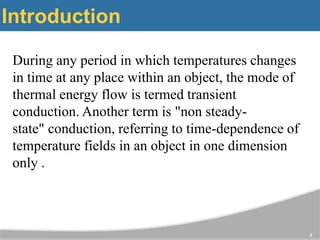
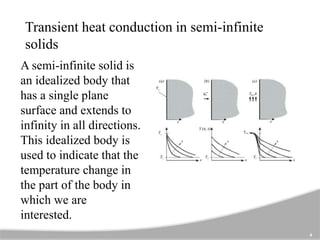
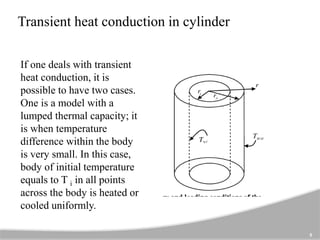
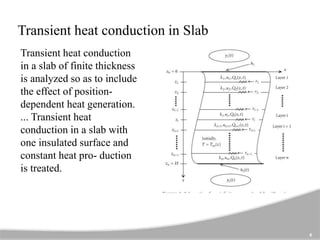
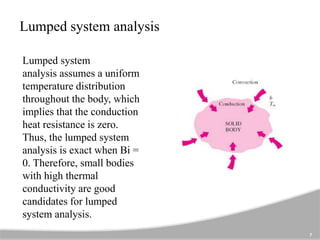
The document discusses one-dimensional transient heat conduction, focusing on time-dependent temperature changes within objects. It covers various scenarios such as lumped thermal capacity models, semi-infinite solids, cylinders, and slabs, with applications in heat exchangers and boiler tubes. Key concepts include uniform temperature distribution and cases where conduction heat resistance is negligible.