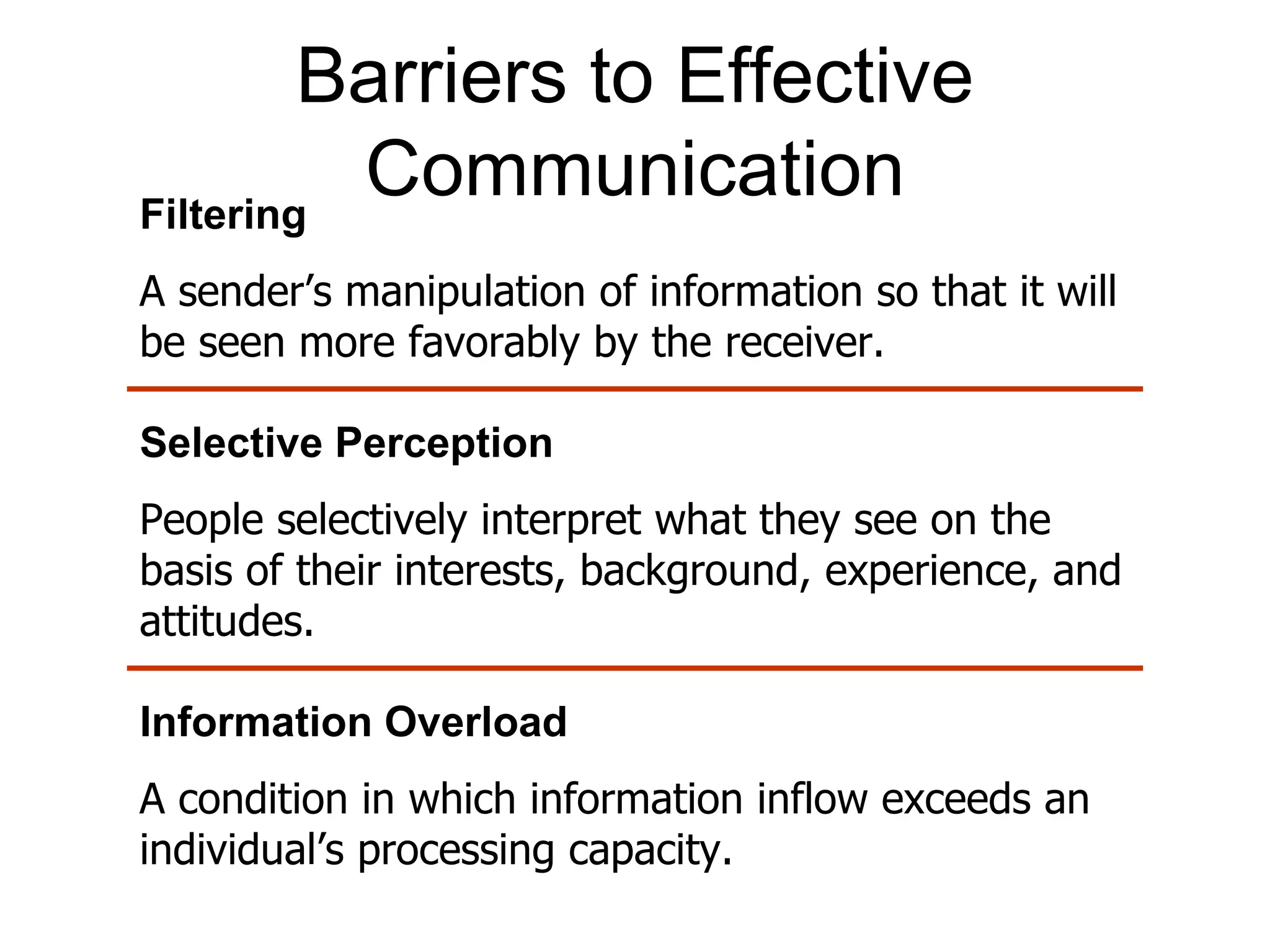
This document discusses interpersonal communication and barriers to effective communication. It covers the basic communication process, the impact of technology, nonverbal communication, informal communication channels like the grapevine, and barriers to communication such as semantics, filtering, and information overload. It provides tips for overcoming communication barriers by clarifying ideas, obtaining feedback, and adapting communication styles.