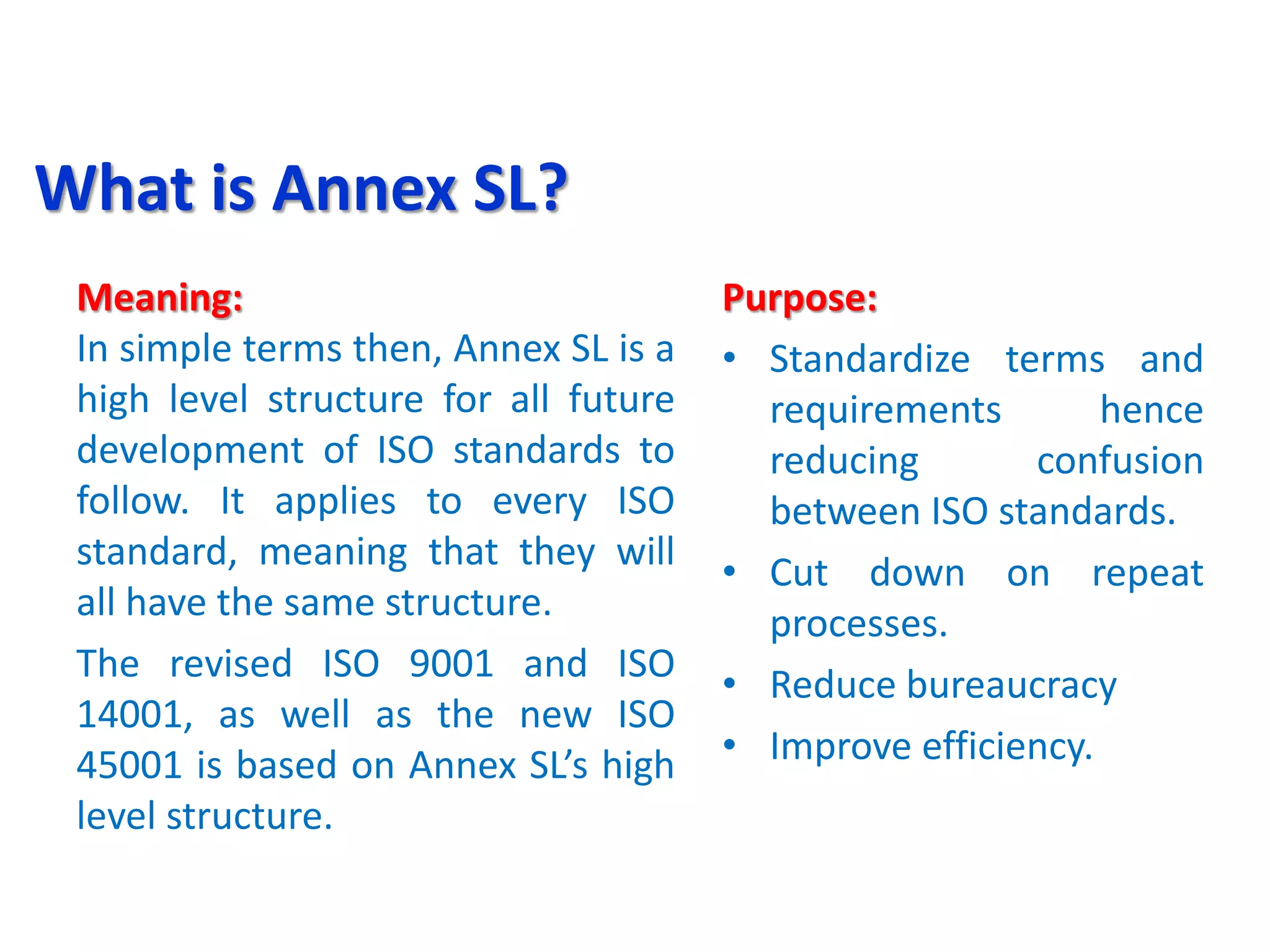
The document provides an overview of ISO 45001, the new international standard for occupational health and safety management systems. It summarizes the key changes between ISO 45001 and the previous OHSAS 18001 standard. Some of the major differences highlighted include ISO 45001 being more process-based rather than procedure-based, considering risks and opportunities rather than just risks, and including the views of interested parties. It also discusses new requirements in ISO 45001 around leadership commitment, consultation and participation of workers, and a more proactive approach to identifying and controlling risks. The document concludes by outlining some high-level steps for implementing an occupational health and safety management system based on ISO 45001.