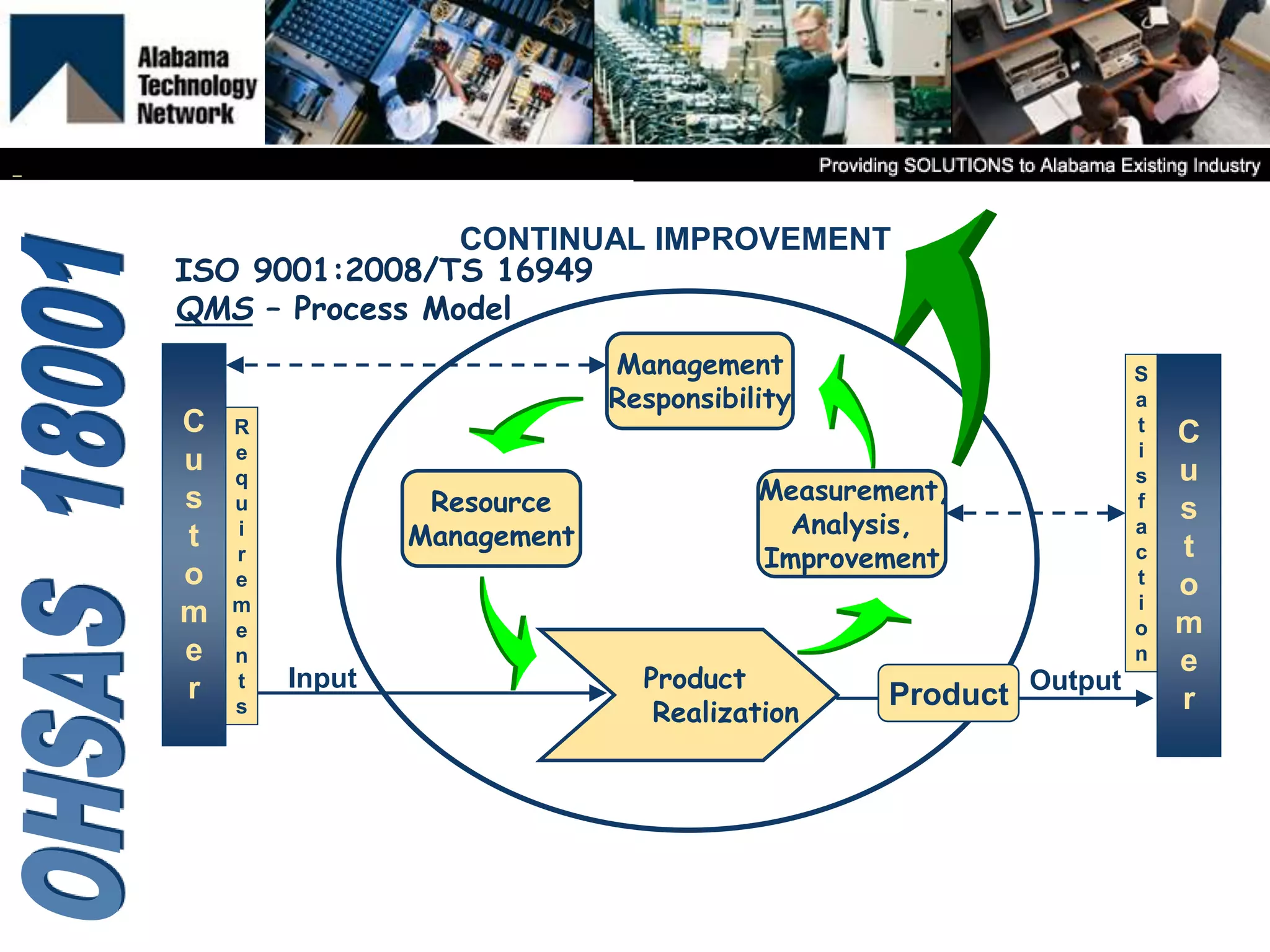
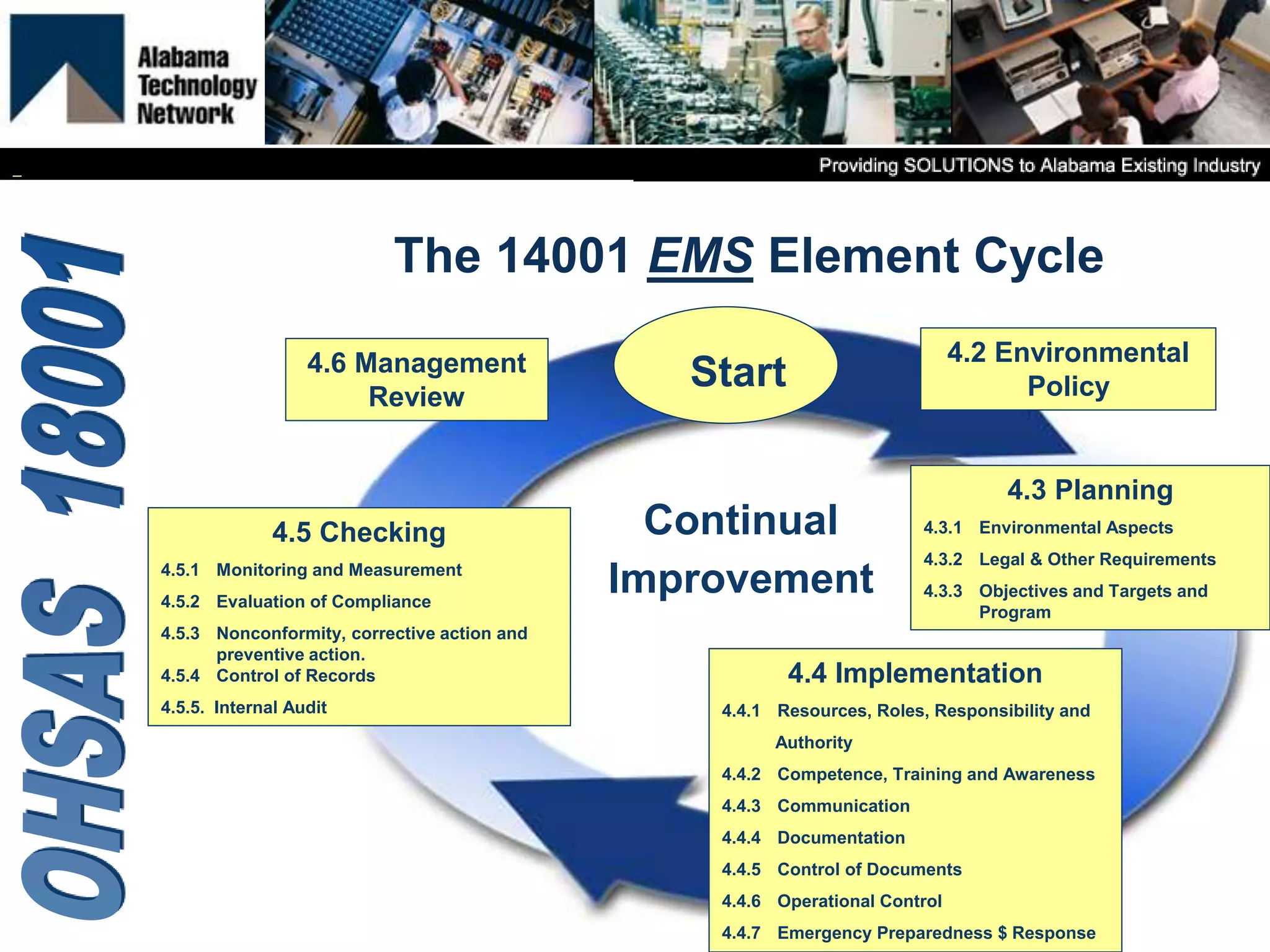
