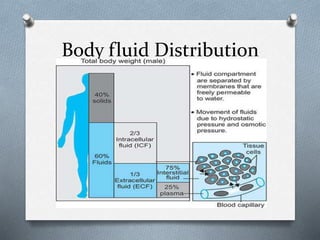
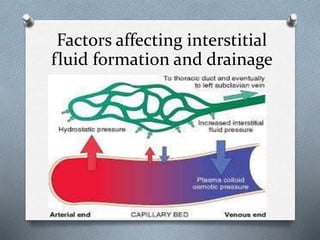
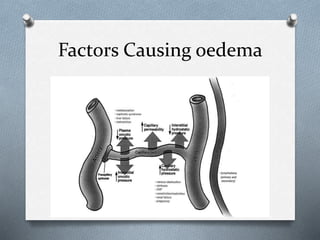
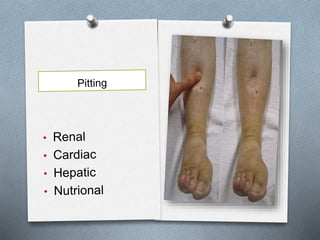
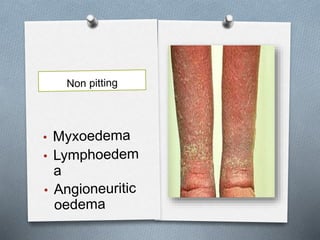
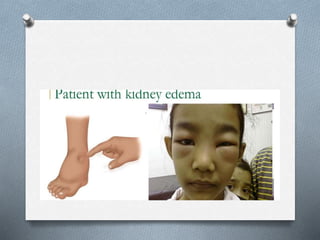
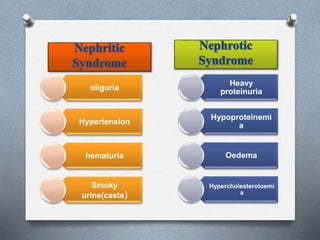
This document discusses different types of jaundice and edema. It defines jaundice as yellowish discoloration of the skin, sclera, or both. It then presents three clinical cases and asks the reader to identify the type of jaundice in each case. The types listed are hemolytic, hepatocellular, or obstructive jaundice. It also defines edema as abnormal accumulation of fluid in interstitial tissue due to disturbed fluid regulation. The types of edema listed are pitting and non-pitting edema. Factors that can cause edema include renal disease, liver disease, heart failure, and nutritional deficiencies.