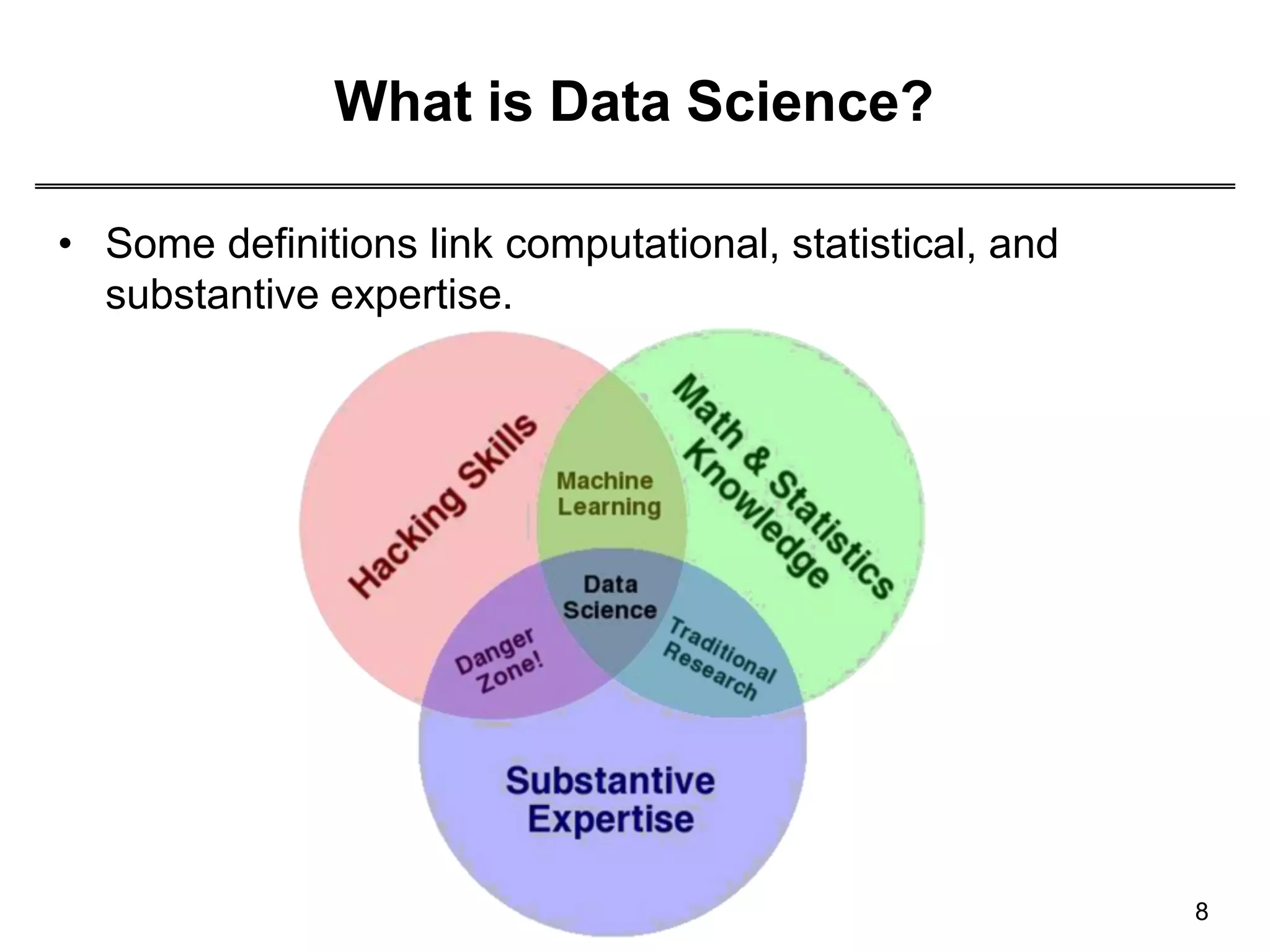
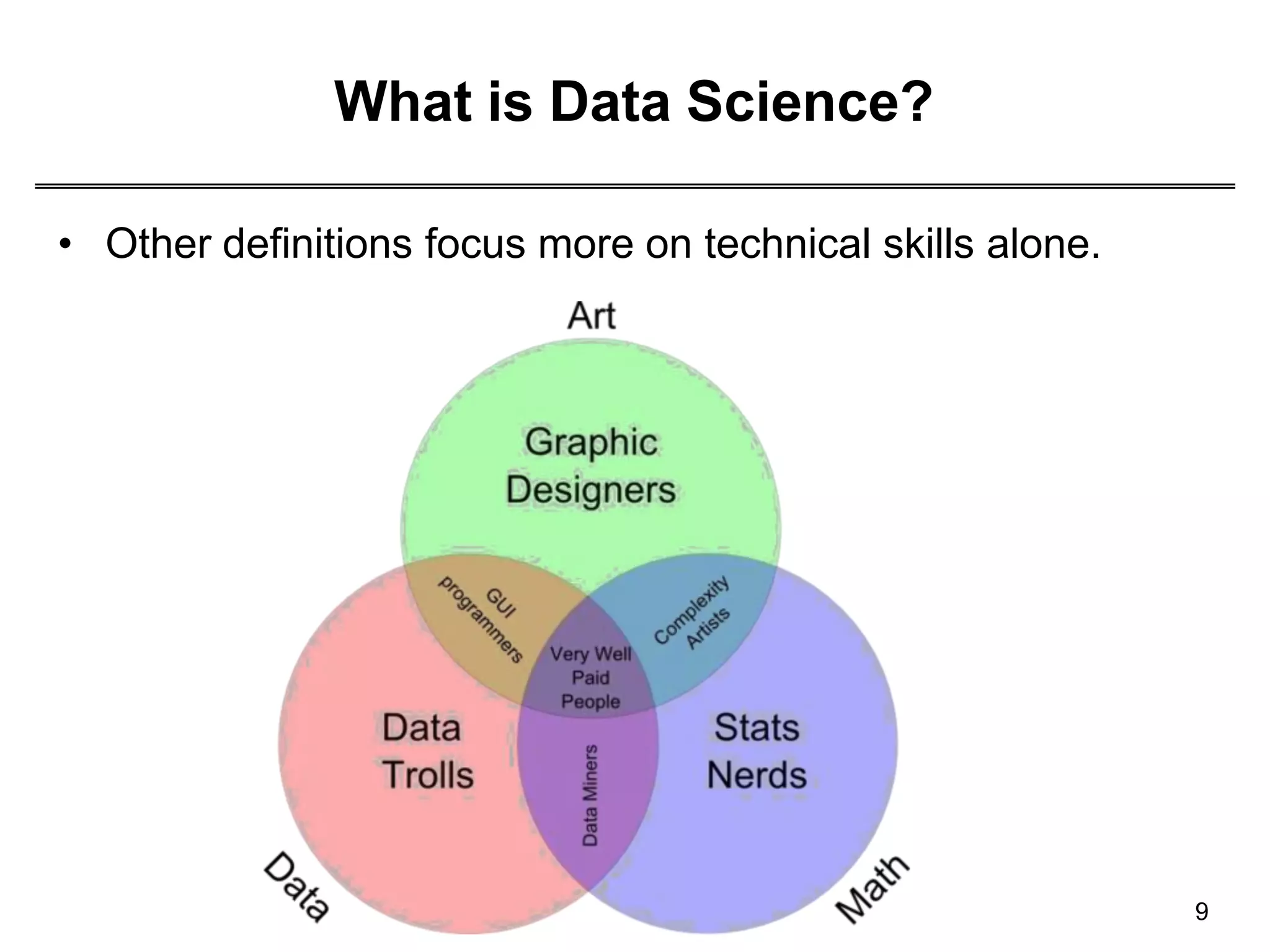
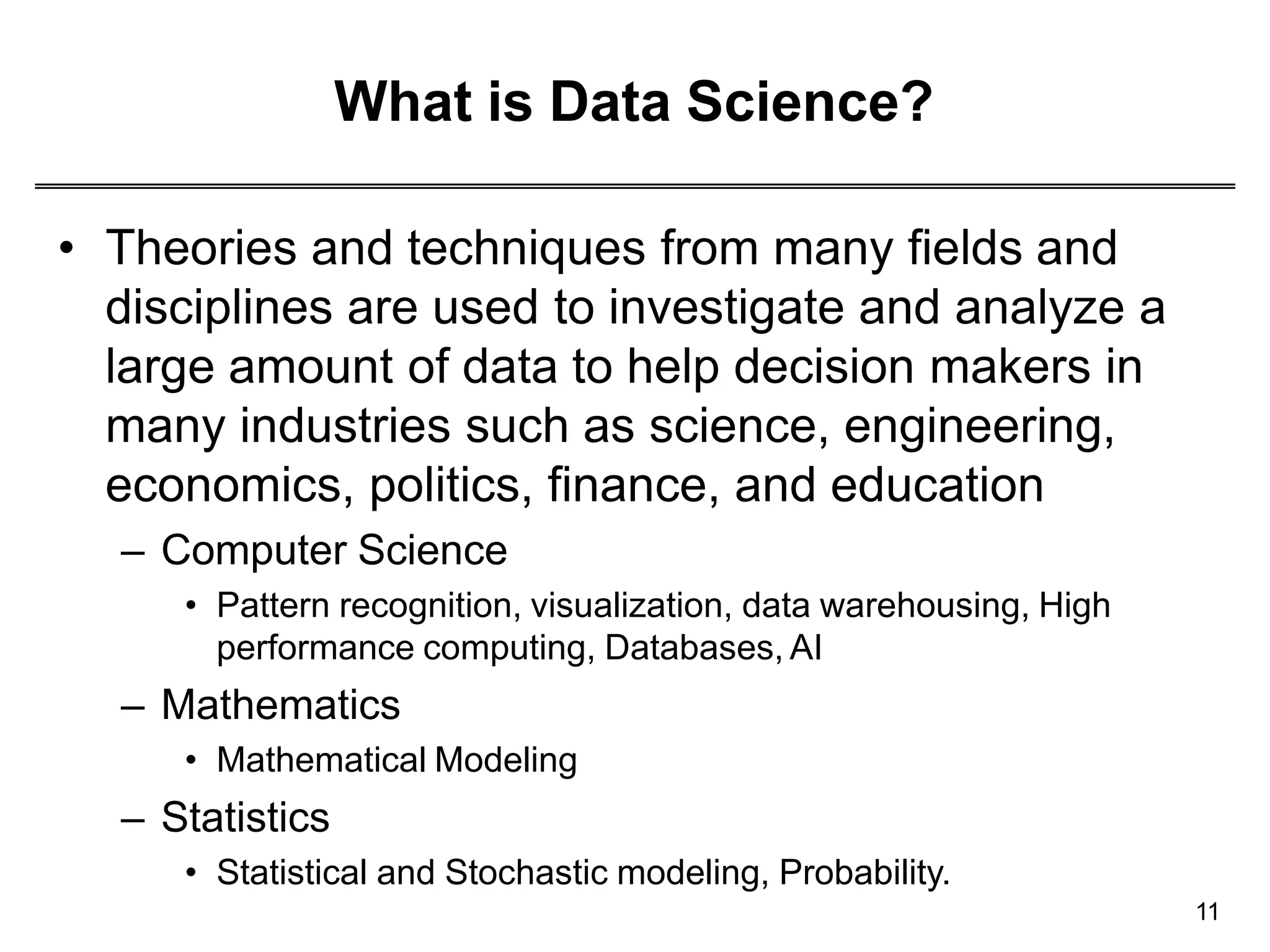