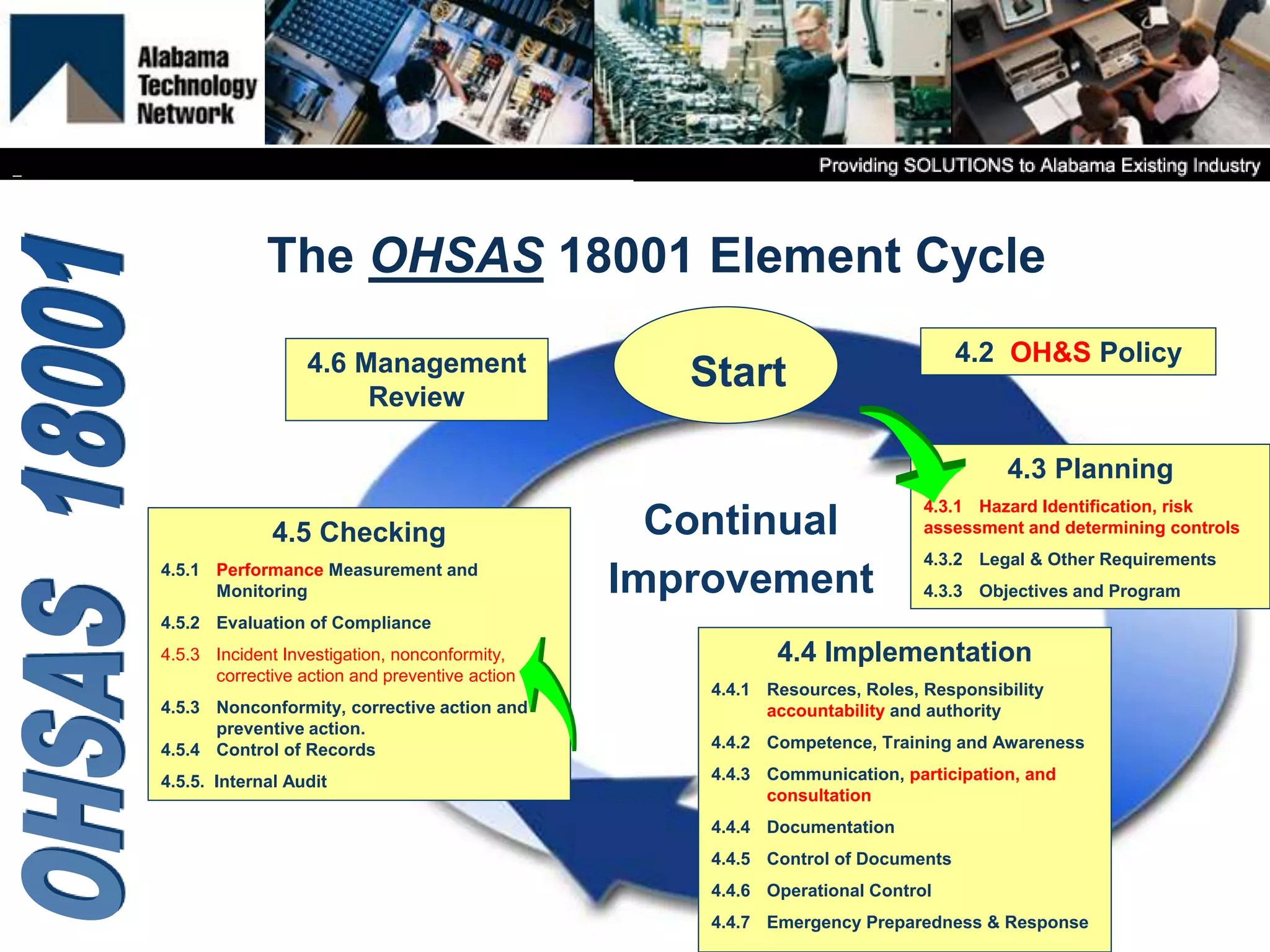
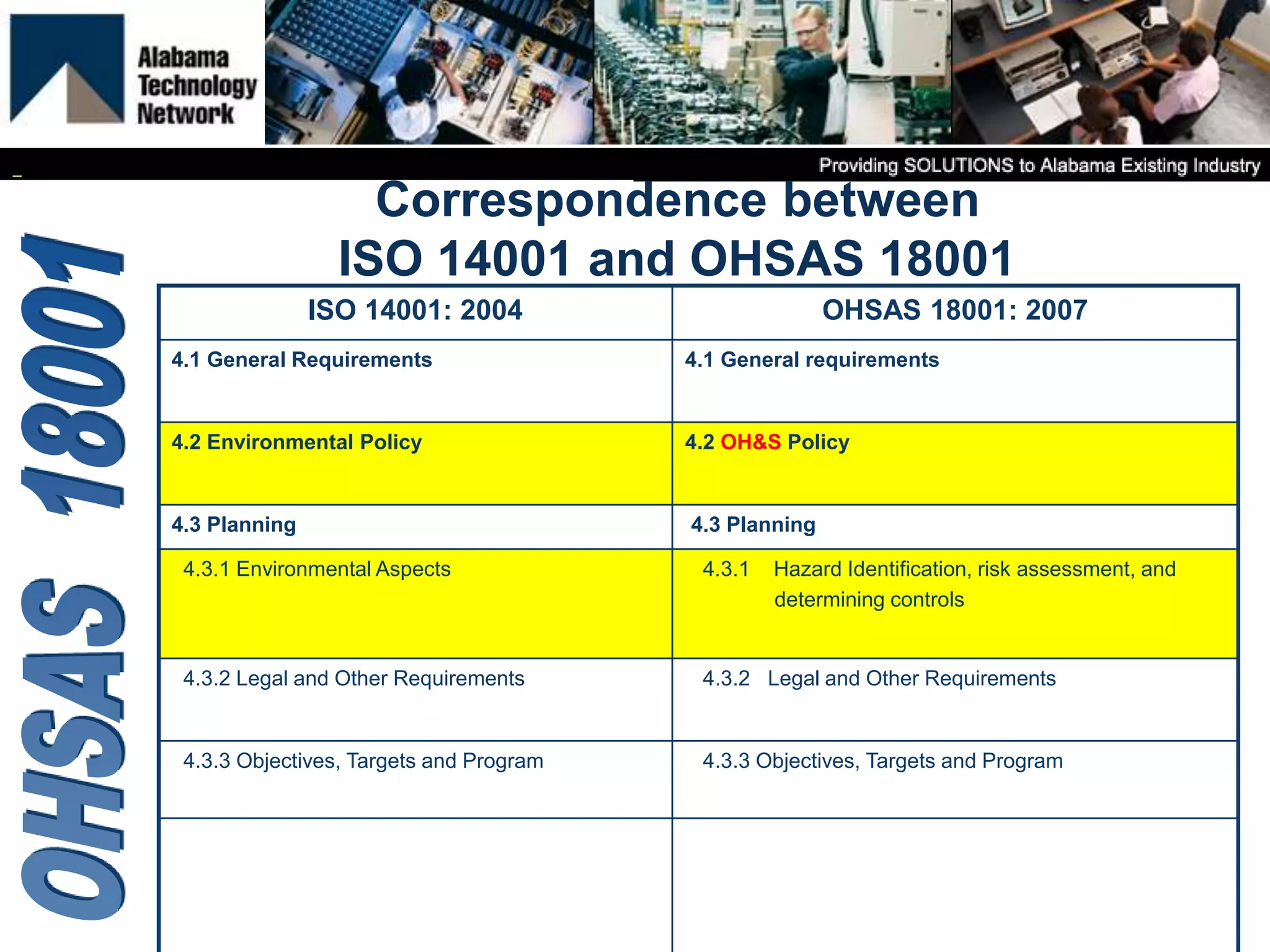
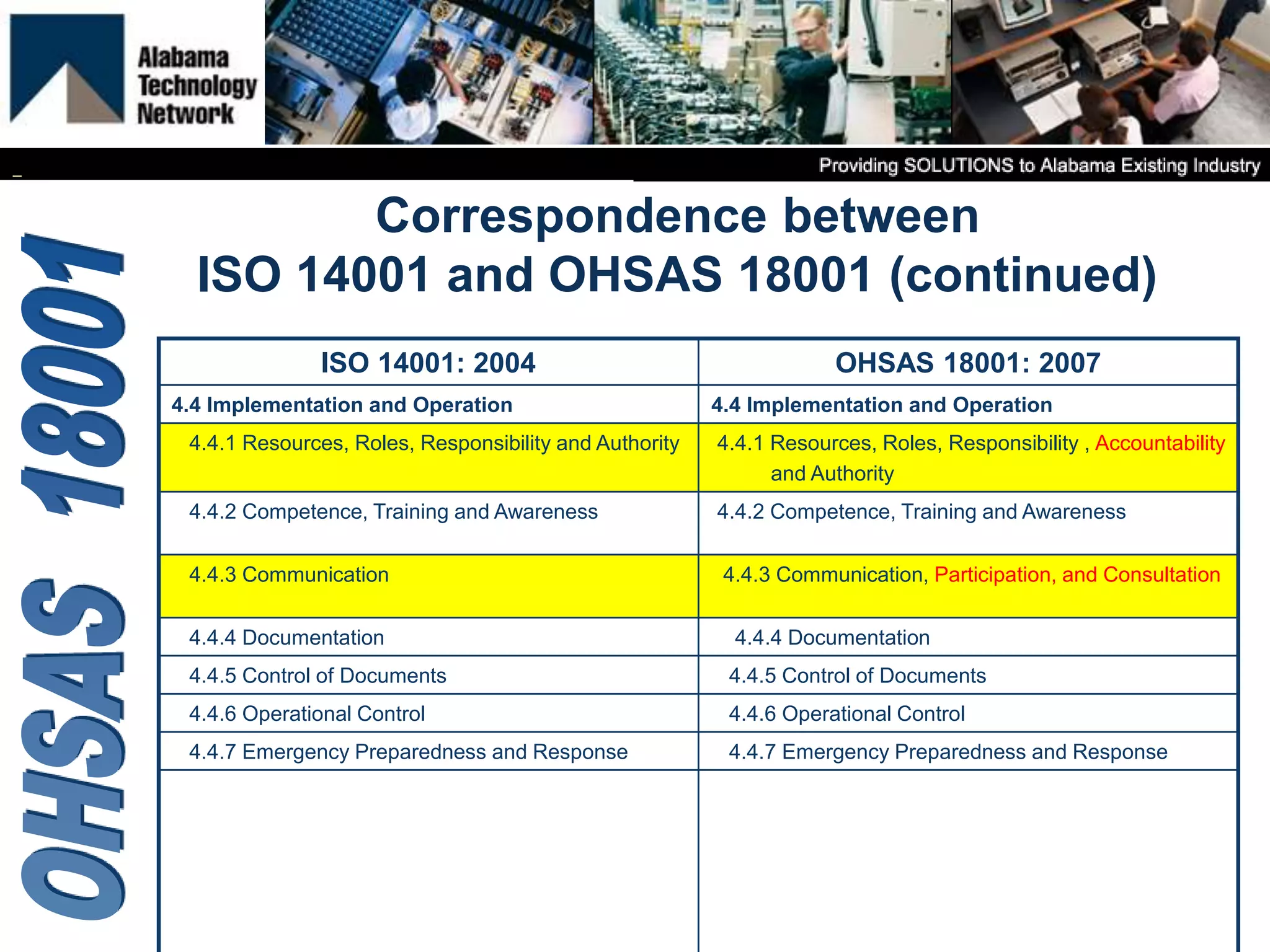
