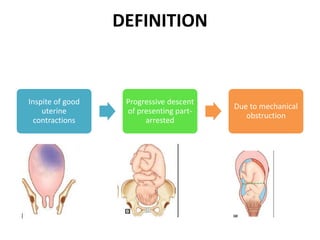
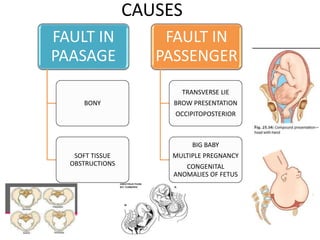
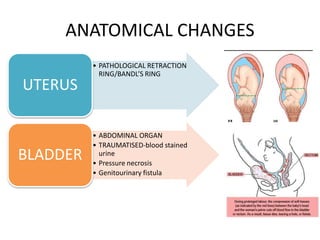
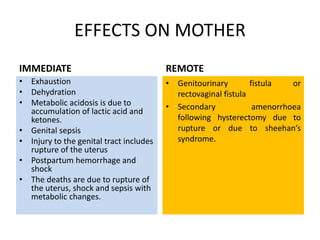
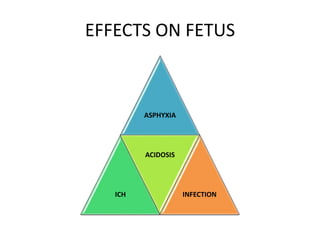
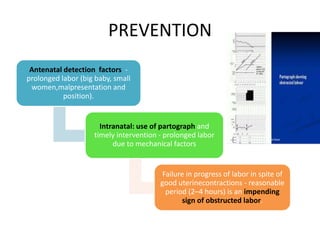
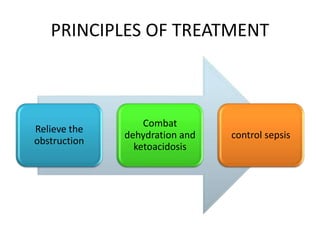
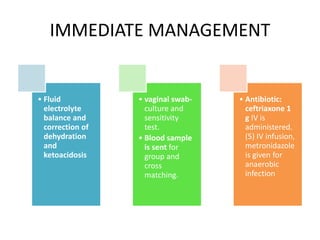
This document discusses obstructed labor, defined as arrested progression of the presenting fetal part during labor due to mechanical obstruction. Causes include faults in the pelvic passageway or fetus. Anatomical changes in the mother include pathological retraction rings and trauma to organs. Effects on the mother are immediate like exhaustion, infection, and hemorrhage or remote like fistulas. The fetus is at risk of asphyxia, infection, and acidosis. Clinical features include continuous pain, exhaustion, tender abdomen, and swollen vagina. Prevention focuses on antenatal detection and timely intervention in prolonged labor. Treatment principles are to relieve the obstruction, combat dehydration and infection, and control sepsis through fluid resuscitation, antibiotics,