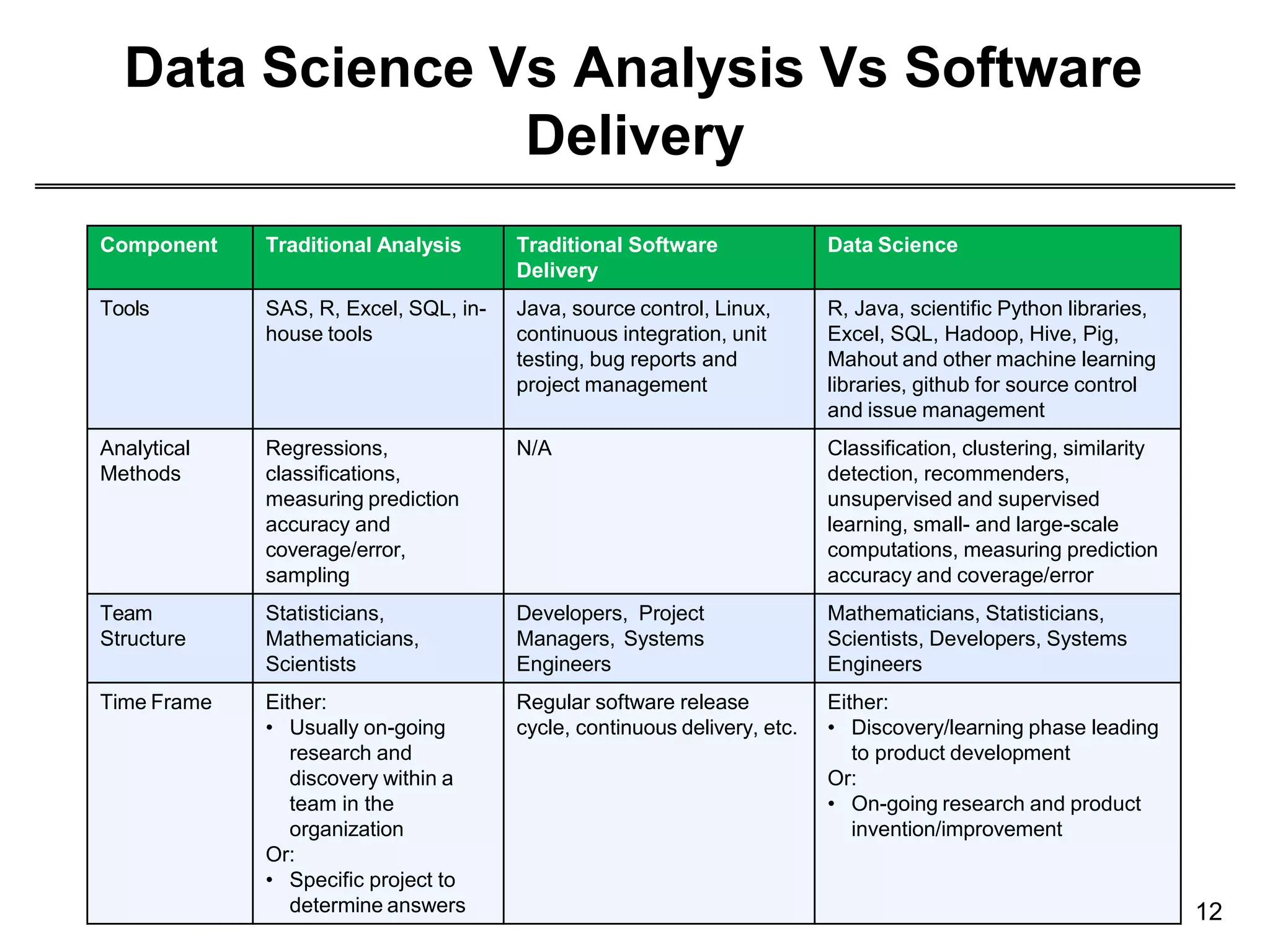
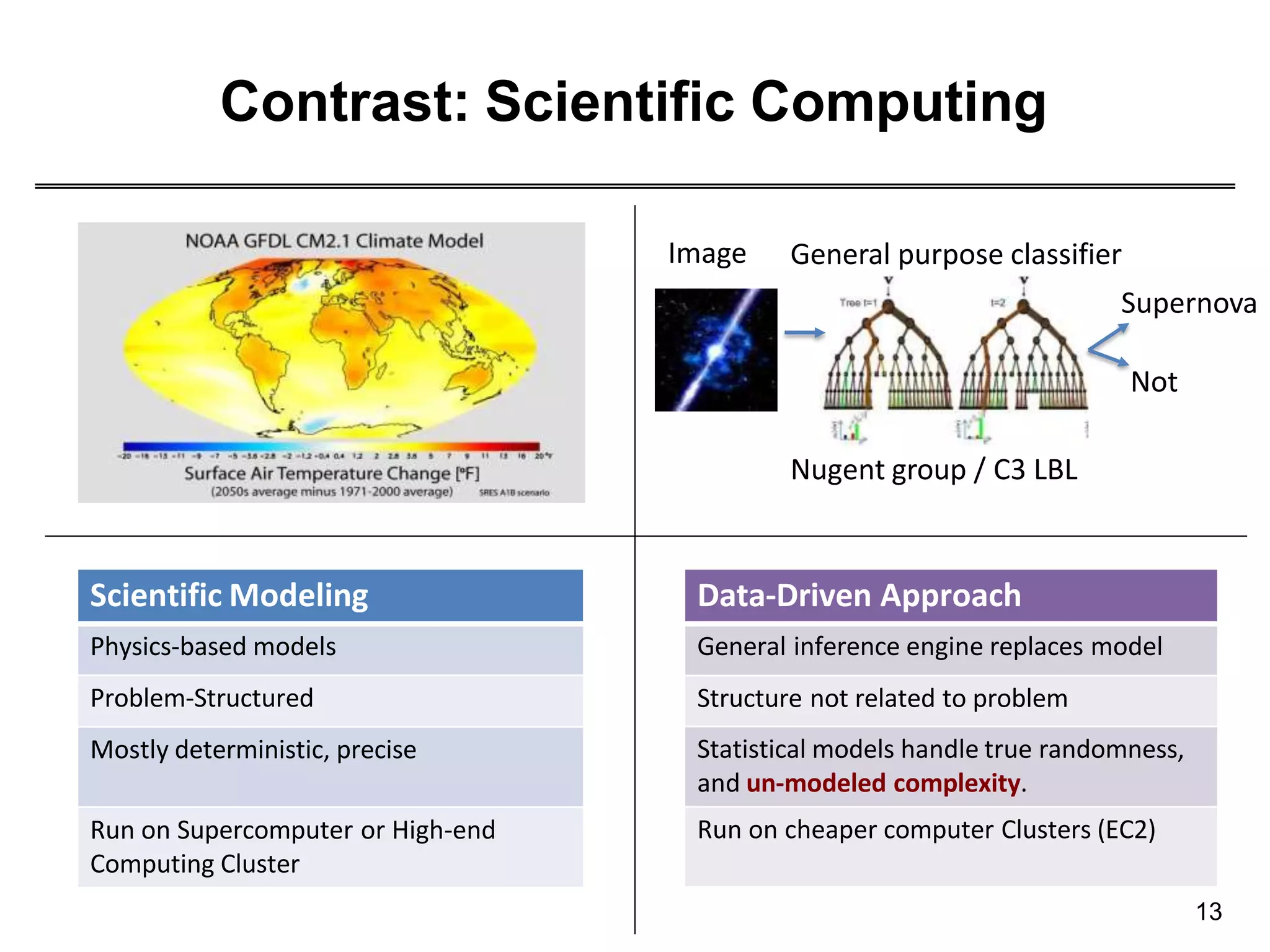
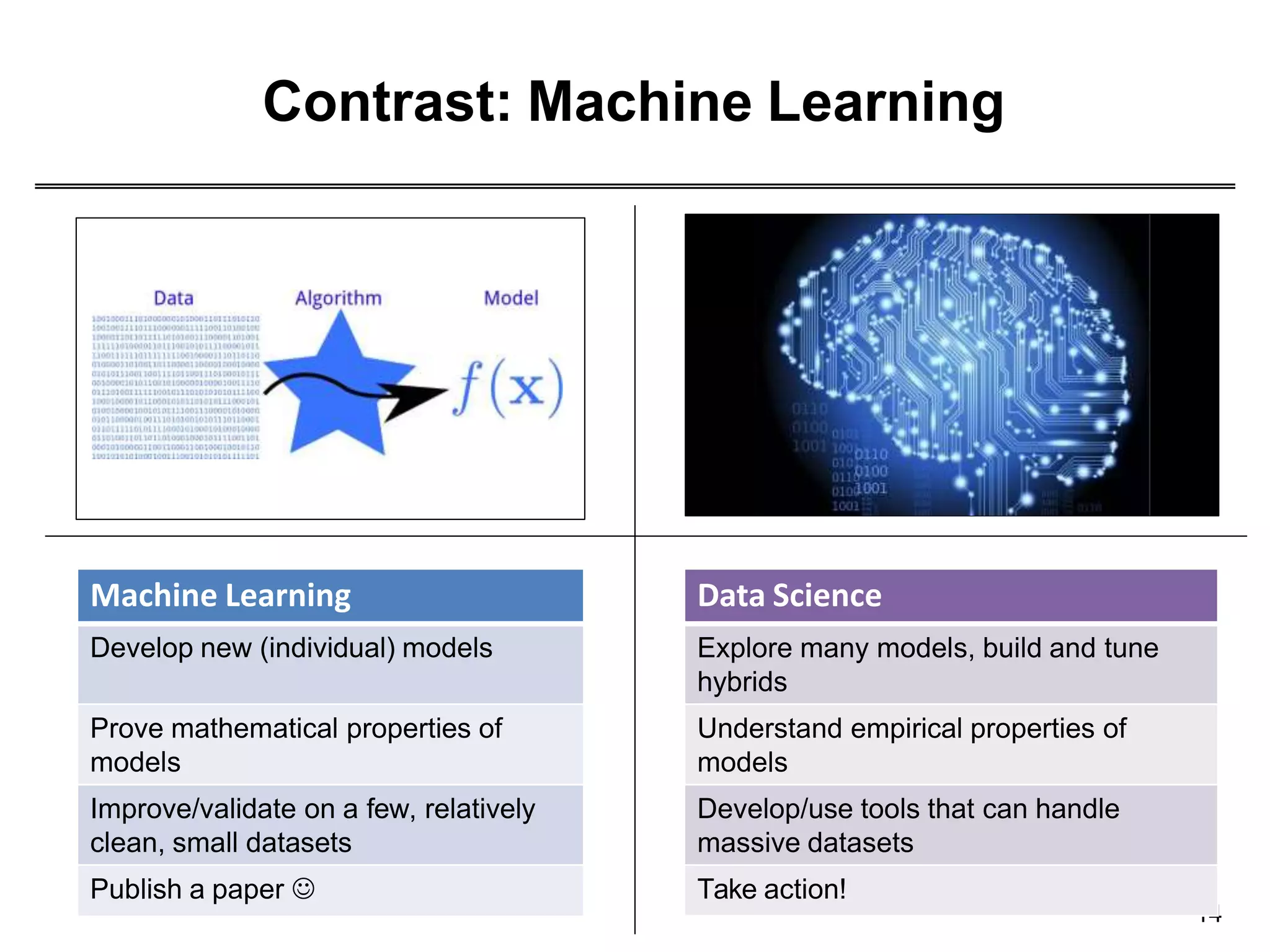
