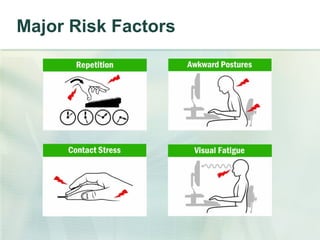
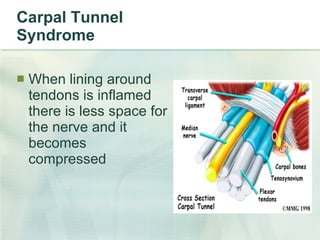
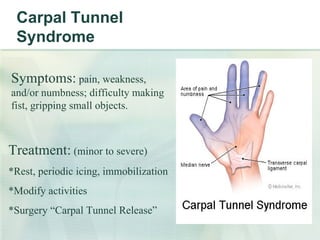
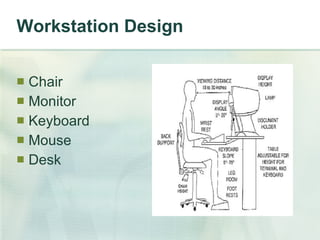
This document summarizes ergonomic risk factors and recommendations for office workstation design to prevent repetitive strain injuries. It identifies major risk factors like carpal tunnel syndrome and discusses neutral posture and positioning of monitors, keyboards, mice and desks. The document recommends exercises to prevent musculoskeletal disorders and concludes by emphasizing notifying supervisors of symptoms, taking an active role in workspace design, and strengthening and improving flexibility both at work and home.