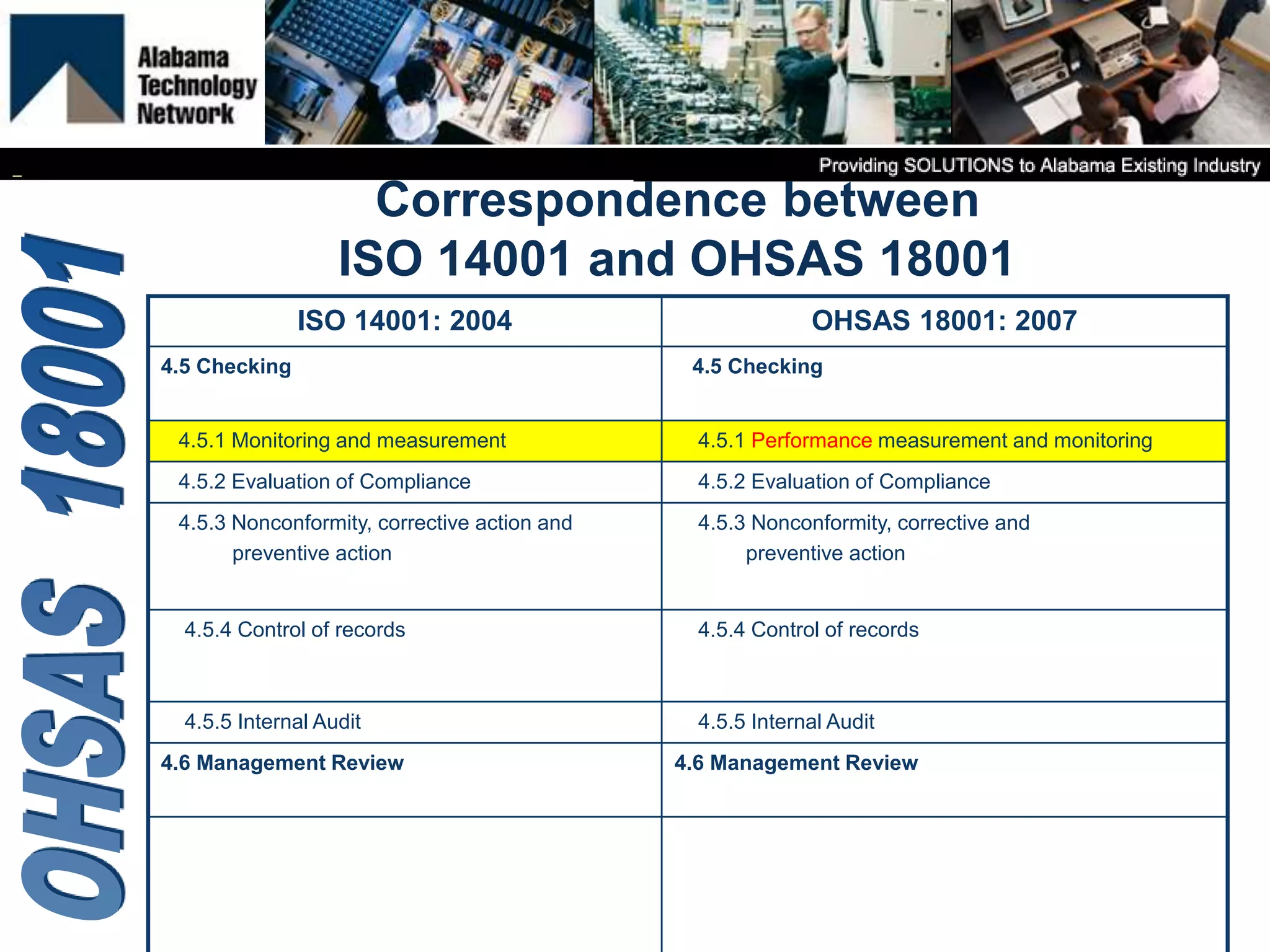
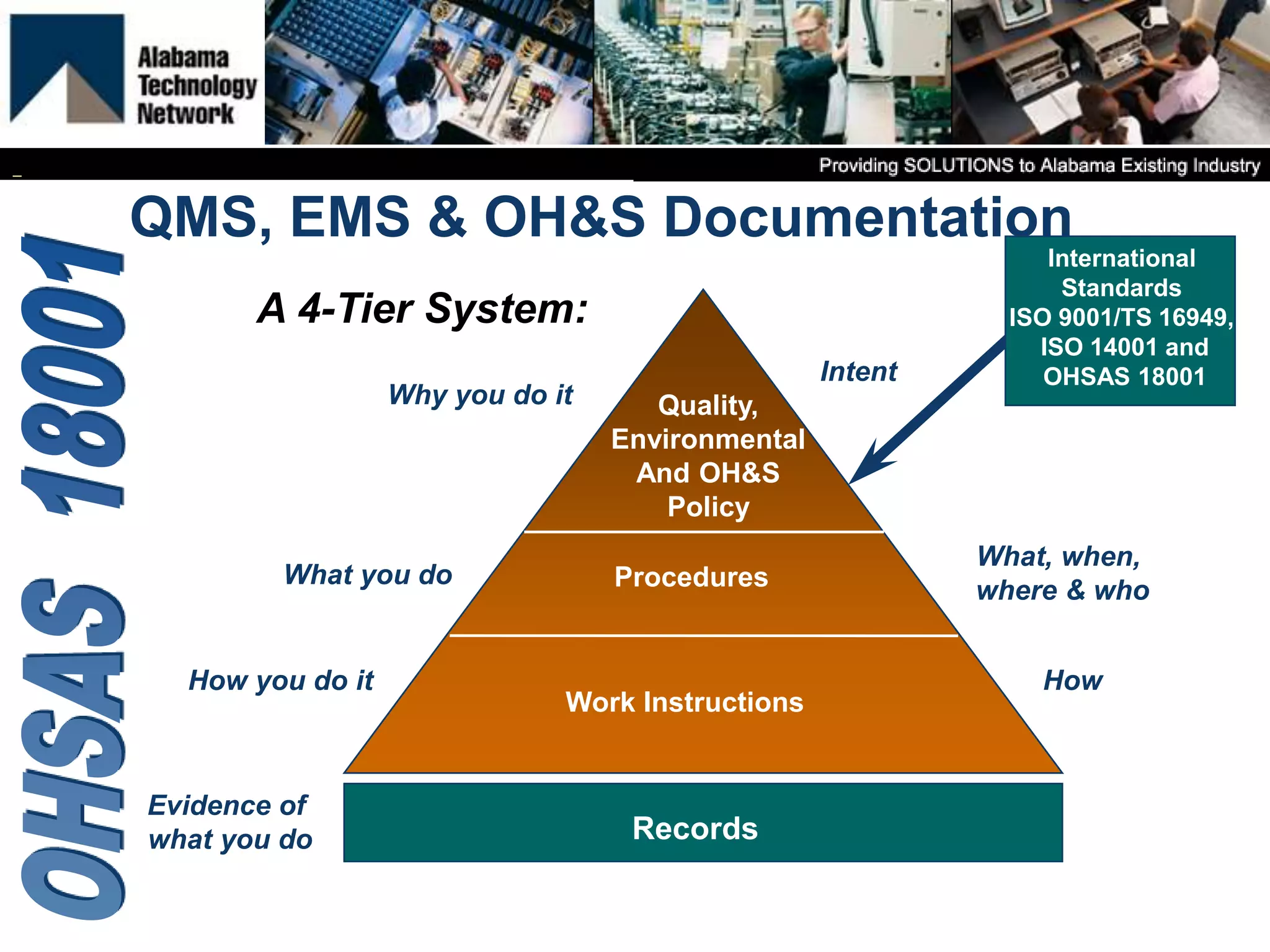
