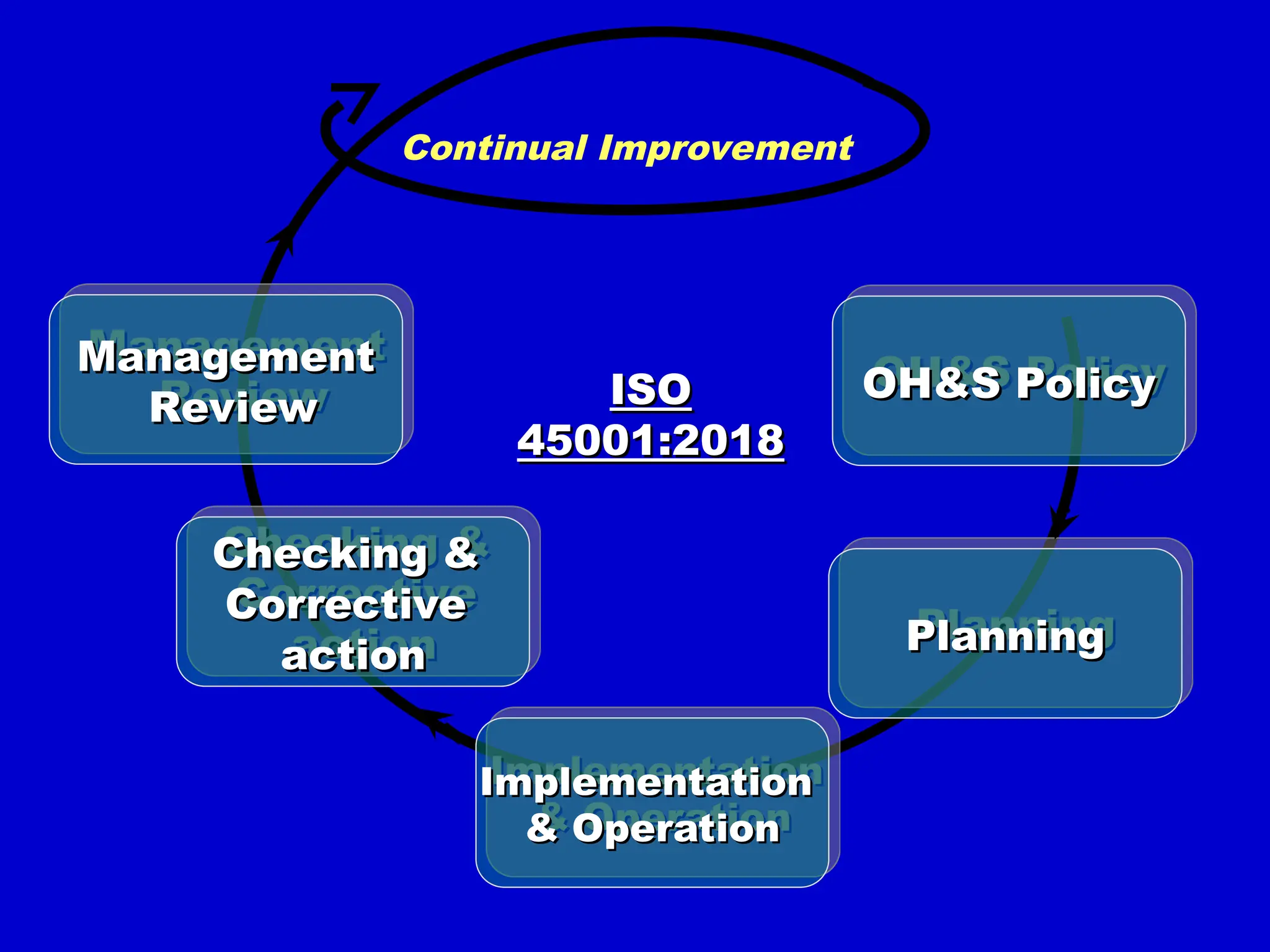
The document outlines the framework of an Occupational Health and Safety Management System (OHSMS) based on ISO 45001:2018, detailing its policies, processes, and procedures to improve occupational health and safety performance. It emphasizes the importance of risk management, worker participation, compliance with legal requirements, and continual improvement in safety practices across organizations. Specific sections address roles, responsibilities, hazard identification, risk assessment, and emergency preparedness, highlighting the commitment of the Dolls Eye Scream Factory to maintaining safe working conditions.