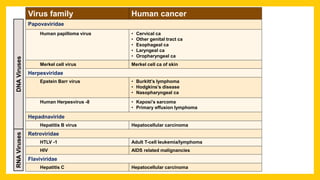
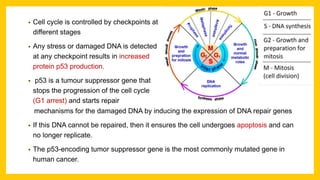
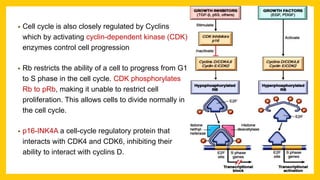
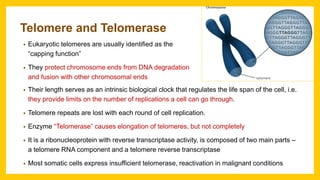
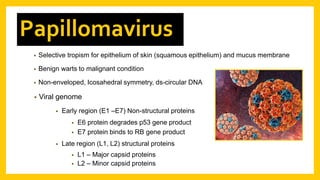
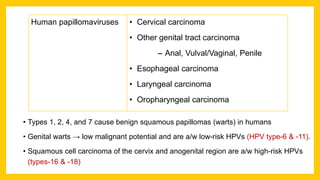
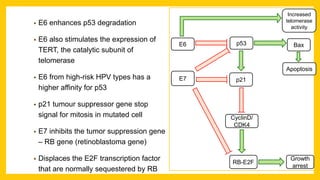
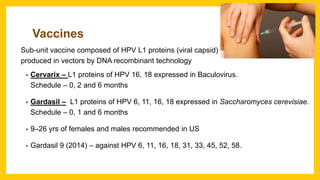
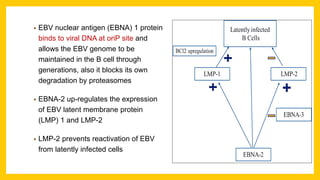
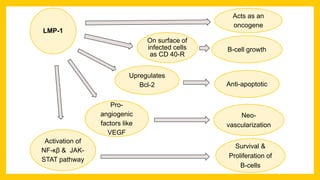
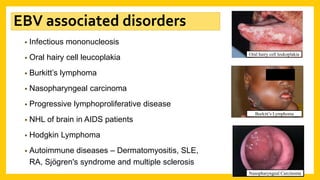
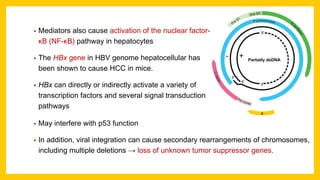
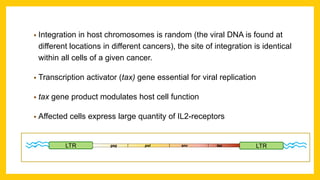
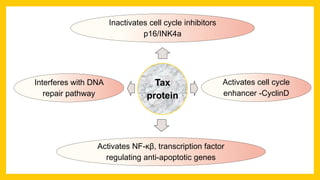
The document discusses various virus families associated with human cancers, including human papillomavirus (HPV), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), hepatitis B and C viruses, and human T-cell leukemia virus (HTLV-1). It outlines the mechanisms through which these viruses can induce cellular transformation and malignancy, focusing on specific viral proteins that interfere with tumor suppressor genes and promote oncogenesis. Additionally, it highlights preventative measures such as vaccines against HPV and the multifactorial nature of hepatitis-related liver cancer.