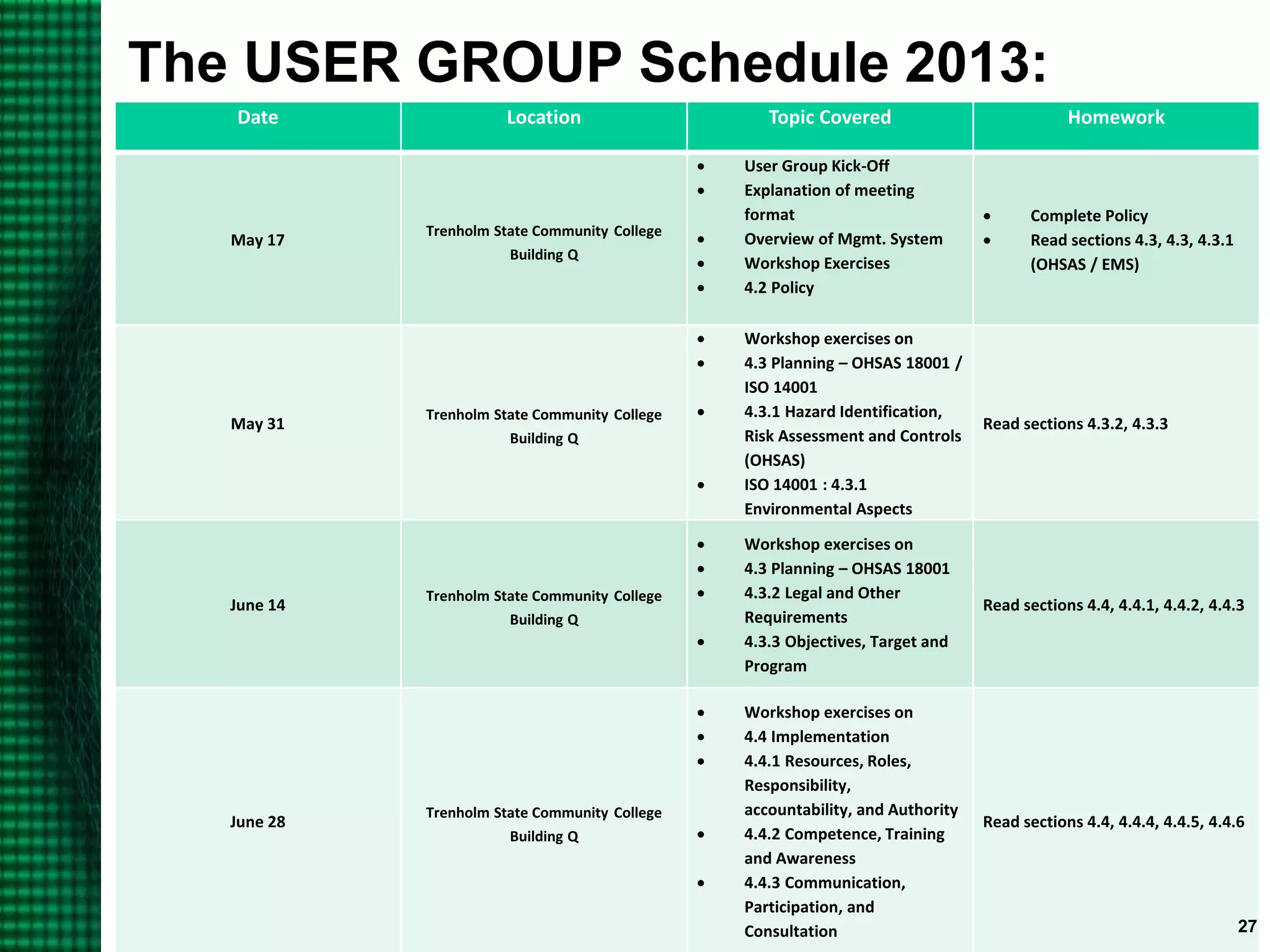
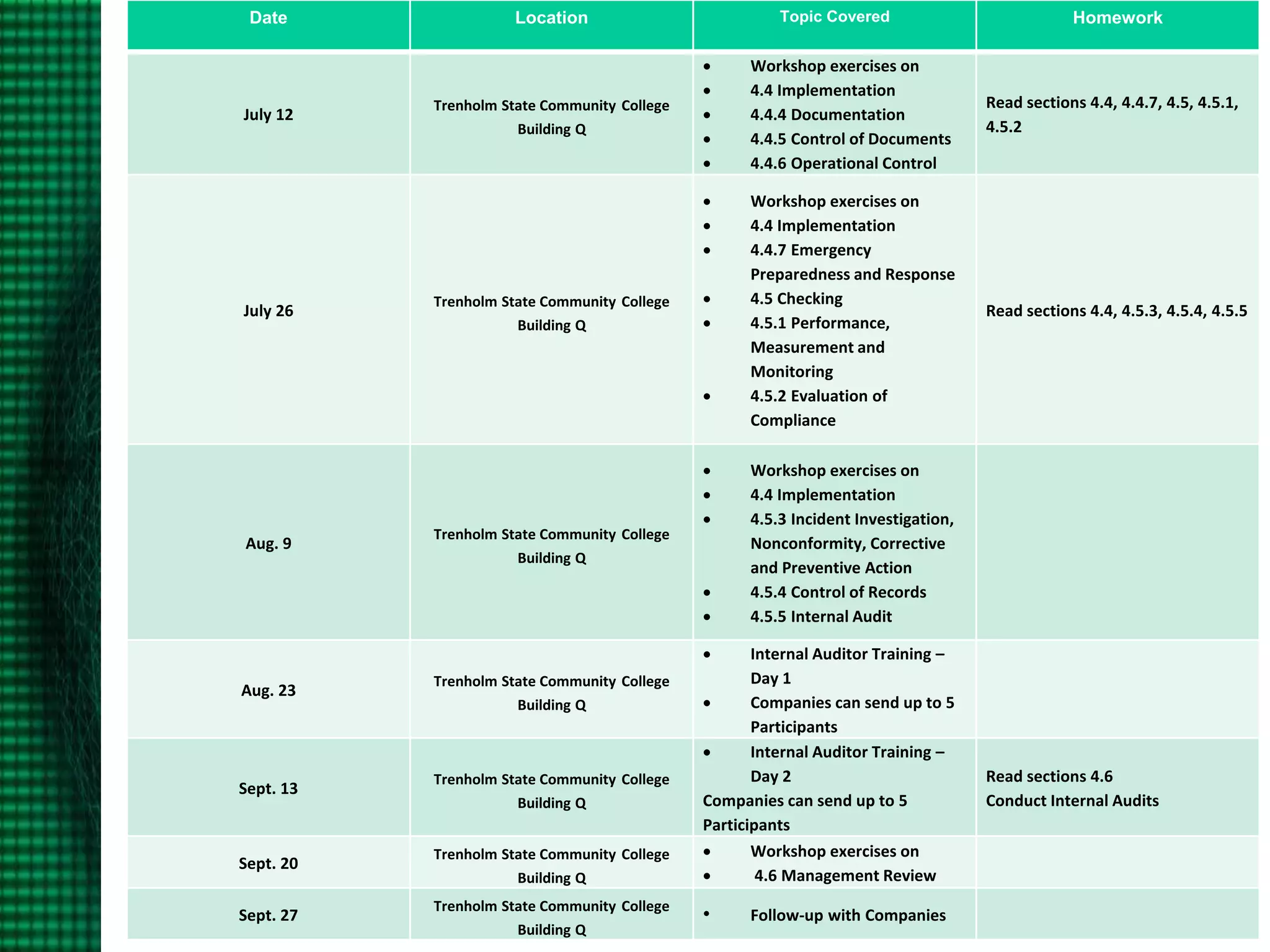
OHSAS 18001 is an occupational health and safety management system standard aimed at improving workplace safety and compliance. Set to be replaced by ISO 45001 in October 2016, the standard emphasizes the identification and management of health and safety risks to all workplace personnel. The document outlines definitions, management processes, and implementation assistance for organizations seeking to adhere to OHSAS specifications.