ; # Lineoleic acid
#<http://rdf.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubchem/compound/CID5282184> . # Ethyl Lineolate
:elMetadata :respresents :molecule .
:molecule :molecularWeight "308.47"^^:gramsPerMol ;
skos:prefLabel "Ethyl Lineolate" ;
skos:notation "C20H36O2" ;
:cas "544-35-4" ;
<http://semanticscience.org/resource/SIO_000212> <http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/
anie.201801332> ;
# is referred to by :availableAt <https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/search?
term=ethyl+linoleate&interface=All&N=0&mode=match%20partialmax&lang=en®i
on=US&focus=product> .
# provenance
:elMetadata dct:contributor orcid:0000-0002-8042-4131 .
orcid:0000-0002-8042-4131 a foaf:Person ;
foaf:name "Myles Axton" ;
pro:holdsRoleInTime [
a pro:RoleInTime ;
pro:withRole scoro:investigator-role ;
] .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fairbydesignslides-200518094333/75/Fair-by-design-53-2048.jpg)