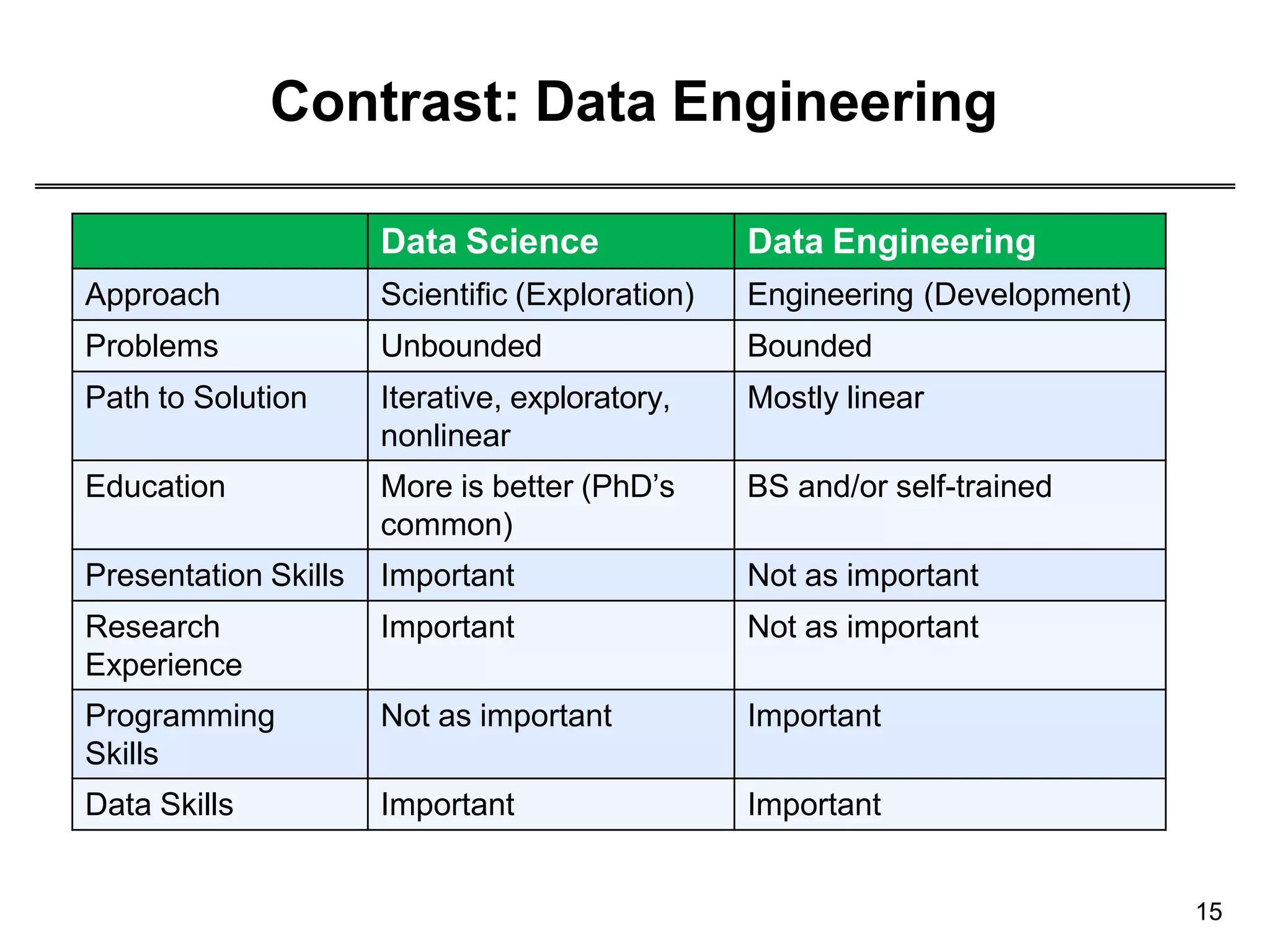
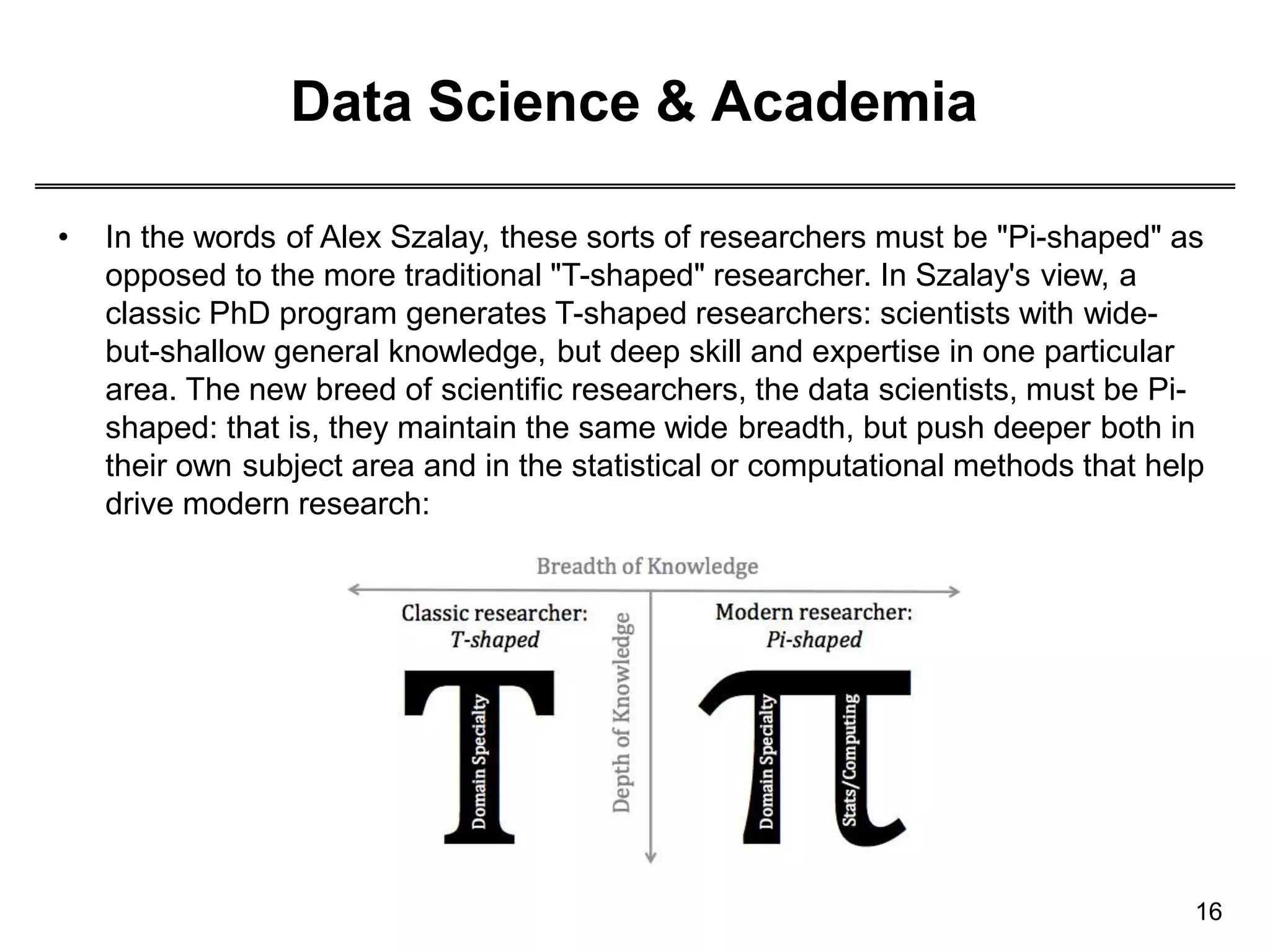
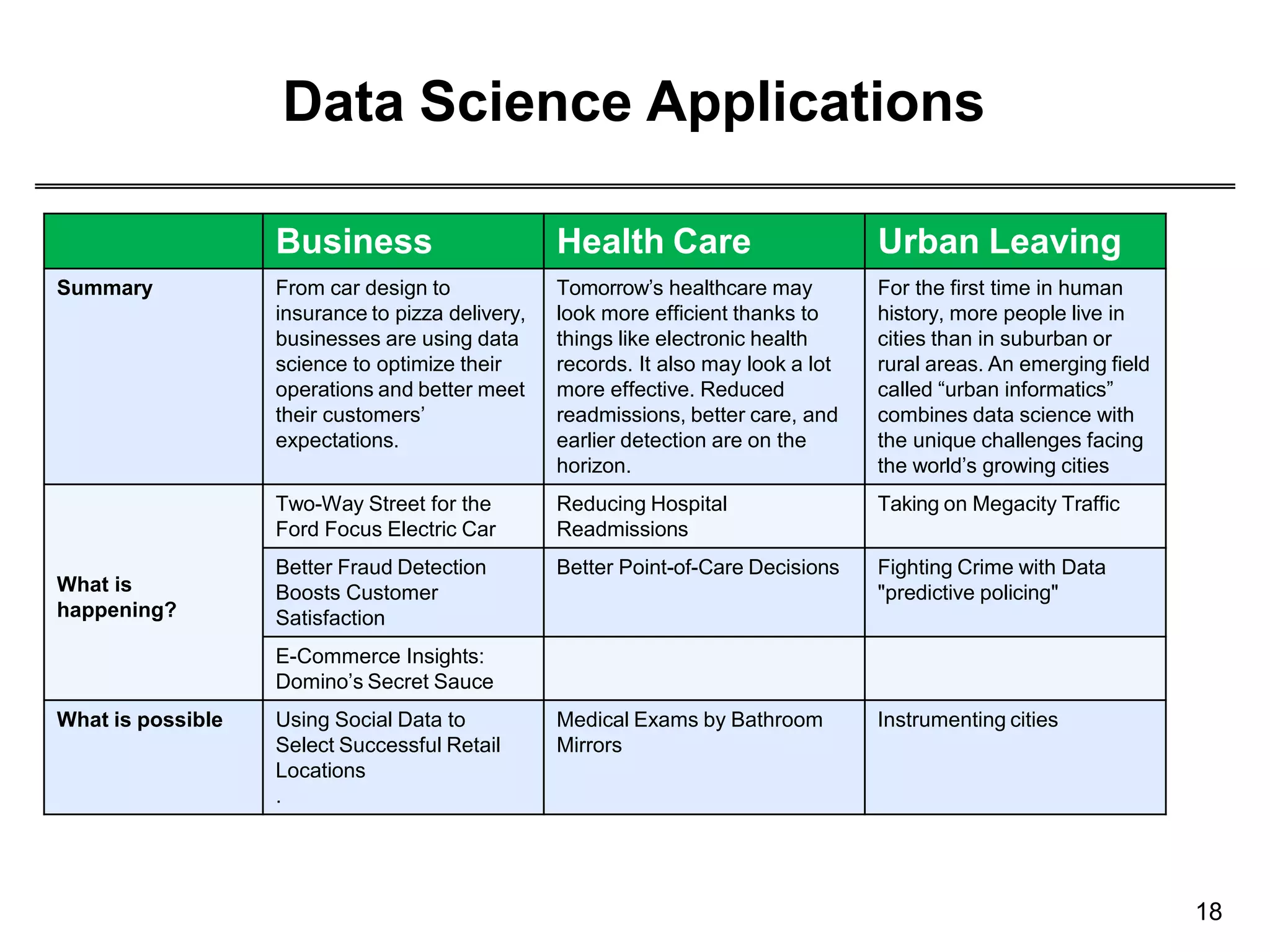
