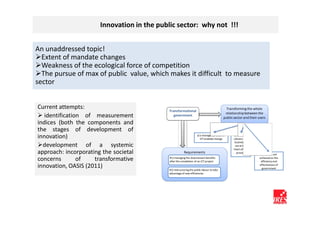
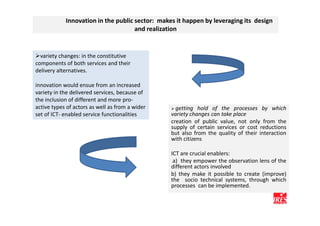
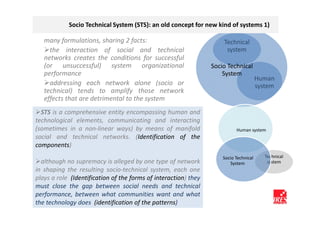
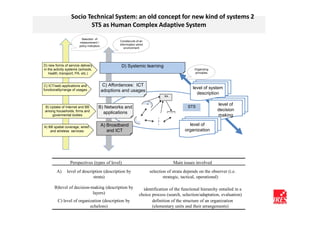
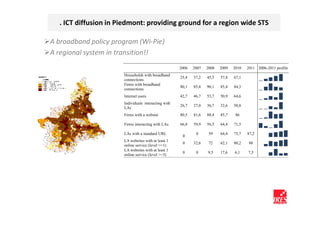
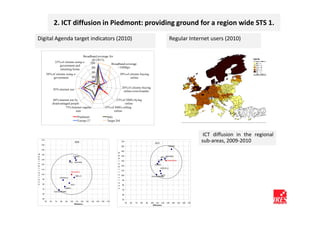
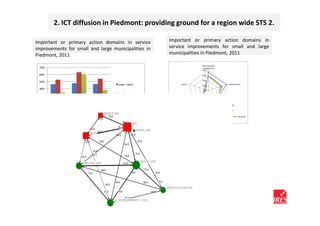
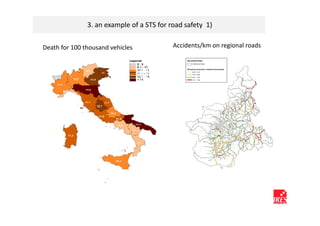
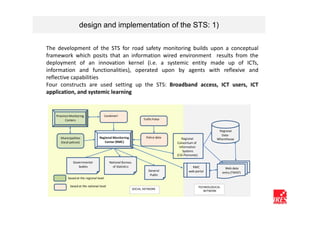
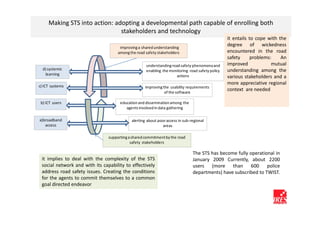
The document discusses how ICT can empower policy innovation through socio-technical systems. It provides an example of a socio-technical system developed in Piedmont, Italy to monitor road safety. The system connects various stakeholders through ICT networks and applications. By improving understanding and collaboration, socio-technical systems can enable innovative policy practices by leveraging the interactions between technology and social networks.