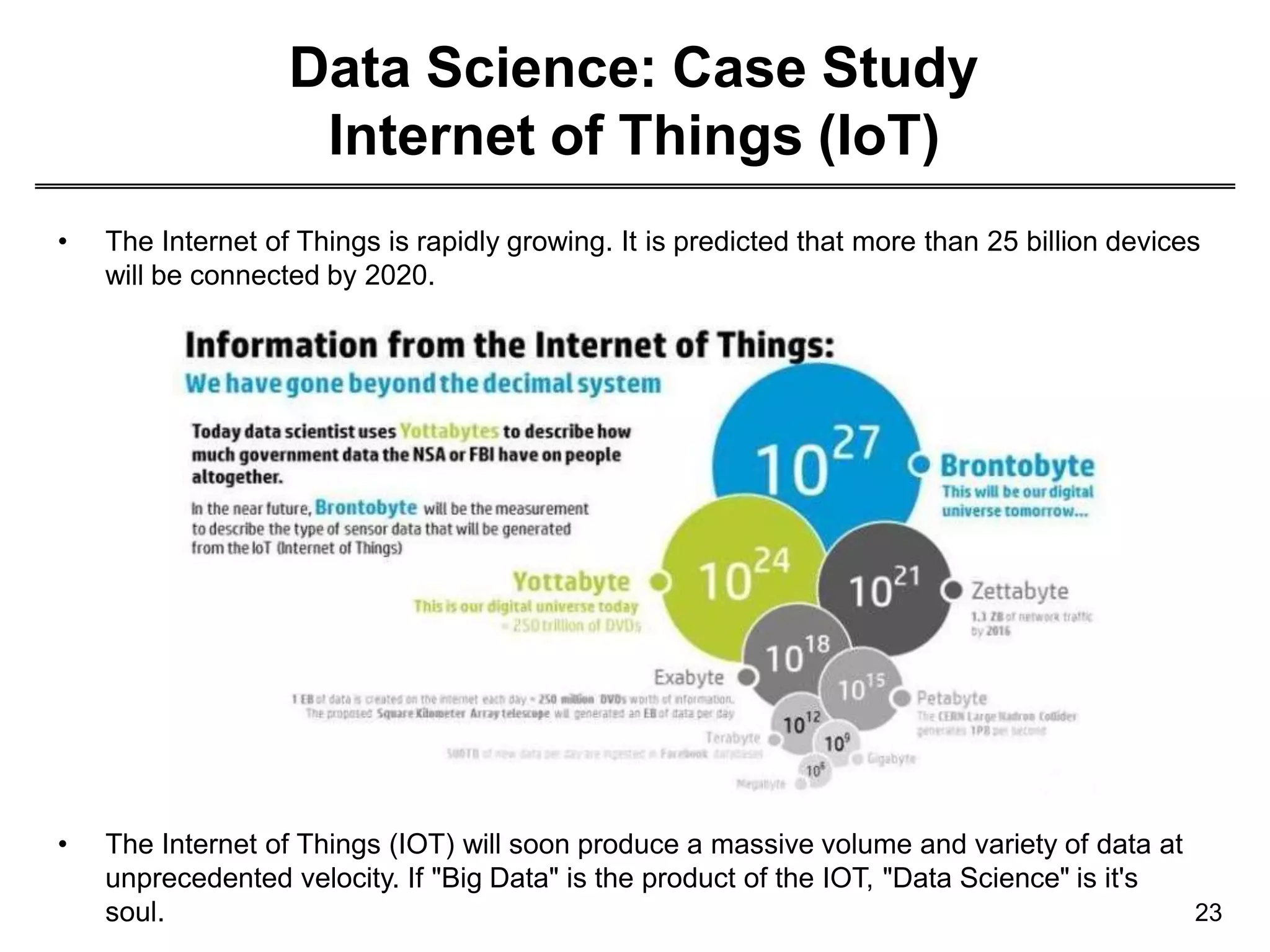
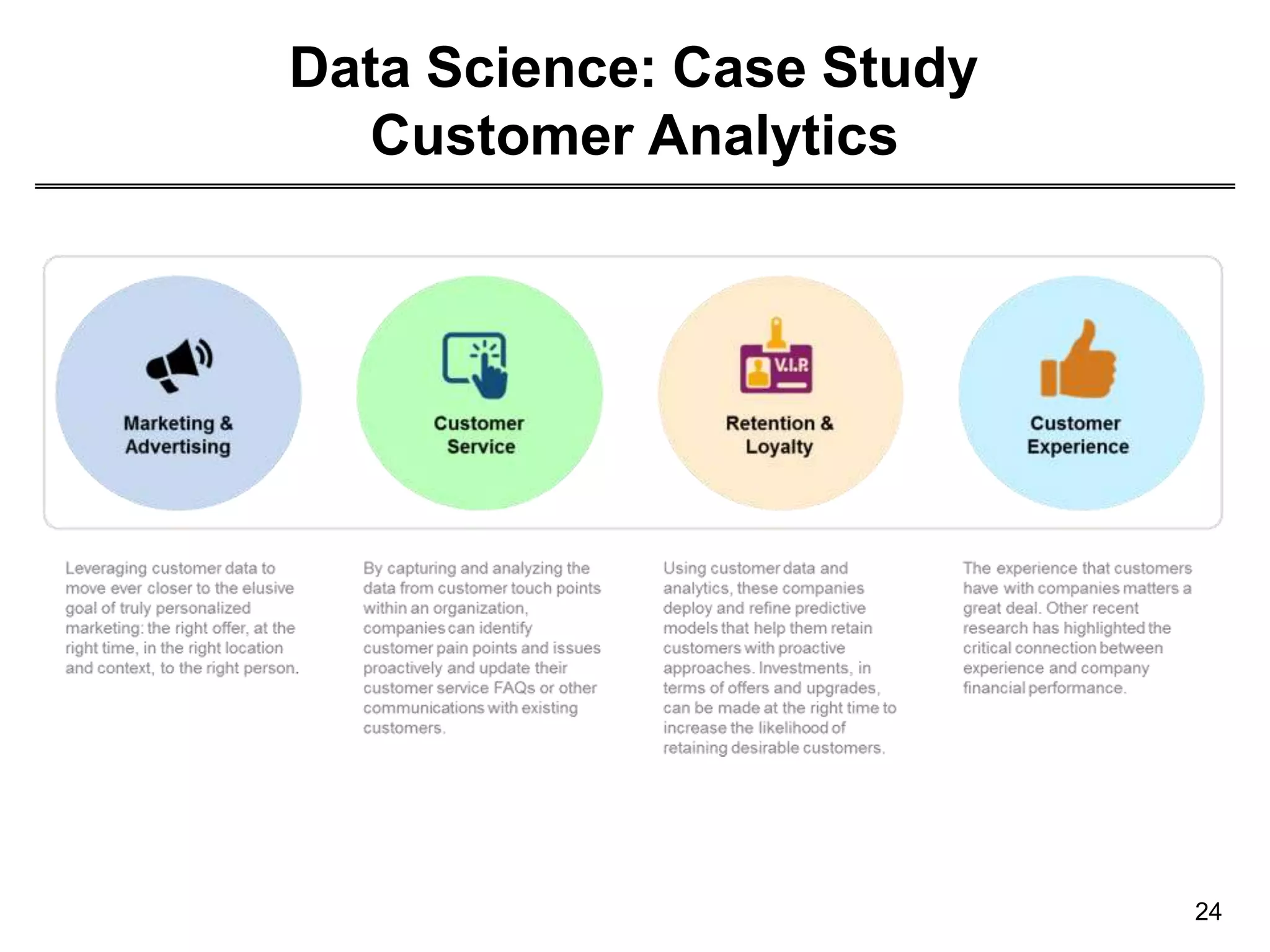
This document provides an overview of data science through discussing big data challenges, defining data science, contrasting it with other fields, and presenting case studies. It explains that data science uses theories from fields like computer science, mathematics, and statistics to analyze large, complex data sets and help organizations make better decisions. Example applications discussed include using data science in healthcare to improve patient care, in elections to micro-target voters, and in cities to address urban challenges through data-driven solutions.